.jpg)
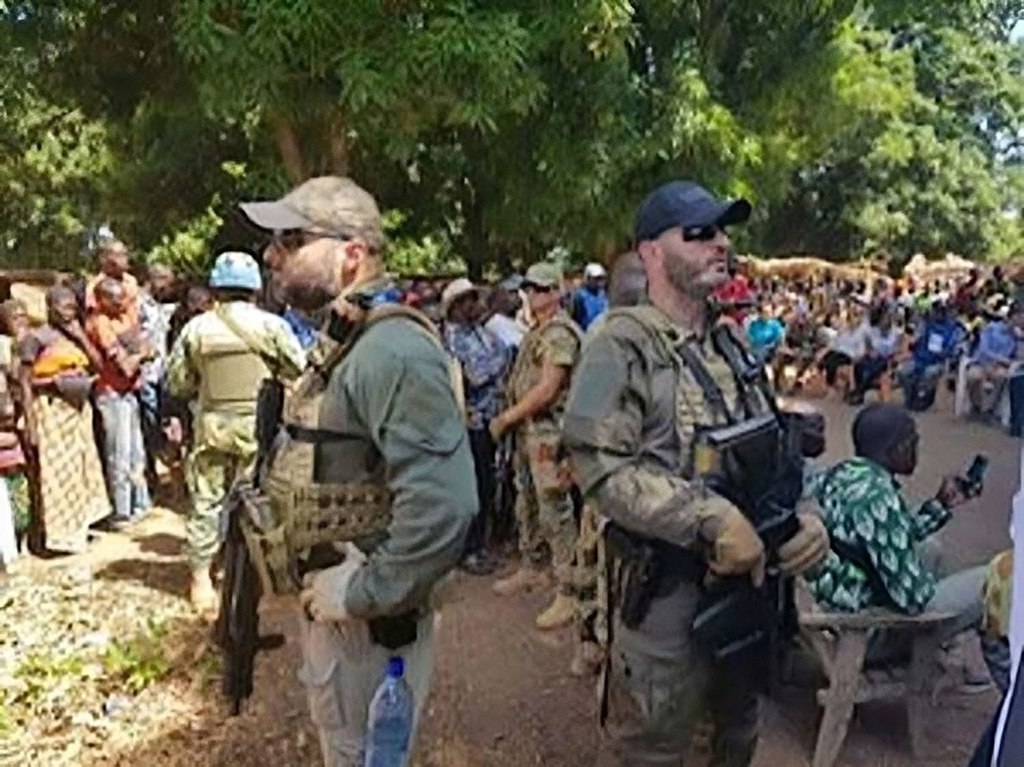
Russian Deputy Defence Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov (left) is heading the newly formed Africa Corps, which under his leadership is set to become a key entity through which the Russian state will project power in West Africa.
“The Africa Corps represents the new incarnation of Russian military influence in Africa.”
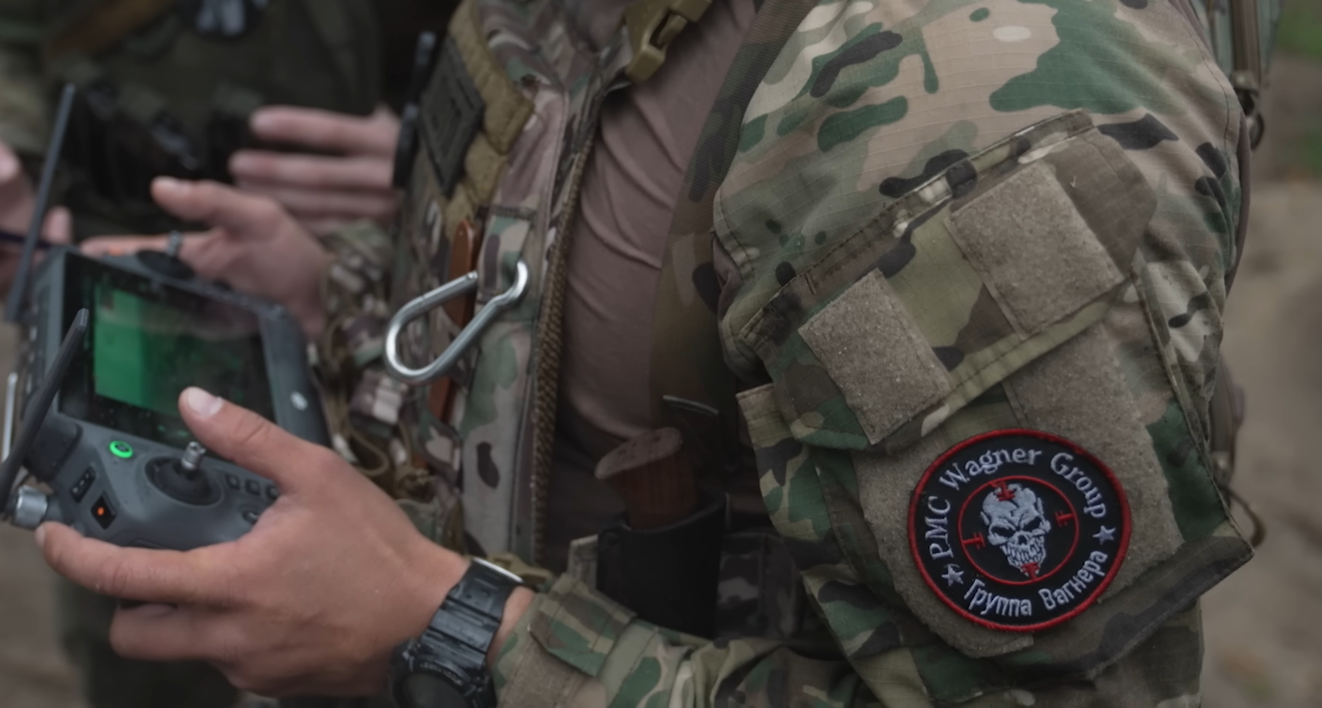
Following the death of Russian Wagner Group founder, Yevgeny Prigozhin, in a suspicious airplane crash near Moscow in 2023, reports have emerged that his successor is Russian Deputy Defense Minister, General Yunus-Bek Evkurov.[i] However, in Africa, the mercenary company’s operation is rebranding as “Africa Corps” whereas the company’s operations elsewhere in the world seem to be retaining the Wagner brand. This new branding may help the company avoid the stigma of its Wagner predecessors for war crimes and smuggling and reduce international pressure against the company in Africa.
The excerpted French-language article in the Chadian publication, alwihdainfo.com, is an African perspective of the differences between Russia’s Africa Corps[ii] and its predecessor Wagner Group. The article acknowledges that Africa Corps is the successor to Wagner Group with important differences. First, it notes that Africa Corps is intended to legitimize the Russian military influence on the African continent while competing with the diminishing presence of the U.S. and European powers. Second, Africa Corps may have a smaller footprint than Wagner in Africa. For example, the article mentions it operates only in Libya, inheriting Wagner’s main bases and most of Wagner’s fighters; Burkina Faso; Mali; Central African Republic and Niger. According to the article, Libya’s position on the Mediterranean Sea facilitates military supply lines and the movement of Africa Corps personnel into Africa. The previous iteration of Wagner had also operated extensively in Sudan and, to a lesser extent, elsewhere in Eastern Africa, including Mozambique and Madagascar.[iii]
Another difference highlighted in the article relates to the way that Africa Corps will operate. Africa Corps is now focusing on providing military support to African countries through instructors, weapons, and developing counter-terrorism strategies with host nations in cooperation with the Russian Ministry of Defense. In contrast, Wagner soldiers directly participated in missions against terrorist or insurgent groups and functioned separate from, albeit in support of, the Russian government. The article indicates that the new Africa Corps will be more sustainable than the previous Wagner Group because of Africa Corps’ formal integration with the Russian state, and the ministry of defense. Further the ministry’s commitment to Africa Corps indicates that Russia is serious about its geopolitical ambitions in West Africa and Africa Corps’ impact on the region will not be fleeting. At a time when Western influence and partnerships with West African states are waning, Africa Corps is becoming the entity through which Russia will reassert itself.
Sources:
Source: “De ‘Wagner’ à ‘Africa Corps’: la Russie toujours présente au Sahel (From ‘Wagner’ to ‘Africa Corps’: Russia always is present in the Sahel),” alwihdainfo.com (French-language Chadian publication with a reputation for independent reporting and being critical of the government), 3 May 2024. https://www.alwihdainfo.com/De-Wagner-a-Africa-Corps-la-Russie-toujours-presente-au-Sahel_a132053.html
Recently, many people have been curious about the difference between the Russian paramilitary group “Wagner” and the “Africa Corps”, which newly appeared on the African scene and which was also founded in Russia to be deployed in African countries. In this analysis, we will seek to explain the difference between the two organizations, how and where they operate, and what their ambitions are in Africa.
Africa Corps is a Russian military company that was created in early 2024 as a replacement for the Wagner Group. This organization reflects Russia’s desire to extend its military influence on the African continent and to provide legitimacy to its official and public presence in the face of the European and American presence. Africa Corps is deployed in 5 countries: Libya, Burkina Faso, Mali, Central African Republic and Niger. Libya represents the core of the corps due to the previous activity of Wagner elements in the city of Tripoli…. Another factor in the choice of Libya as the headquarters of this corps is its strategic geographical location due to its connection with the Mediterranean coast, which ensures military supply lines and movement of corps members to other countries The Africa Corps’ modus operandi is entirely dependent on providing military support to African countries such as instructors and weapons. The company also is concerns with the development of strategies in cooperation with the Ministry of Defense, such as is the case in Mali and Niger… In short, the Africa Corps represents the new incarnation of Russian military influence in Africa.
Notes:
[ii] Since the death of Russian Wagner Group founder and CEO, Yevgeny Prigozhin, in a suspicious airplane crash near Moscow in 2023, reports have emerged that his successor is Russian Deputy Defense Minister, General Yunus-Bek Evkurov. For a profile of Evkurov, which argues that he “has the full backing of Russia’s military establishment and will not have to beg for ammunition or restrict himself to the use of contractors and mercenaries,” see: Andrew McGregor, “Yunus-Bek Yevkurov: A Profile of Russia’s New Ingush African Corps Leader,” Militant Leadership Monitor, Volume: 15 Issue: 3, 18 April 2024. (URL?) The article notes that under Yevkurov “the Africa Corps will have greater access to resources, but will be expected to be self-sufficient in many ways. This means Wagner-style associations with business interests will likely continue, although disentangling these interests from the Wagner network will be challenging.” In addition, it asserts that “Improving battlefield performance will be a priority for Yevkurov. Thus far, Russian fighters have not proven any more effective in eliminating Sahelian terrorist formations than their French predecessors.”
[iii] See, for example, Brian Katz, Seth G. Jones, Catrina Doxsee, Nicholas Harrington, “Moscow’s Mercenary Wars: The Expansion of Russian Private Military Companies, CSIS, September 2020, https://russianpmcs.csis.org/
Image Information:
Image: Russian Deputy Defence Minister Yunus-Bek Yevkurov (left) is heading the newly formed Africa Corps, which under his leadership is set to become a key entity through which the Russian state will project power in West Africa.
Source:kremlin.ru, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Deputy_Defence_Minister_Yunus-Bek_Yevkurov_and_Wagner_leader_Andrei_Troshev.jpg
Attribution: CC x 4.0