PRK state media’s recent turn toward more matter-of-fact reporting and abandonment of its trademark rhetorical belligerence is in and of itself noteworthy. This probably reflects PRK desire to see how politics will play out in the USA and KOR.
In the lead-up to the January 2025 inauguration of U.S. President Trump, the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea’s (PRK) media landscape has been rather quiet, focusing instead on domestic political issues and reporting about the news in a matter-of-fact manner, rather than its typically belligerent tone.
Why is the PRK remaining quiet? First, North Korea is dealing with two major political events at once: the return of the Trump administration in the United States and the impeachment and likely removal of the president of South Korea. As regards the strategy of silence vis-à-vis the United States, Kim Jong Un had a personal relationship with President Trump that may lead the PRK to decide that discretion is the better part of valor, at least at first. When it comes to South Korea, the PRK media is likely staying silent to preserve its options because it expects the pro-engagement and accommodationist left to win any election to replace the ousted Yoon. This would potentially allow the PRK to receive aid and other concessions from the South.
Indeed, while notable, this approach is not unsurprising. This understated and matter-of-fact account typifies North Korean state media reporting on foreign and military matters in the period between the U.S. presidential election and the inauguration of the new administration on 20 January.
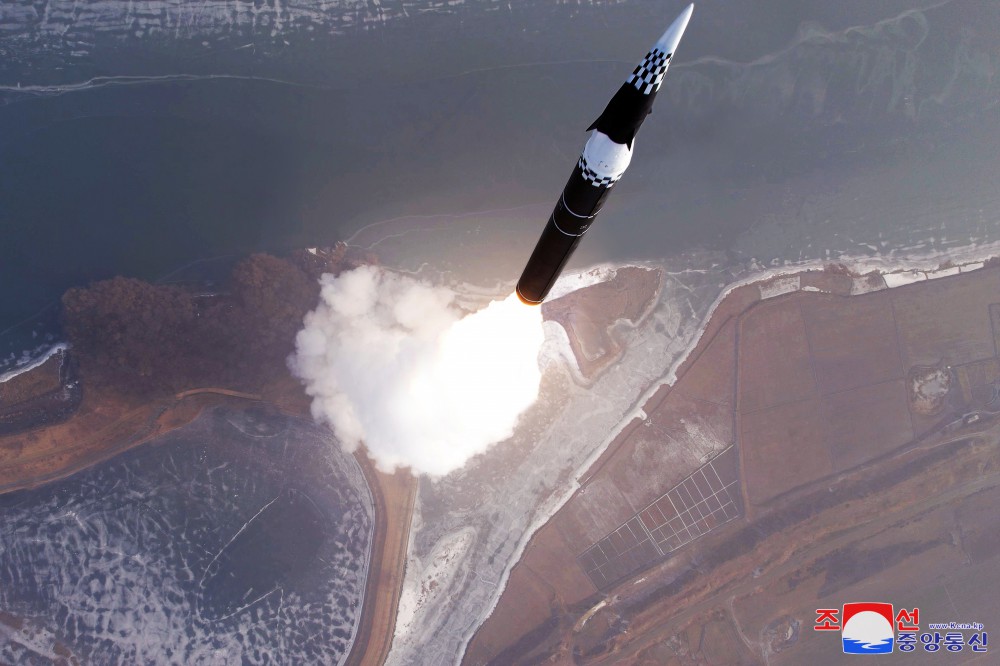
Second, to the extent that it is reporting, what is North Korean media talking about? On 6 January 2025, state central broadcaster KCNA published an article heralding what North Korea claimed to be the successful test of a new type of hypersonic vehicle. The report does not take the characteristic step of labeling the United States as the cause of PRK weapons development, instead focusing on Kim Jong Un’s pride in the scientists and how possessing this capability puts North Korea in the realm of world military powers. The article even notes that the test did not negatively affect the security of its neighbors and is for defensive purposes. KCNA published similar articles for a launch on 14 January 2025.[i]
Instead, South Korean media has made little mention of the topics that seem to concern it most. As concerns the South Korean constitutional crisis, North Korea has had just one observed report on the martial law crisis in South Korea in its externally facing media after having spent months issuing threats at increasingly higher levels of authoritativeness. Similarly, North Korean state media did not mention President Trump until a 22 January two-sentence report that he had been inaugurated.[ii] State media has published its commonplace articles detailing observed U.S. military activities in the region[iii] and a propagandistic accounting of the U.S. defense budget,[iv] but these appear to be pro forma. For the fifth year in a row, Kim Jong Un also did not give a public New Year’s Address to the nation.[v],[vi] PRK leaders traditionally used annual New Year’s addresses to announce major military milestones and defense priorities for the coming year. Moreover, the leaders would lay out foreign policy objectives. These speeches provided valuable insights for those observing the PRK from overseas.
Sources:
“조선민주주의인민공화국 미싸일총국 신형극초음속중장거리탄도미싸일시험발사 진행 (DPRK Missile Administration Succeeds in Test-fire of New-type Intermediate-range Hypersonic Ballistic Missile),” Korean Central News Agency (North Korean state-owned broadcaster), 7 January 2025. http://kcna.kp/kp/article/q/0e333077f3ca892b65f0abad00e47aef.kcmsf
The Missile Administration of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea successfully conducted a test-fire of a new-type intermediate-range hypersonic ballistic missile on January 6.
The test of the new strategic weapon system is part of the plans for the development of the national defence capabilities to raise the durability and effectiveness of the strategic deterrent against the potential enemies in conformity with the changing regional security environment.
Expressing great satisfaction over the result of the test-fire, the respected Comrade Kim Jong Un, with regard to the new weapon system, said:
The current test-fire proved without doubt that we are steadily upgrading the powerful new-type weapon systems like the intermediate-range hypersonic ballistic missile to cope with different security threats posed by the hostile forces against our state at present.
A few countries in the world might possess such a weapon system.
This is clearly a plan and effort for self-defence, not an offensive plan and action.
The hypersonic missile system will reliably contain any enemies in the Pacific region that can affect the security of our state.
We have acquired a technical force which is by no means easy to achieve.
This is a remarkable achievement and a special event in strengthening the self-defensive capabilities, which we should be proud of.
I express thanks to all the researchers and technicians and the workers of munitions industry enterprise, who contributed to the successful development of the new-type strategic weapon system.
The hypersonic glide vehicle of the missile, fired northeastward at a launch site in a suburb of Pyongyang, made a flight along the scheduled trajectory, attaining its first peak height of 99.8 kilometres and the second peak height of 42.5 kilometres at the speed amounting to twelve times of the speed of sound, and accurately landed on the simulated target waters in the open sea 1 500 kilometres away.
The test-fire had no negative impact on the security of the neighbouring countries.
The development of the defence capabilities of the DPRK aiming to be a military power will be further accelerated.
Notes:
[i] For more information, see: “극초음속미싸일시험발사 진행 (Hypersonic Missile Launch Test Conducted),” Korean Central News Agency (KCNA, major state-owned broadcaster), 15 January 2024.
[ii] See: “극초음속미싸일시험발사 진행 (Donald Trump Inaugurated as U.S. President,)” Rodong Sinmun (major Workers Party-owned newspaper for general consumption), 22 January 2025. http://rodong.rep.kp/ko/index.php?MTJAMjAyNS0wMS0yMi1OMDMxQDE1QDNAQDBAMzE==
[iii] For more information, see: “조선민주주의인민공화국 외무성 대외정책실장 담화 발표 (Statement by the Director of the Foreign Policy Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea),” Korean Central News Agency (KCNA, major state-owned broadcaster), 18 January 2025. http://kcna.kp/kp/article/q/64e900f5bd0353837ca02d7babcce3ad002dfbba9ac7d0a69e1e969df566d4026a47505ba5268fd7749c0fe11e4b24b4.kcmsf
[iv] See: “조선중앙통신사 론평 미국의 방위예산증가는 전지구적동란의 증대를 예고한다, (Commentary by the Korean Central News Agency: U.S. Defense Budget Increase Portends Increased Global Turmoil),” Korean Central News Agency (primary state-owned broadcaster), 18 January 2025.
http://rodong.rep.kp/ko/index.php?MTJAMjAyNS0wMS0xOC1OMDMwQDE1QDJAQDBAMzA==; for English mirrored link, see: https://kcnawatch.org/newstream/1737174772-447573523/kcna-commentary-on-u-s-increase-in-defence-budget/
[v] See: “Why Kim Jong Un Ditched the Iconic New Years Speech and Penned a Tender Letter,” NK News, 1 January 2021.
[vi] New Year’s is among the most important cultural holidays in Korea. New Year’s is usually celebrated with leaders giving speeches, announcing resolutions, and goals for the year ahead. It is probable that Kim Jong Un still gives these speeches, but they are no longer broadcast for outsiders.
Image Information:
Image: North Korean state media published this image of its purported new hypersonic vehicle tested on 6 January 25.
Source: http://kcna.kp/siteFiles/photo/202501/PIC0086739.jpg
Attribution: KCNA, state news agency of North Korea. Not subject to copyright because North Korea has not signed on to the international conventions protecting its or other state’s copyrighted materials.