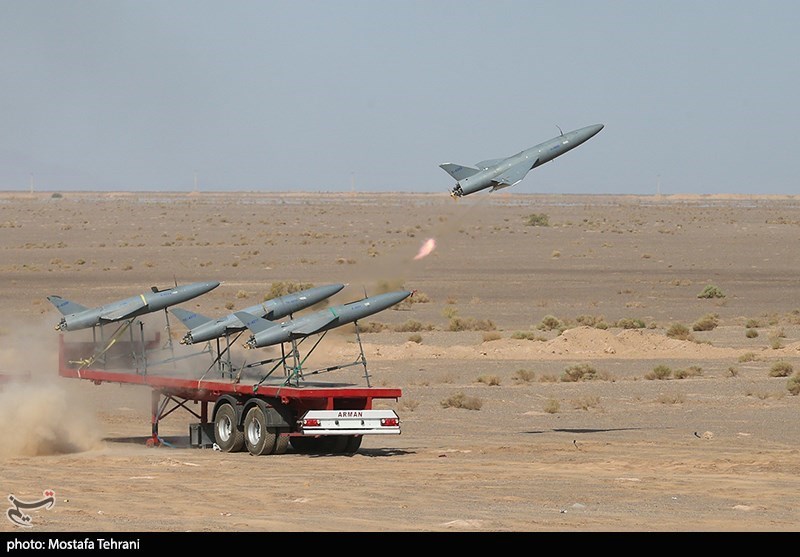
Iranian drones have assisted Sudan SAF to gain a military advantage over the rival RSF paramilitary faction.
“Cooperation between the two countries [Sudan and Iran] increased in various fields since their recent resumption of diplomatic relations.”
Summary: The Sudanese Armed Forces received Iranian drones to gain a military advantage in urban warfare over the rival Rapid Support Forces paramilitary faction. This development deepens Sudan-Iran relations and boosts Iran’s hope for greater access to the Red Sea.
On 25 May, the Sudan News Agency published the excerpted Arabic-language article on the meeting in Tehran between Sudan’s foreign minister, Hussein Awad Ali, and Iran’s foreign minister, Ali Bagheri. The article discussed the deepening relations between the two countries amid a backdrop of Iranian attempts to expand its influence in the Red Sea[i] and to sell drones to the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF). The SAF is combatting the rival Rapid Support Forces (RSF) paramilitary faction for control of Sudan in a civil war.[ii] According to the article, the two foreign ministers pledged they would cooperate at the highest levels since resuming diplomatic relations in October 2023.[iii]
Drones will be the most important aspects of the two countries’ cooperation. In particular, the Iranian Ababil-3 flies low to evade radar detection and is ideal for urban combat missions.[iv] The RSF is trained in and accustomed to non-conventional warfare, including urban combat, where it initially gained an advantage over the SAF. However, the SAF’s superior weaponry, such as Iranian drones, is now neutralizing the initial RSF advantage. Although the RSF’s advances exceeded those of the SAF in the first half-year after the conflict broke out in April 2023, the Battle of Omdurman in February 2024 became a turning point when the SAF captured the city and continued advancing afterwards.[v] If Iranian drones support the SAF to retake control of more Sudanese territory, especially around the capital Khartoun, the SAF will become closer, or at least more ingratiated, to Iran. This will facilitate Iranian efforts to gain access to the Sudanese Red Sea coast. This will, in turn, strengthen Iran’s geopolitical position in the region, with its Houthi proxies in Yemen on the eastern side of the RedSea and the SAF in Sudan on the western side.
Sources:
“وزير الخارجية المكلف يلتقي القائم بأعمال وزير الخارجية الإيراني(Interim Foreign Minister Meets with Acting Iranian Foreign Minister),” suna-sd.net (Arabic-language public Sudanese news agency, which commits to independent and balanced reporting), 8 May 2024. Image:https://suna-sd.net/posts/%D9%88%D8%B2%D9%8A%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D9%83%D9%84%D9%81-%D9%8A%D9%84%D8%AA%D9%82%D9%8A-%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%82%D8%A7%D8%A6%D9%85-%D8%A8%D8%A3%D8%B9%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%84-%D9%88%D8%B2%D9%8A%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%AE%D8%A7%D8%B1%D8%AC%D9%8A%D8%A9-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%A5%D9%8A%D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%86%D9%8A
Acting Foreign Minister Ambassador Hussein Awad Ali met today in Tehran with Acting Iranian Foreign Minister Ali Bagheri, where he gave him condolences from the Chairman of the Sovereignty Council, the Sudanese government, and the Sudanese people on the death of Iranian President Ibrahim Raisi and Minister Foreign Ministry Hussein Amir Abdullahian and their colleagues in a helicopter crash.
Cooperation between the two countries increased in various domains since their recent resumption of diplomatic relations and their reopening the two embassies again. They agreed to expedite the opening of the two countries’ embassies under the leadership of their respective ambassadors and to contribute to advancing relations between the two countries at a rapid pace to the highest level.
Notes:
[i] See, for example: Mohammed Yassin, “Reports about Iran’s Bid for Naval Base in Sudan Sparks Controversy,” Asharq al-Awsat, 4 March 2024. https://english.aawsat.com/world/4891051-reports-about-iran%E2%80%99s-bid-naval-base-sudan-sparks-controversy
[ii] The Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) are led by General Abd al-Fatah al-Burhan and are engaged in military conflict with the Rapid Support Forces (RSF) paramilitary faction, which is led by Mohamed Hamdan Dagalo (“Hemedti”). In April 2023, al-Burhan called the RSF a “rebel” movement and formally dissolved it, which led to civil war. In early 2024, the RSF still had the upper hand in the fighting, but now the SAF appears to have the military advantage. See: Andrew McGregor, “Gold, Arms, and Islam: Understanding the Conflict in Sudan,” Terrorism Monitor Volume: 21 Issue: 9, April 2023. https://jamestown.org/program/gold-arms-and-islam-understanding-the-conflict-in-sudan/
[iii] Sudan severed relations with Iran in 2016 in opposition to Iranian sectarianism and under the geopolitical
influence of Saudi Arabia. However, in an effort to balance against the West, Sudan sought closer relations with Iran. Sudan and Iran’s restoration of relations only two weeks after Hamas’ massacre in Israel on October 7, 2023, and despite a previous thaw in Sudanese-Israeli relations, has only put the SAF’s relations with the West further under strain. See: Mohamed Yassin, “What is Sudan’s Purpose of Diplomatic Approach with Iran?,” Asharq al-Awsat, 22 January 2024. https://english.aawsat.com/features/4805441-what-sudans-purposediplomatic-approach-iran
[iv] See: “Sudan’s small but deadly drone fleet could turn the tide of war,” Military Africa, 22 April 2023. https://www.military.africa/2023/04/sudans-small-but-deadly-drone-fleet-could-turn-the-tide-of-war/
[v] See: Ashraf Abdelaziz, “Sudan war: ‘Iranian drones played decisive role in Omdurman battle.’” Dabanga Sudan, 17 March 2024. https://www.dabangasudan.org/en/all-news/article/sudan-war-iranian-drones-played-decisive-role-in-omdurman-battle.
Image Information:
Image: Iranian drones have assisted Sudan SAF to gain a military advantage over the rival RSF paramilitary faction
Source: Tasnim News Agency, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Iranian_drone_exercise_in_2022_-_Day_2_(52).jpg
Attribution: CC x 4.0