An image of Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan from 2023. Armenia is currently taking steps to distance itself from both the CSTO and Russia.
“The CSTO, instead of fulfilling its obligations to Armenia in the field of security, on the contrary, creates security problems. And this position, I say frankly, is a threat to the national security of Armenia.”
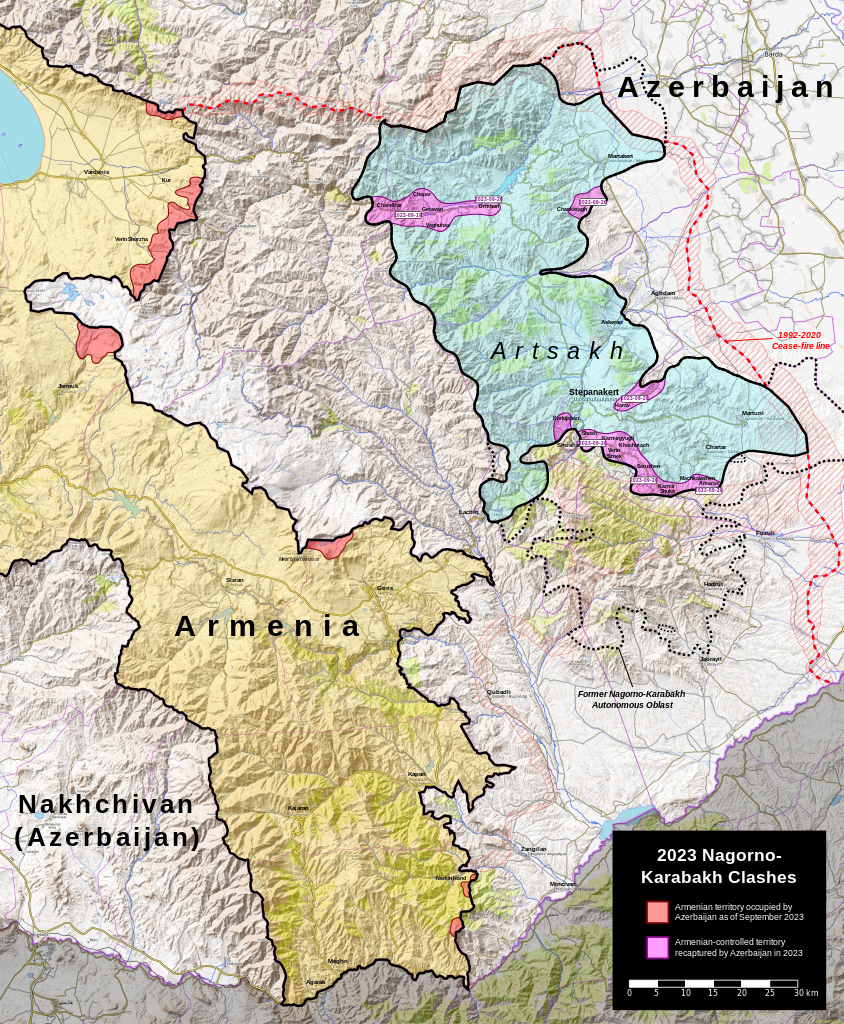
Armenia has been critical of both Russia and the Russian-led Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) over their responses to the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War and the subsequent clashes between Armenia and Azerbaijan. Some Armenian officials have even called for the country to leave the CSTO and limit cooperation with Russia, though Armenia has continued to engage with both since the end of the 2020 war because of a lack of other options.[i] The accompanying excerpted article from the independent news website Kavkazskiy Uzel, reports that Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan announced on 22 February 2024 that Armenia had ended its participation in the CSTO, though he did not go as far as to say that Armenia is leaving the organization. The article notes that the decision is based on the CSTO’s responses to the 2020 war and the numerous clashes between Armenia and Azerbaijan since then. The article also relays that Armenia has been critical of the Russian peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh for not favorably dealing with Azerbaijan’s blockade of the breakaway region and not preventing Azerbaijan’s operation in September 2023, which ended with Azerbaijan regaining full control of the region. The article ends with a statement from Pashinyan, who claims that the CSTO is a threat to the national security of Armenia. Based on this statement, it is possible that Armenia will leave the CSTO, but the country will still be home to a Russian military base and Russian border guards in its territory for the foreseeable future.[ii] In a seemingly related development, the second excerpted article, from the Armenian news website News.am, reports that Armenia has notified Moscow that Russian border guards will need to be removed from the Zvartnots International Airport. Armenia’s Foreign Minister Ararat Mirzoyancommented that Armenian border guards are capable of taking over duties at the airport. The article clarifies that Armenia is not asking the Russian border guards to leave their positions on the border with Turkey or Iran, but only to leave the airport. While this development has yet to play out, it is one step Armenia has taken to rely less on Russia.
Sources:
“Главное о критике Арменией ОДКБ и Кремля (The heart of Armenia’s criticism of the CSTO and the Kremlin),” Kavkazskiy Uzel (independent news website reporting on the Caucasus), 29 February 2024. https://www.caucasianknot.com/articles/386973
After Russia’s refusal to intervene in the armed conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan in the fall of 2020, Armenia’s confidence in the benefits of participation in the Collective Security Treaty Organization weakened to the point of threats to leave the CSTO. The “Caucasian Knot” has prepared a report on how the degree of Armenia’s unfriendly rhetoric towards Russia increased and what steps Armenia took in its attempts to look for an alternative to the CSTO…
During the escalation of the Karabakh conflict in 2020, Armenia turned to the CSTO for help. Moscow responded by saying that it could not help, since the borders of Armenia were not violated and the war took place on the territory of Nagorno-Karabakh…the Kremlin limited itself to political support for Yerevan, and after that it sent peacekeepers to the Karabakh… conflict zone.
At a meeting with Putin on December 27, 2022, the Armenian prime minister again recalled the responsibility of Russian peacekeepers. “The Lachin corridor has been blocked for almost 20 days. This is the area of responsibility of Russian peacekeepers in Nagorno-Karabakh. And I want to remind you that according to the trilateral statement of the presidents of the Russian Federation, Azerbaijan and the Prime Minister of Armenia, the Lachin corridor should be under the control of Russian peacekeepers,” said Pashinyan…
On September 21, 2023, the day after the end of hostilities in Karabakh, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan sharply criticized Russian peacekeepers. “The Russian peacekeeping contingent was supposed to guarantee the safety of the civilian population…We bear our share of responsibility. But I don’t think that we should turn a blind eye to the failures that the Russian peacekeeping force had contingent,” he said…“Due to the inaction of the Russian peacekeeping contingent, over 100 thousand Armenians left their homes and native places in Nagorno-Karabakh in a week,” Pashinyan said…
On February 22, 2024, Prime Minister of Armenia Nikol Pashinyan, in an interview with France 24 TV channel, stated that the CSTO reaction did not correspond to reality in relation to the Republic of Armenia, in particular in 2021 and 2022. “And, obviously, this could not go unnoticed by Armenia. Today, in practice, we have actually frozen our participation in this agreement in this organization,” said the Prime Minister of Armenia…
On February 28, 2024, answering questions from deputies in the Armenian parliament, Nikol Pashinyan stated that “The CSTO, instead of fulfilling its obligations to Armenia in the field of security, on the contrary, creates security problems. And this position, I say frankly, is a threat to the national security of Armenia…”
“Armenia FM comments on Russian border guards’ presence on Turkey border,” News.am (Armenian news website), 7 March 2024. https://news.am/eng/news/811212.html
Armenian Foreign Minister Ararat Mirzoyan explained how Yerevan informed Moscow about the matter of the Russian border guards at Zvartnots International Airport of the Armenian capital city of Yerevan.
At Thursday’s press conference, the FM confirmed the statement by the secretary of the Council of Armenia regarding the aforementioned matter, and stated that the Russian side was informed about the initiative to remove the Russian border guards from Zvartnots airport…
“Now we believe that Armenia is institutionally capable of independently implementing border guard service at the [Yerevan] airport, about which we have informed the Russian side. I believe that this will be enough for the Russian side and the matter will be over,” Mirzoyan noted, adding that it is about the entire package of jurisdiction at the airport…To the question about the presence of Russian border guards in other places in Armenia, for example on the Turkish border, the minister responded that the matter is only about Zvartnots airport. “Therefore, we are talking only about the airport,” added the Armenian FM.
Notes:
[i] Russia and the CSTO have had separate responses to the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War and subsequent clashes between Armenia and Azerbaijan. Russia deployed a peacekeeping mission to Nagorno-Karabakh as part of the ceasefire agreement, but the peacekeepers are not affiliated with the CSTO. The CSTO declined to intervene in the 2020 war or the clashes on the grounds that the organization stated Armenia itself was not attacked in any of the instances and thus, does not necessitate a collective defense response from the organization.
[ii] Russia’s 102nd Military Base is located near the city of Gymuri, Armenia with an estimated 3,000 soldiers garrisoned there, while Russian border guards provide security on Armenia’s borders with Turkey and Iran as well as operating at the Zvartnots International Airport outside of the capital Yerevan.
Image Information:
Image: An image of Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan from 2023. Armenia is currently taking steps to distance itself from both the CSTO and Russia.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Nikol_Pashinyan_-_2023_(cropped).jpg
Attribution: CCA 2.0