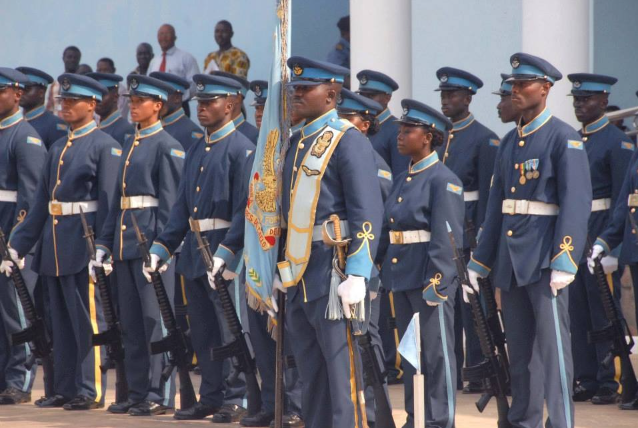
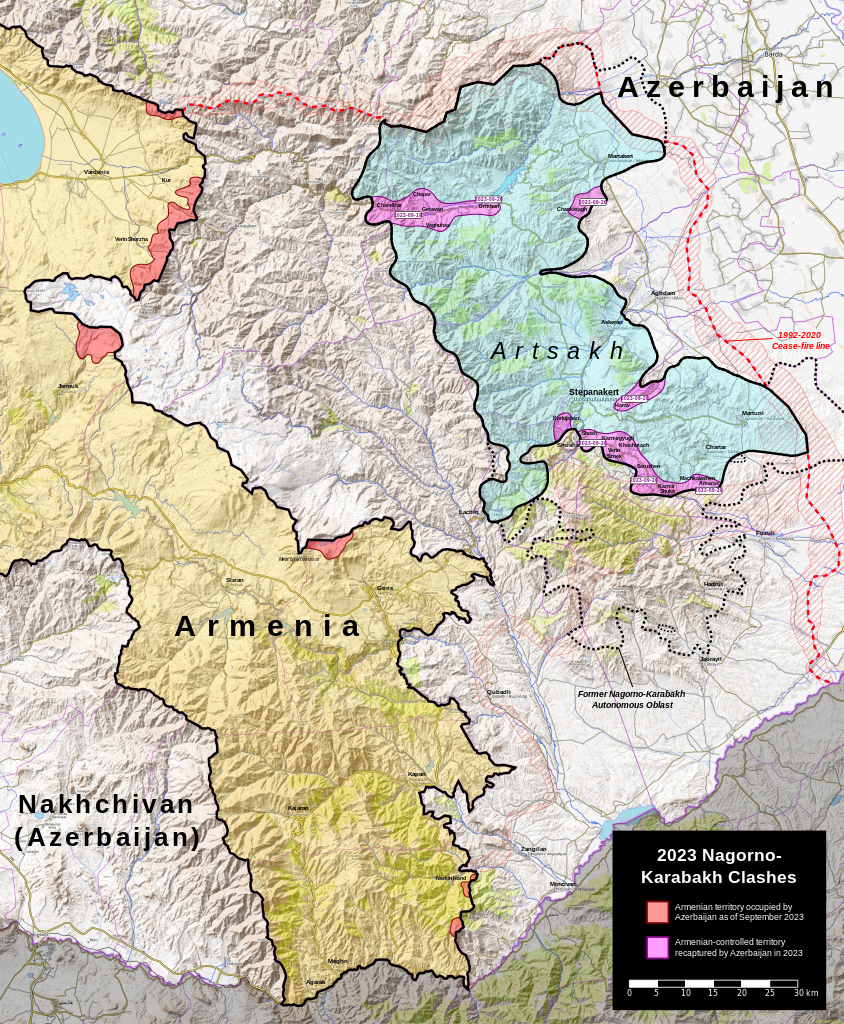
Members of the Kofi Annan International Peacekeeping Training Center honor guard stand in formation during a welcoming ceremony for Ivory Coast Gen. Soumaila Bakayoko.
“If ECOWAS chooses a particular option to resolve the regional crisis, Côte d’Ivoire will follow this option in solidarity with other member states.”
On 29 September, the Turkish website of Anadolu News Agency published the excerpted French-language article on Côte d’Ivoire’s intention to comply with the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) if the organization military intervenes in Niger. The article notes that ECOWAS has threatened to intervene militarily in Niger to reinstall deposed president Mohamed Bazoum to power. A spokesperson for Côte d’Ivoire’s government confirmed that the country will not make any decision regarding Niger unilaterally but will respect the outcomes of ECOWAS member states’ debates.
The decision to follow ECOWAS into battle in Niger differs from Côte d’Ivoire’s announcement in November 2022 that it would withdraw its forces from the United Nations Multidimensional Integrated Stabilization Mission in Mali (MINUSMA), despite MINUSMA’s continued counterinsurgency efforts against al-Qaeda and Islamic State-loyal militants. According to the excerpted French-language article in tvmonde5.com, Côte d’Ivoire’s withdrawal from MINUSMA came after Mali’s coup leaders alleged that Ivorian troops who entered Mali to operate with a German contingent were “mercenaries.”[i] Côte d’Ivoire’s commitment to ECOWAS and reduction in military support to MINUSMA can be interpreted as a reflection of how opposition parties have been permitted to participate in Ivorian politics and how other reforms have improved electoral competition since 2020.[ii] Côte d’Ivoire is willing to support military efforts to restore democratically elected civilian rulers, such as Bazoum, to power. However, the country is refraining from offering its troops for regional military efforts to support governments, such as in Mali, that refuse to return power to democratically elected leaders and that express allegiance towards Russia, including its proxy, Wagner Group.
Sources:
“L’option d’une intervention militaire de la Cédéao au Niger reste possible (The option of ECOWAS military intervention in Niger remains possible),” Anadolu News Agency (Turkish state-run news agency aligned with the ruling Justice and Development Party (AKP)), 29 September 2023. https://www.aa.com.tr/fr/afrique/loption-dune-intervention-militaire-de-la-c%C3%A9d%C3%A9ao-au-niger-reste-possible/3003520
The option of military intervention by the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) in Niger remains on the table and Côte d’Ivoire will comply with the decisions adopted collectively by the community “if ECOWAS decides on this option,” said Ivorian government spokesperson Amadou Coulibaly. The government spokesperson affirmed that Côte d’Ivoire is a member that respects its commitments in ECOWAS.
In Niger, members of the presidential guard took power on July 26, pushing aside President Mohamed Bazoum and announcing the suspension of the Constitution and the formation of a National Council for the Safeguarding of the Homeland. ECOWAS threatened to intervene militarily to enable Bazoum to regain power and considered this an option ready to be implemented alongside strict punitive measures.
“La Côte d’Ivoire va retirer progressivement ses soldats du Mali (Ivory Coast will withdraw its soldiers from Mali gradually),” tvmonde5.com (French public television broadcaster’s website focusing on worldwide affairs affecting France), 16 November 2022. https://information.tv5monde.com/afrique/la-cote-divoire-va-retirer-progressivement-ses-soldats-du-mali-1424754
Côte d’Ivoire indicates that the soldiers and other elements active within MINUSMA will not be relieved in August 2023.Relations between Côte d’Ivoire have become significantly strained in recent months, particularly after the arrest last July of 49 Ivorian soldiers in Bamako.
Notes:
[i] The bilateral dispute between Côte d’Ivoire and Mali reached a culmination in January 2023 when Côte d’Ivoire honored 49 soldiers after they were released from detention in Mali, where there were held for half a year, and returned home. Only weeks before their release from detention, a Bamako court had sentenced most of the Ivorian soldiers to 20 years in prison and others to death for being “mercenaries”. Although Ivorian soldiers had been invited to Mali by the German contingent of MINUSMA, the Malian coup leaders alleged the “Sahel Aviation Service (SAS),” which is a private company, transported the Ivorian soldiers. In contrast, the Wagner Group, which is affiliated to the Russian government, was welcomed into Mali by the Malian coup leaders. It is possible that the Ivorian and German governments’ criticism of the coup in Mali and lack of transition back to democracy underscored the Malian coup leaders’ initial actions to detains the Ivorian soldiers. See; “Mali detains Ivorian soldiers, accuses them of being mercenaries,” Rfi.fr, 12 July 2022. https://www.rfi.fr/en/africa/20220712-mali-detains-ivorian-soldiers-accuses-them-of-being-mercenaries
[ii] The U.S. State Department notes that since the Ivorian president’s election to a third term in 2020, the country’s democratic processes have been “generally considered free.” Similarly, the election monitoring group, New Dawn, assessed that the latest Ivorian local and regional elections in September 2023 “had gone smoothly.” Consistent with these democratic trends, Ivorian foreign policy has become increasingly aligned with ECOWAS and its member-states’ oppositions to military coups in West Africa. See; “2022 Country Reports on Human Rights Practices: Cote d’Ivoire,” U.S. Department of State, 2023. https://www.state.gov/reports/2022-country-reports-on-human-rights-practices/cote-divoire. See also; “Sweeping win for ruling party in Ivory Coast local and regional elections,” france24.com, 5 September 2023. https://www.france24.com/en/africa/20230904-sweeping-win-for-ruling-party-in-ivory-coast-local-and-regional-elections
Image Information:
Image: Members of the Kofi Annan International Peacekeeping Training Center honor guard stand in formation during a welcoming ceremony for Ivory Coast Gen. Soumaila Bakayoko.
Source: MSG Montigo White https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/43/Members_of_the_Kofi_Annan_International_Peacekeeping_Training_Center_honor_guard_stand_in_formation_during_a_welcoming_ceremony_for_Ivory_Coast_Gen._Soumaila_Bakayoko%2C_the_Economic_Community_of_West_African_130626-A-ZZ999-016.jpg
Attribution: CC x 2.0