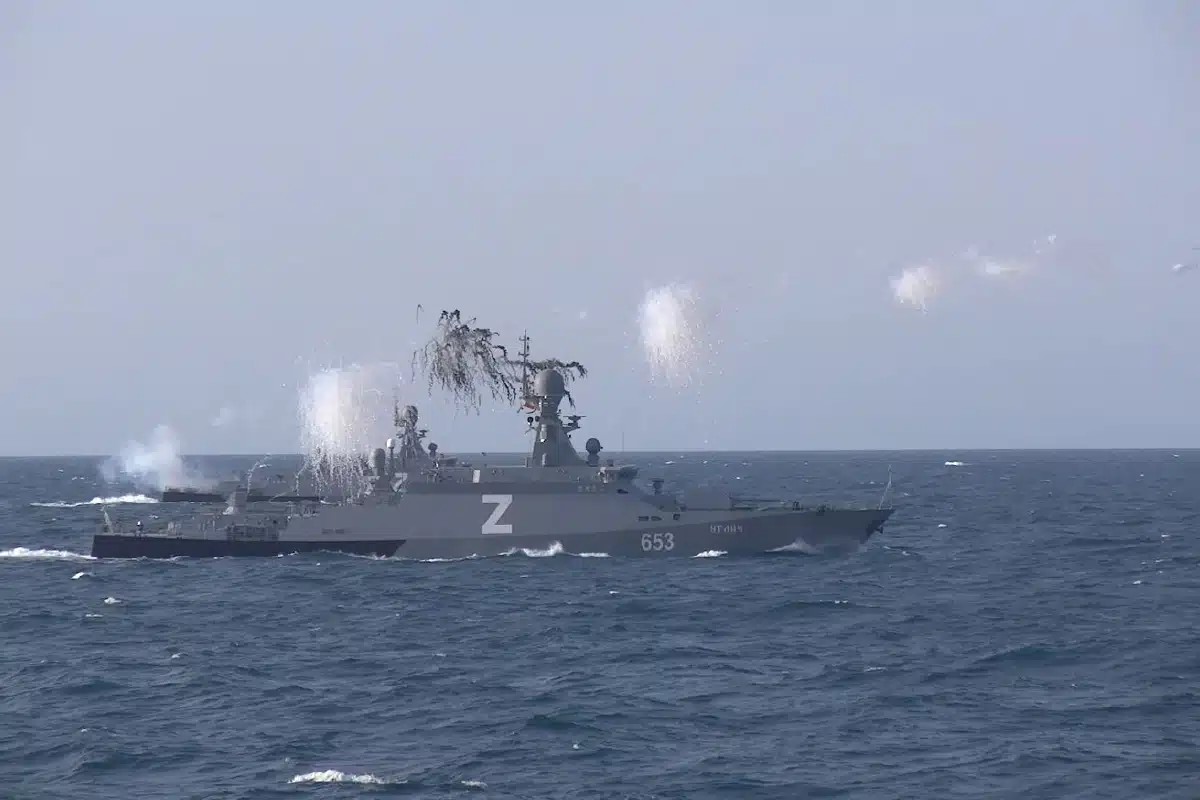
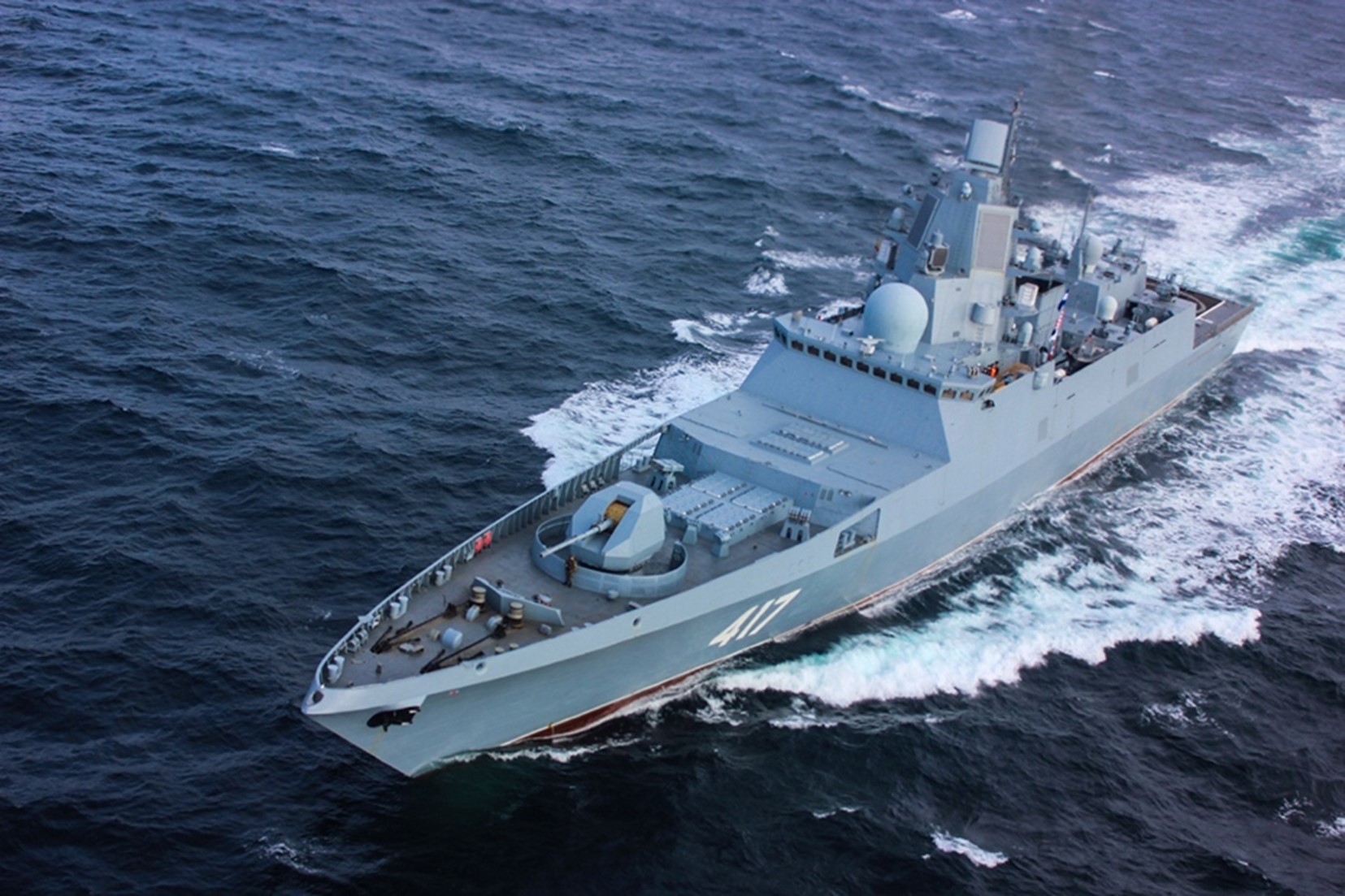
Russian Buyan-M corvette Uglich of the Caspian Flotilla firing countermeasures during maneuvers part of Ocean-2024. Note the letter “Z” in reference to forces involved in the invasion of Ukraine. The Caspian is essentially a Russian lake, the only other significant naval power in the Caspian is Iran and most of Iran’s naval forces are deployed and focused on the contentious Middle East.
“The maneuvers… involve more than 400 warships, submarines and auxiliary fleet support vessels, more than 120 aircraft and helicopters of the naval aviation of the Navy and the Aerospace Forces, about 7,000 units of weapons, military and special equipment, as well as more than 90 thousand personnel.”
Russia conducted its largest naval exercise in more than 30 years, likely to dispel the notion of its failures against Ukraine in the Black Sea.[i] According to the excerpted article by Russian flagship news outlet Ria Novosti, the exercise, known as Ocean-2024 strategic command and staff exercise, took place across the globe, with maneuvers in the Pacific and Arctic Oceans, the Mediterranean, Caspian, and Baltic Seas.[ii]
The Novosti article claims Ocean-2024 maneuvers involved more than 400 vessels and more than 90,000 personnel. Four Chinese naval vessels also participated in Ocean-2024, part of the Pacific Fleet maneuvers. Scenarios included fighter interception of hostile aircraft intent on bombing the surface fleet. In the case highlighted, the attack aircraft was an IL-38 anti-submarine maritime patrol aircraft—no match for the MiG-31BMs sent to intercept. The tactics practiced were tried-and-true naval drills, reflecting long-standing naval threats that still exist but do not consider the ongoing evolution in naval warfare, including drone and counter-drone scenarios, the types of naval warfare that have proved devastating to Russia’s Navy in the Black Sea. While prudent to train in general naval combat operations, Moscow’s failure to reset the exercise to reflect the current and future threat environment begs the question if Ocean-2024 was more a public relations operation, especially in the wake of the U.S.-led RIMPAC naval exercise earlier in the year. Russia’s Ocean-2024 is likely serves as a morale booster for its Navy at a time when it has not been able to restore any operational capability in the Black Sea.
Sources:
“МиГ-31БМ перехватили условного противника на учениях “Океан-2024” (MiG-31BM intercepted a mock enemy during the Ocean-2024 exercises),” Ria Novosti (mainstream Russian media outlet), 15 September 2024. https://ria.ru/20240915/istrebiteli-1972773873.html
MOSCOW, 15 Sep – RIA Novosti. A pair of MiG-31BM interceptors intercepted a mock enemy over the neutral waters of the Sea of Japan as part of the Ocean-2024 exercises, the Russian Defense Ministry reported.
“A pair of high-altitude MiG-31BM interceptor fighters, while performing a flight mission to provide fighter-air cover for the Pacific Fleet’s naval strike group over the neutral waters of the Sea of Japan, intercepted a mock enemy as part of the Okean-2024 strategic command and staff exercise,” the statement said.
It is noted that as part of the exercise, the role of an airspace violator was played by an Il-38 aircraft, which attempted to approach a detachment of naval ships to launch a bomb strike on it. And the crews of the MiG-31BM interceptor fighters, having received coordinates from the radio engineering units, took off from one of the airfields, reached the designated area and independently classified the target, after which they launched long-range tactical air-to-air missiles at it.
“After completing the task, the crews of the fighters practiced elements of air combat with mock enemy fighters performing cover missions “enemy” bombers,” the ministry added.
Russian Navy formations and units began the Okean-2024 strategic command and staff exercises on Tuesday, which will last until September 16. The exercises are being held in a bilateral format under the general leadership of the Navy Commander-in-Chief, Admiral Alexander Moiseyev.
The maneuvers, which will take place in the waters of the Pacific and Arctic Oceans, the Mediterranean, Caspian and Baltic Seas, involve more than 400 warships, submarines and auxiliary fleet support vessels, more than 120 aircraft and helicopters of the naval aviation of the Navy and the Aerospace Forces, about 7,000 units of weapons, military and special equipment, as well as more than 90 thousand personnel.
“Ocean” is the code name for naval exercises conducted by the General Command of the USSR Navy in 1970, 1975, 1977, 1983 and 1985. The “Ocean” exercises (maneuvers) were the largest operational and combat training events of the USSR Navy in the post-war period and the largest in world history for their time.
Notes:
[i] For a western perspective on Ocean-2024, see: “Ocean-2024 – Russian Navy Flexes Its Muscles, China Assists,” Naval News (Europe based naval focused news service), 13 September 2024. https://www.navalnews.com/naval-news/2024/09/ocean-2024-russian-navy-flexes-its-muscles-china-assists/
[ii] Notably, no maneuvers took place in the Black Sea, once a naval strongpoint for Russia built upon its Black Sea Fleet, but now under constant threat from Ukrainian naval drones. Ukrainian surface drones have wreaked enough havoc and forced Moscow to redeploy and scatter its Black Sea Fleet to various ports on the eastern Black Sea.
Image Information:
Image: Russian Buyan-M corvette Uglich of the Caspian Flotilla firing countermeasures during maneuvers part of Ocean-2024. Note the letter “Z” in reference to forces involved in the invasion of Ukraine. The Caspian is essentially a Russian lake, the only other significant naval power in the Caspian is Iran and most of Iran’s naval forces are deployed and focused on the contentious Middle East.
Source: Russian Ministry of Defence, published by Naval News, https://www.navalnews.com/naval-news/2024/09/ocean-2024-russian-navy-flexes-its-muscles-china-assists/