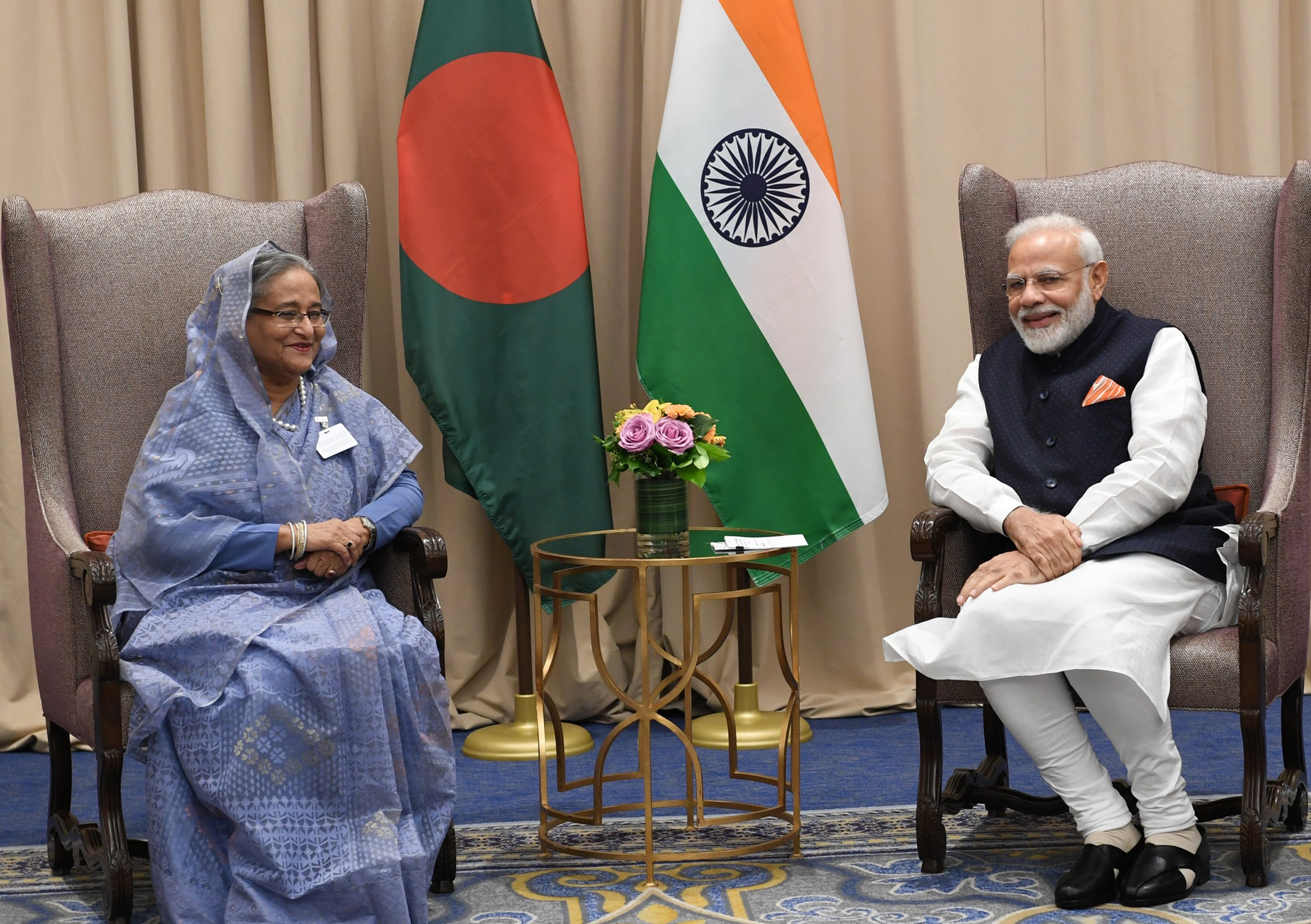
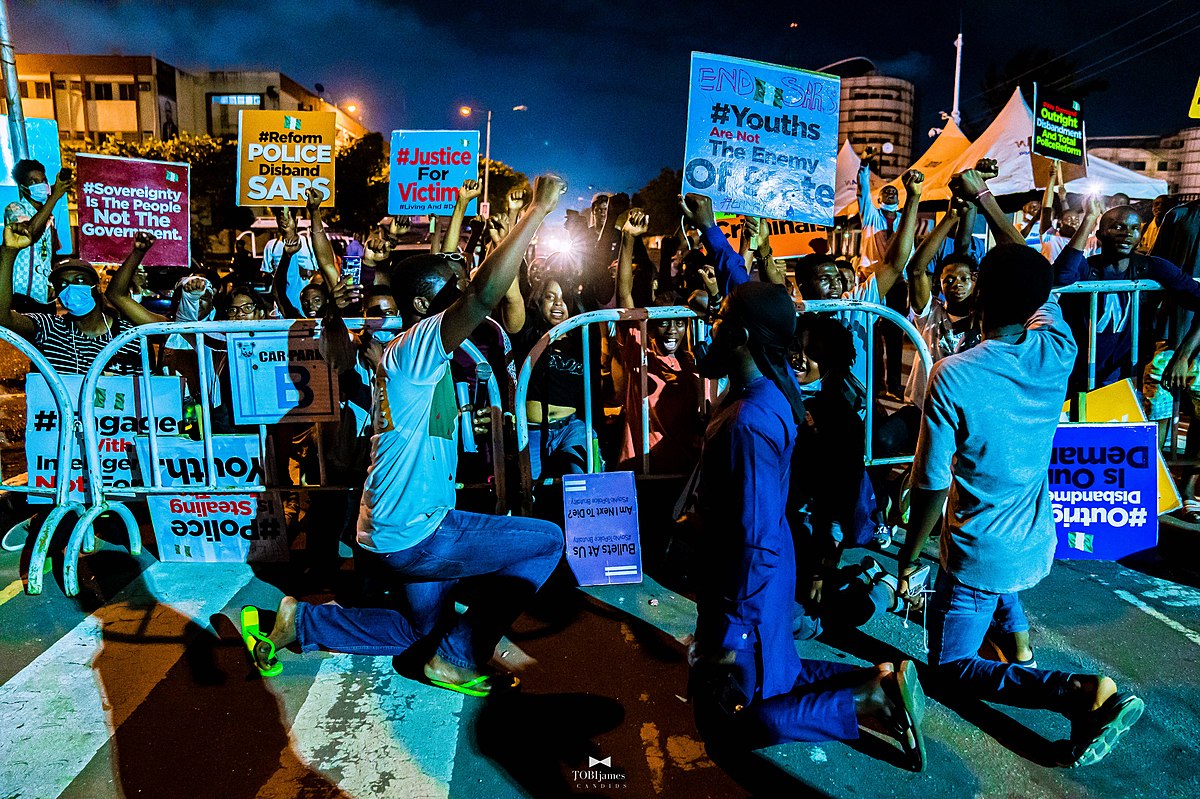The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi meeting the Prime Minister of Bangladesh, Ms. Sheikh Hasina, in New York, USA on September 27, 2019.
“Referring to the ongoing Russia-Ukraine as well as Israel-Hamas conflicts and the current situation in Bangladesh, the Minister exhorted the Commanders to ‘analyze these episodes, predict the problems that the country may face in the future, and stay prepared to deal with the unexpected.”
In early August 2024, protests in Bangladesh resulted in the collapse and resignation of the government of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina. While this did not result in an immediate threat for India, the accompanying excerpted article shows how the situation in Bangladesh will remain a security issue for India. The article from the Indian independent think tank The Centre for Land Warfare Studies examines what happened in Bangladesh and outlines what India can do to adjust. The author, a retired Indian Army general, provides some background on what led to Sheikh Hasina’s resignation.[i] As the author points out, the history between India and Bangladesh has at times been contentious, but India and Hasina had favorable relations for a number of years due to Hasina’s working closely with India on security issues. This included India and Bangladesh cooperating to resolve their border and maritime disputes and Hasina working with India to help end its conflict with the United Liberation Front of Assam.[ii] The author goes on to note how China has gained considerable influence in Bangladesh through exports of weapons. He also mentions that because the Bangladeshi Army has played a role in the regime change, India should reach out to work closely and strengthen military ties. This could set up further competition between India and China in the region. Lastly, the author states that India needs to do everything possible to protect Indian nationals and ethnic minorities in Bangladesh, with the latter group referencing the Hindu religious minority in the country. The majority Muslim population in Bangladesh has periodically attacked Hindus, but Hasina’s government has provided them with protection. Indian Prime Minister Modi and the interim government in Bangladesh appear to have established positive relations, but the status of Hindus in Bangladesh could be a point of contention and an issue for India to resolve.
Sources:
Lt Gen PS Rajeshwar, (Ret), “India – Bangladesh Relations: Navigating The Turmoil,” The Centre for Land Warfare Studies (independent think tank in India), 16 August 2024. https://www.claws.in/analysis-india-bangladesh-relations-navigating-the-turmoil/
The developments of 5 August had resulted in very short notice to Indian authorities…What appeared initially to be a student movement against the quota system for descendants of freedom fighters in government jobs finally turned into a call for the resignation of the then Prime Minister…
Under these circumstances, how does one look at the strategic dimensions of India-Bangladesh relations? The ties between the two nations were forged through the sacrifices of people in both countries during the Liberation War of 1971. The economic, cultural, and linguistic aspects were strengthened further during the last 15 years of the Sheikh Hasina rule.
Bangladesh has a special place in our policy matrix and security calculations…She shares a more than 4000 km border, much of which abuts our critical NE region. In a significant 2015 agreement, the border was simplified by exchanging enclaves trapped in each other’s territories…The two countries also settled their maritime dispute amicably. Earlier, in 2010, the Awami League government had helped India by removing all camps of Indian rebel groups, which broke the back of the ULFA, pushing it to a peace agreement.
India has been very concerned about China’s influence in Bangladesh, from participating in China’s Belt and Road Initiative in 2016 to importing 72% of its arms from China in 2019-2023…
Second is our strategic intelligence, which must be comprehensively improved to anticipate such abrupt events better…
Fifth, since the Bangladesh Army has played a defining role in this crisis and could remain a key factor, we must strengthen our military-to-military ties.
Finally, we need to do everything to secure Indian nationals while insisting on the safety and protection of minority communities in Bangladesh, lest there be a backlash back home.
Notes:
[i] For a more detailed timeline and background on the protests in Bangladesh in 2024, see: “From job quota to Sheikh Hasina’s resignation: Timeline of the Bangladesh student protests,” The Hindu, 5 August 2024. https://www.thehindu.com/news/international/from-protests-to-sheikh-hasina-resignation-timeline-of-bangladesh-student-protest/article68488361.ece
[ii] The ULFA was a militant group that had operated out of Bangladesh with a goal of establishing an independent government in India’s State of Assam (bordering Bangladesh) until Hasina’s government agreed to eliminate its safe have in Bangladeshi territory. India and the ULFA reached a peace agreement in December 2023, see: Gaurav Dwivedi, “The Path To Peace: ULFA’s Journey From Insurgency To Accord,” NDTV, 29 December 2023. https://www.ndtv.com/india-news/the-path-to-peace-ulfas-journey-from-insurgency-to-accord-4763730
Image Information:
Image: The Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi meeting the Prime Minister of Bangladesh, Ms. Sheikh Hasina, in New York, USA on September 27, 2019
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:The_Prime_Minister,_Shri_Narendra_Modi_meeting_the_Prime_Minister_of_Bangladesh,_Ms._Sheikh_Hasina,_in_New_York,_USA_on_September_27,_2019_(1).jpg