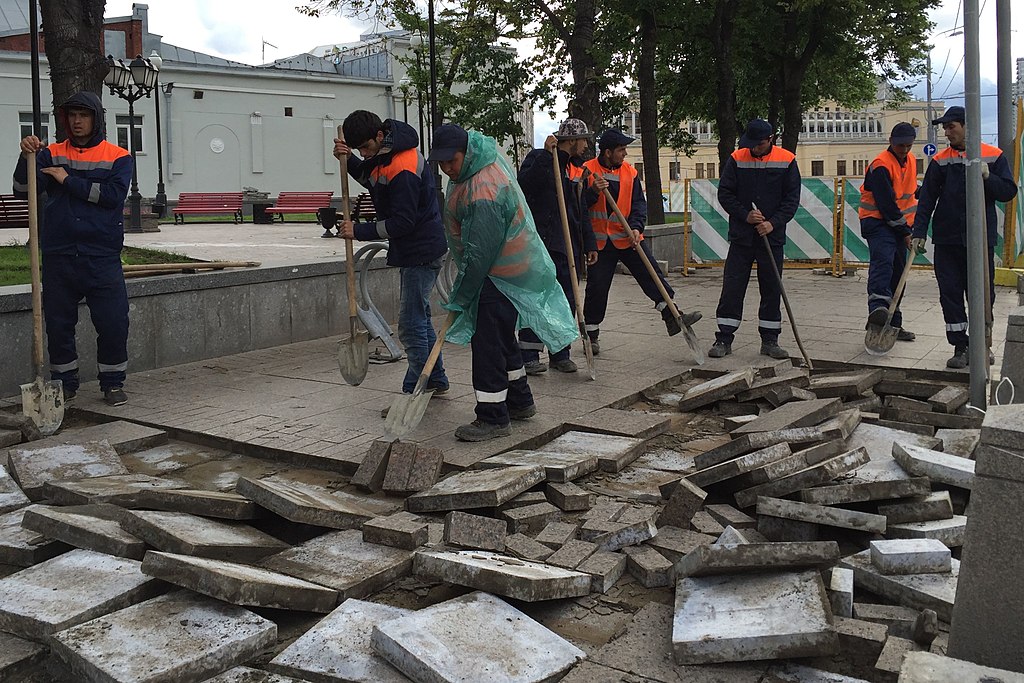
Migrant workers in Moscow, Russia.
“But, digging trenches for money and being citizens of another country, they violate the laws and customs of war and become criminals.”
Russia has stated that it will not draft migrant workers in the country and send them to fight in Ukraine. While this has been largely true, the accompanying excerpted article from the Russian-language independent news website Kloop reports that Central Asians are doing non-lethal work on Russia’s behalf within the zone of conflict in Ukraine.[i] According to the article, Russia has contracted workers from Central Asia to construct fortifications in occupied areas of Ukraine. The article notes that private military contractor the Wagner Group, which is one of the Russian companies involved in building defensive structures in Ukraine for use by the Russian military, has recruited migrant workers to work there with promises of a good salary and other benefits. The article also mentions how “the work did not require documents,” an incentive for Central Asians looking to work for Russian entities without needing to officially register to do so.
Such contracted work in Ukraine carries many risks. The article confirms the deaths of 84 workers in Luhansk who had been building such defensive structures, though it is unknown if this number included any Central Asian citizens. Other non-combat hazards of working in occupied Ukraine include poor working conditions, less pay than promised, and possible prosecution if they are captured by Ukraine. Such migrant workers could also face charges in their home countries, including possible loss of citizenship in Kyrgyzstan. Indeed, Kyrgyzstan and Uzbekistan have repeatedly warned their citizens that they can face prosecution in their home countries for serving as combatants in the war in Ukraine, with exceptions for those who hold Russian citizenship and are required to serve in the Russian armed forces. While the article is concerned about the fate of these migrant workers, there have been only a few examples of the Kyrgyzstani and Uzbekistani governments opening a case against an individual for fighting in Ukraine, and in each case these individuals fought for Ukraine against Russian forces. The article concludes that migrants are likely to continue working in Ukraine and that authorities in Central Asia will not interfere as the work provides an economic benefit Because of the importance of remittances to the economies in the region.
Source:
“Тюрьма и смерть за копейки. Мигрантов зовут рыть окопы для российской армии (Jail and death for a kopek. Migrant workers are being called to dig trenches for the Russia army),” Kloop (independent Russian-language news website in Kyrgyzstan), 2 March 2023. https://kloop.kg/blog/2023/03/02/tyurma-i-smert-za-kopejki-migrantov-zovut-ryt-okopy-dlya-rossijskoj-armii/
Migrant workers from Central Asia are being called to construct trenches for the Russian military, including in the occupied territories of Ukraine. They are offered up to 6,000 rubles a day for this work. But the real working conditions do not justify this money: dozens of workers are killed by the Armed Forces of Ukraine, employers are deceptive, and in their home countries, migrants are threatened with jail time and loss of citizenship.
…It was announced in October 2022 by the founder of the Wagner Group, businessman Yevgeny Prigozhin, that Russia will build defensive structures along the front line. And since November, Russian websites and Telegram groups of migrant workers from Central Asian countries started publishing announcements about the recruitment of workers to dig trenches, dugouts, anti-tank ditches, and strengthen structures for the military… Announcements about the recruitment of workers for the “arrangement of defensive lines” appeared on the Russian websites Headhunter, Avito, and at least two regional-scale announcement sites…
Employers are willing to pay from 45,000 to 180,000 rubles a month for the risk, or from 300 rubles ($4) per hour. In addition, they promised a lot of free things: travel, medical examination, accommodation, three meals a day. The requirements are to be in good health and between 20 and 50 years of age…A feature of some of the announcements in these groups was that the work did not require documents…The authors of ads in telegram groups for migrants also offered help from the employer in obtaining Russian citizenship if the employee worked on the “trenches” for at least four months.
…84 workers recruited from Novosibirsk, who responded to these vacancies, died from the strike of the Armed Forces of Ukraine on the occupied territory of the Luhansk region…Whether among them came from Central Asia or not, is still unknown…President Vladimir Putin, at a meeting with the government, confirmed that workers who were building “defensive structures” in the occupied territories had died.
In addition to the danger of dying from shelling from Ukraine, other troubles await the workers: unsanitary conditions, unheated living quarters and “the attitude is worse than for cattle.” This was told by “Present Time”…The Baza telegram channel also writes about this, citing one of the Tajiks, Aminjon. According to him, they were paid three times less than the promised amount. Other workers were even less fortunate: one had an attack of appendicitis, and another lost a hand, but they did not receive any adequate medical care. After Aminjon went to the police, they began to call him with threats, now he is afraid to leave the house.
Migrants can be prosecuted for at least four criminal offenses for digging trenches for the Russian military, especially in the occupied territories of Ukraine, human rights activist and migrant rights specialist Valentina Chupyk warns.
According to her, if such migrants are caught by the Ukrainian military, they will be tried for illegally crossing the border of Ukraine, as they dig trenches in the occupied territories – for this they face two to five years in prison…If Ukrainians find out that a migrant works for PMC Wagner or contributes to the illegal activities of the occupying authorities (for example, if the migrant was hired by the state), he will be sentenced in Ukraine for up to 20 years for complicity in the activities of a terrorist organization.
According to the Convention on the Laws and Customs of War on Land, migrants who dig trenches are not equated with combatants (combatants). But, digging trenches for money and being citizens of another country, they violate the laws and customs of war and become criminals. Therefore, they cannot surrender as prisoners of war, but can only turn themselves in to the legal authorities of Ukraine – and after that receive a life sentence.
It is difficult to say whether the construction of facilities for a clearly military purpose abroad will be interpreted in the homeland of migrants as participation in the conflict. However, the Embassy of Kyrgyzstan in Russia warned that, according to the Criminal Code of the Kyrgyz Republic, the participation of citizens of the Kyrgyz Republic in hostilities on the territory of foreign states is punishable by imprisonment for up to 10 years with confiscation of property.
In addition, for participation in armed conflicts or hostilities on the territory of a foreign state, a citizen of Kyrgyzstan can be deprived of citizenship.
Now the danger of punishment at home may seem insignificant to diggers, because Kyrgyzstan is critically dependent on Russia. In 2022, the transfers of individuals from there to the republic set a historical record, exceeding $2.7 billion…The authorities of Kyrgyzstan clearly do not want to quarrel with Moscow and are selective about the participation of their citizens in hostilities. Those who fight for Ukraine or simply support it, the authorities tend to punish, but those who fight for Russia do not. Thus, nothing is heard about investigations into the deaths of Kyrgyz citizens who fought with Ukraine on the side of the Russian Federation…However, the foreign policy environment can change quickly. If at some point it becomes profitable for the authorities of Kyrgyzstan to demonstrate neutrality or a critical attitude towards Russian aggression, the citizens of the country, who today are digging trenches in the occupied Ukrainian lands, may end up in prison. Or lose citizenship.
Notes:
[i] A few resources have become available for Central Asians who are illegally drafted or not allowed to leave Russia, including contact information for organizations in Russia that help migrant workers. These have been distributed through media in the region amid reports that Central Asians have been drafted or denied permission to leave Russia. See: “Что делать, если вас пытаются мобилизовать или не выпускают из России? (What to do if you are possibly mobilized or not allowed to leave Russia),” Asia-Plus, 9 March 2023. https://asiaplustj.info/ru/news/tajikistan/society/20230309/chto-delat-esli-vas-pitayutsya-mobilizovat-ili-ne-vipuskayut-iz-strani
Image Information:
Image: Migrant workers in Moscow, Russia.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Moscow,_Vozdvizhenka_Street,_destroying_solid_pavement_with_spades_(30645492273).jpg
Attribution: CCA 2.0