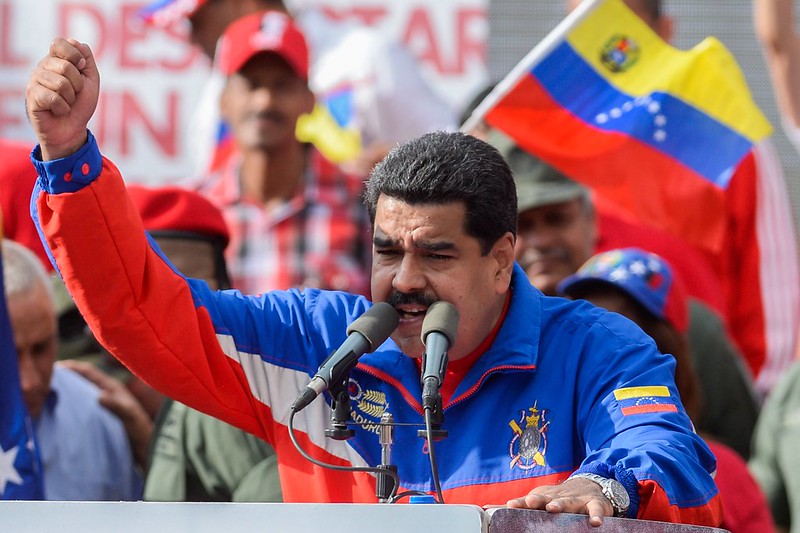
Maduro pushed the December 3rd referendum, partially as a distraction from his abysmal poll numbers.
“The Venezuelan president, Nicolás Maduro, ordered the immediate exploration and exploitation of oil, gas and mines in the territory of Essequibo, an area in dispute with Guyana, just one day after the ‘yes’ victory was announced in the referendum that claimed sovereignty over the territory.”
In December 2023, the Maduro regime of Venezuela oversaw a referendum about a long-disputed region called the Essequibo, which represents more than two-thirds of neighboring Guyana’s territory.[i] The Essequibo region—roughly the size of the state of Florida—has been administered by Guyana for more than 100 years, according to an arbitral award in Paris in 1899. The Maduro regime announced that 95 percent of Venezuelans who voted approved all five questions on the referendum. This included an explicit rejection of the recent jurisdiction granted to the International Court of Justice upon referral of the case by the UN’s Secretary General, as well as a commitment by the Venezuelan state to recover the territory by all means necessary “within the law.”[ii] Accordingly, the first excerpted article from Chilean news outlet La Nación reported that Maduro announced the creation of a new Venezuelan state called Guayana Esequiba, constituted by the territory of Essequibo. Maduro followed the announcement by encouraging state-owned enterprises to exploit the natural resources of the Essequibo area, as well as a small mobilization of troops and equipment near the border.[iii] According to La Nación, this has given rise to the possibility of inter-state conflict, a rare worry in Latin America. However, many countries in the region, as well as Venezuela’s political opposition, have interpreted Maduro’s threats to annex the Essequibo as a domestic ploy aimed at distraction. In the excerpted article from Argentina’s Urgente24, Venezuelan opposition leaders claimed that the referendum was a nationalistic distraction. The outlet says that Maduro is looking for a change in narrative after the recent successes of the country’s opposition, including the election of María Corina Machado, as the unified opposition candidate to face Maduro. Distraction or not, Maduro’s actions have engendered an environment that is rife with possibilities for miscalculation as both sides stake out maximalist positions.[iv]
Sources:
“Maduro propone ley que busca anexar esequibo a Venezuela: Pide explotar recursos naturales (Maduro proposes a law that seeks to annex Essequibo to Venezuela: He asks to exploit natural resources),” La Nación (a Chilean daily with over one hundred years reporting on the region), 6 December 2023. https://www.lanacion.cl/maduro-propone-ley-que-busca-anexar-esequibo-a-venezuela-pide-explotar-recursos-naturales/
The Venezuelan president, Nicolás Maduro, ordered the immediate exploration and exploitation of oil, gas and mines in the territory of Essequibo, an area in dispute with Guyana, just one day after the ‘yes’ victory was announced in the referendum that claimed sovereignty over the territory. Through a government act broadcast on radio and television, the president ordered that they immediately proceed ‘to grant operating licenses for the exploration and exploitation of oil, gas and mines in the entire area of our Guayana Esequiba.’
“Referéndum y nueva ‘Guyana Esequiba:’ Maduro distrae (Referendum and new ‘Guyana Esequiba:’ Maduro distracts),” Urgente24 (an Argentine outlet with both opinion and news) 6 December 2023. https://urgente24.com/mundo/referendum-y-nueva-guyana-esequiba-maduro-distrae-n564799
For her part, the Venezuelan presidential candidate María Corina Machado, who won the opposition primaries and who could dethrone Maduro if there is no fraud, spoke about it…and described it as a distraction from the success of the opposition primaries. ‘It is a way to distract attention from the monumental success that the primaries were and create cohesion in the different sectors of the ruling party around an element that awakens patriotic sentiment but that had a very low participation rate.’
Notes:
[i] For more information and background on the manufactured crisis and Venezuela’s claims, see: Ryan C. Berg and Christopher Hernandez-Roy, “The Entirely Manufactured and Dangerous Crisis over the Essequibo,” Center for Strategic and International Studies, 8 December 2023. https://www.csis.org/analysis/entirely-manufactured-and-dangerous-crisis-over-essequibo
[ii] For more information on the referendum questions and the dispute itself, see: Julia Symmes Cobb, “Explainer: What is the border dispute between Venezuela and Guyana?,” Reuters, 6 December 2023. https://www.reuters.com/world/americas/what-is-border-dispute-between-venezuela-guyana-2023-12-06/
[iii] For more information on troop and equipment deployments to the border with Guyana, bolstered with satellite imagery analysis, see: Christopher Hernandez-Roy et al., “Miscalculation and Escalation over the Essequibo: New Insights Into the Risks of Venezuela’s Compellence Strategy,” Center for Strategic and International Studies, February 9, 2024, https://www.csis.org/analysis/miscalculation-and-escalation-over-essequibo-new-insights-risks-venezuelas-compellence.
[iv] In response to the possibility of conflict, Brazil brought both parties to the table on the island nation of St. Vincent, negotiating the Argyle Declaration, which commits both sides to a peaceful resolution of the border dispute. However, the Maduro regime abrogates agreements frequently. For more information on the Argyle Declaration, see: “The Joint Declaration of Argyle for Dialogue and Peace between Guyana and Venezuela,” Government of Barbados, 14 December 2023. https://www.foreign.gov.bb/the-joint-declaration-of-argyle-for-dialogue-and-peace-between-guyana-and-venezuela/.
Image Information:
Image: Maduro pushed the December 3rd referendum, partially as a distraction from his abysmal poll numbers.
Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/125816678@N05/39329361431
Attribution: Flickr, CC BY-NC 2.0 DEED