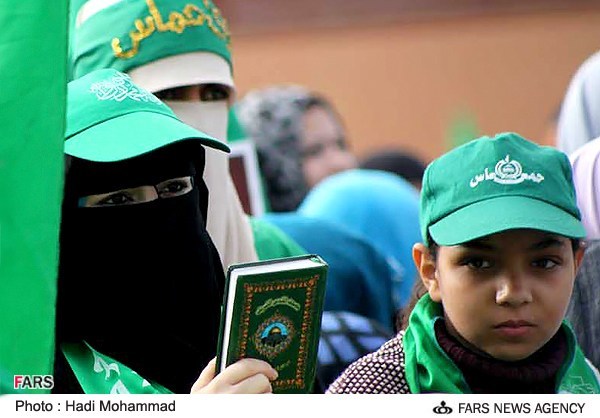
Hamas supporters in Gaza, including families and children, attending the 25th anniversary of the movement’s founding, December 2012.
“Houthi vehicles carrying slogans of supporting Gaza roam the villages with forms to register children and youth into these training courses.”
Hamas, and the Houthis in Yemen, both of whom have seen their popularity grow since 7 October, are capitalizing on conflict in Gaza to recruit new generations of young men into their culture of “Islamic Resistance.”[i] According to the first accompanying excerpt from an op-ed published recently in the Qatari-aligned al-Araby al-Jadeed, Hamas’s prior youth training efforts have been critical to its ability to withstand the Israeli campaign. The author mentions the “Futawwa” (youth) training program, which allowed Hamas to spread its “resistance” ideology across Gaza throughout the 2010s.[ii] The second and third accompanying excerpts, from the prominent Saudi dailies al-Sharq al-Awsat and al-Watan, respectively, illustrate how both Hamas and the Houthis have used their growing popularity since 7 October to launch recruitment campaigns, especially targeting the youth. Youth indoctrination is critical for both groups, and both have put substantial efforts into it over the past decade.[iii] The Houthi Movement and Hamas in Gaza share much in common. They are both mobilized movements with Islamic ideological underpinnings that act as de facto governments in their respective regions despite not formally being recognized as such by the international community. The key difference between them is doctrinal—the former are adherents of the Zaydi branch of Shia Islam while the latter is a Sunni, Muslim Brotherhood-affiliated movement. For both groups, though, “the culture of resistance” is a critical component that arguably supersedes sectarian differences. Perhaps to a greater degree than previously, a focus on sectarian differences seems secondary and increasingly irrelevant in the current context. Instead, Hamas and the Houthis—alongside Shia-majority Lebanese Hezbollah and the “Islamic Resistance of Iraq”—may coalesce into a transnational, cross-sectarian “Islamic Resistance” movement that should be thought of as distinct from the 2010s, Iran-led “Axis of Resistance.”[iv] Both on the Sunni and the Shia side, the new generation of fighters coming of age in the shadow of conflict in Gaza will presumably be less interested in sectarian differences or other intra-Islam disputes than in the fight against Israel.
Sources:
“How and why has Gaza held out?” al-Araby al-Jadeed (Qatari-aligned daily) https://www.alaraby.co.uk/opinion/كيف-صمدت-غزّة-ولماذا
What is the secret of this resilience? … After the attempted coup against the Hamas government and the separation of Gaza from the West Bank, the Gaza Strip fell under a tight siege, and the local “Gaza Authority” found itself under a unique state of “independence.” It was able to make whatever decisions it wanted regarding its society, especially in the fields of education and curriculum making… Specifically, the Hamas Authority introduced the “Futawwa” program into the curricula of its schools, aiming to train students specifically in weapons use and field skills.
“Hamas seeks to exploit the Gaza war in the Lebanese camps,” al-Sharq al-Awsat (prominent Saudi daily), 4 December 2023. https://aawsat.com/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8%D9%8A/%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85%D8%B4%D8%B1%D9%82-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%B1%D8%A8%D9%8A/4708376-%C2%AB%D8%AD%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B3%C2%BB-%D8%AA%D8%AD%D8%A7%D9%88%D9%84-%D8%A7%D8%B3%D8%AA%D8%AB%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%AD%D8%B1%D8%A8-%D8%BA%D8%B2%D8%A9-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D9%85%D8%AE%D9%8A%D9%85%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D9%84%D8%A8%D9%86%D8%A7%D9%86
On Monday, the Lebanese branch of the Hamas movement announced the establishment of the “Vanguards of the Al-Aqsa Flood.” This is an organization with military dimensions, as the statement suggested…
In a statement, the movement called on “young and heroic men” to join the “vanguard of the resistance.” The movement’s sources explained that “this project is linked to Lebanon and does not aim exclusively to gather more fighters, but rather to include more individuals in Hamas who are active in more than one sector.” A statement issued by the movement linked the establishment of these vanguards to “affirming the role of the Palestinian people, wherever they are, in resisting the occupation by all available and legitimate means,” and to “complementing what Operation Al-Aqsa Flood achieved, and benefiting from scientific and artistic energies and capabilities.”
“Houthis recruit children through seminars on war in Gaza,” al-Watan (prominent Saudi daily), 18 November 2023. https://www.alwatan.com.sa/article/1137388
A Yemeni source in Sanaa said that the most rejoicing over what is happening in Gaza is among the Houthi militias, who rose up directly to restore their dilapidated ranks and support their disintegrating fronts… The source stated that Houthi vehicles carrying slogans of supporting Gaza roam the villages with forms to register children and youth into these training courses, a method that does not differ from previous methods of recruitment. However, the Houthis have developed new tricks to entice children and youth to enroll in these malicious courses. This includes sending young graduates to the streets to talk about their participation in previous courses, graduating them without any assignments, and giving them monthly salarie
Notes:
[i] Several opinion polls confirm these groups’ rising popularity, including:
“Wide public support for Hamas’ offensive on October the 7th, but the vast majority denies that Hamas has committed atrocities against Israeli civilians,” Palestinian Center for Policy and Survey Research, 13 December 2023. https://www.pcpsr.org/en/node/963
“How the Israel-Hamas War in Gaza Is Changing Arab Views,” Arab Barometer, 14 December 2023. https://www.arabbarometer.org/media-news/how-the-israel-hamas-war-in-gaza-is-changing-arab-views/;
“New Poll Sheds Light on Saudi Views of Israel-Hamas War,” The Washington Institute for Near East Policy, 21 December 2023. https://www.washingtoninstitute.org/policy-analysis/new-poll-sheds-light-saudi-views-israel-hamas-war; “Arab Public Opinion about the Israeli War on Gaza,” Doha Institute, 10 January 2024. https://www.dohainstitute.org/en/Lists/ACRPS-PDFDocumentLibrary/arab-opinion-war-on-gaza-press-release-en.pdf
[ii] Much has been written on the program over the past decade. See for instance: “Gaza teens graduate from Hamas military school,” Ynet News, 24 January 2013. https://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-4336807,00.html
and “Training Fighters of Future Across Gaza,” New York Times, 14 January 2014. https://www.nytimes.com/2014/01/15/world/middleeast/training-fighters-of-future-across-gaza.html
[iii] For more on Hamas youth recruitment, see: “The Road to October 7: Hamas’ Long Game, Clarified,” CTC Sentinel, October/November 2023. https://ctc.westpoint.edu/the-road-to-october-7-hamas-long-game-clarified/; For the Houthis, see: “Yemen: Houthis Recruit More Child Soldiers Since October 7,” Human Rights Watch, 13 February 2024. https://www.hrw.org/news/2024/02/13/yemen-houthis-recruit-more-child-soldiers-october-7
[iv] The idea of an “Islamic Resistance” axis is not new. However, it bears distinguishing the emergent post-7 October Islamic Resistance from the Iran-led “Axis of Resistance.” The latter coalesced in the early 2010s, during the fight against ISIS and in support of the Syrian regime, and at a time when Hamas was estranged from Iran and its proxies. As such, the Axis of Resistance emerged as a primarily Shia organization focused on countering Sunni extremism in Syria and Iraq (or, for the Houthis, fighting against Saudi Arabia and its Yemeni allies). Israel remained part of the discourse, but it was not the axis’s primary focus.
Image Information:
Image: Hamas supporters in Gaza, including families and children, attending the 25th anniversary of the movement’s founding, December 2012.
Source: https://media.farsnews.ir/Uploaded/Files/Images/1391/09/18/13910918213433966_PhotoL.jpg
Attribution: CCA-SA 4.0 Intl.