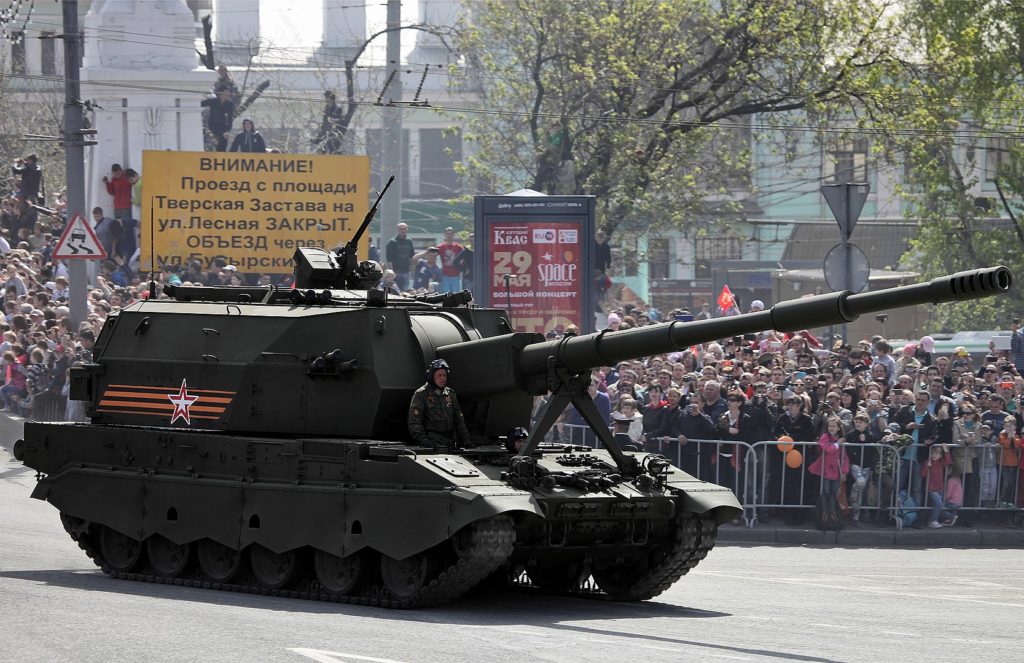
Early variant of the 152mm self-propelled gun 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV on parade in Moscow, 2015. The Koalitsiya-SV is set to be fielded in 2024.
“It became clear that a large-scale war requires a lot of equipment. It needs to be constantly improved, adapting to new weapons that the enemy has, damaged vehicles need to be repaired somewhere. And the priority in rearmament shifted towards the army.”
According to the 10 January excerpted article from the Russian state-owned domestic news outlet RIA Novosti, Russia will increase its defense spending in keeping with the release of Russia’s federal budget in October 2023 that dedicated “almost 11 trillion rubles” ($117 billion) to the armed forces.[i] The article notes plans to grow the armed forces by nearly half a million men, while most of the funds will be earmarked for weapons and equipment, whose procurement is informed by lessons learned in Ukraine. The emphasis is on ground forces but includes new spending on air and naval assets. As it articulates: “In recent decades, the ground forces of many countries have been financed on a residual basis—the United States relied on the Air Force and Navy. Russia was no exception in this regard, but the Ukrainian conflict put everything in place.”
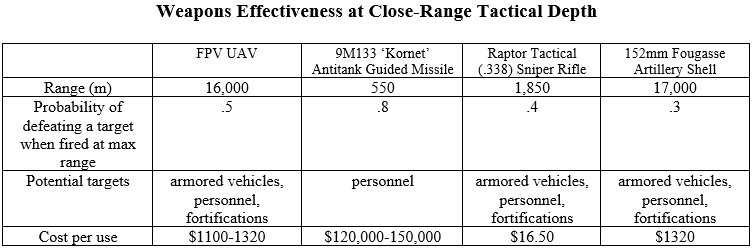
Increasing the quantity and quality of its armor, tanks, and artillery is a primary focus, according to the article. Russia will ramp up production of improved variants of the T-90M Proryv [RG1] , T-72B3M [RG2] , and T-80BVM [RG3] main battle tanks. Artillery is also being updated with the introduction of the upgraded 152-mm Msta-S [RG4] self-propelled gun[ii] and the latest Malva [RG5] -wheeled howitzer, which entered service in late 2023.[iii] Russia’s newest artillery system, the 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV [RG6] , is projected to be fielded in 2024. The weapon systems and upgrades reflect immediate application of lessons learned from the Ukrainian battlefield. Ukraine seemed to have an edge when NATO-manufactured long-range weapons arrived on the battlefield and Russian units were forced to move their command and logistic lines farther from the front lines. The article notes that the Koalitsiya-SV “will become the longest-range weapon in the Russian Army, able to fire a “high-explosive fragmentation projectile at a range of 40 kilometers, and a guided projectile at 70 kilometers…more than enough [distance] for effective counter-battery warfare.” Drones are also featured in Russia’s defense plans for this year.[iv] The “long-awaited Izdeliye-53, another version of the Lancet [RG7] kamikaze drone,” is projected to be fielded in 2024. Like long-range artillery, the Izdeliye-53 could have an immediate battlefield impact as it is said to have a range of more than 60 kilometers. The much-publicized increase in Russian defense spending, and the types of weapons Russia will field, based on lessons learned in Ukraine, could put additional pressure on Ukraine and its Western partners just to maintain the status quo.
Sources:
Andrey Kots, “Приоритеты на будущее. Чем вооружат армию России в 2024-м (Priorities for the future. What will the Russian army be armed with in 2024?)” RIA Novosti (Russian state-owned domestic news outlet), 9 January 2024. https://ria.ru/20240109/perevooruzhenie-1917044593.html?in=t
… Earlier, back in January 2023, Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced an increase in the size of the army to one and a half million people by 2026.
…
At the end of October, Finance Minister Anton Siluanov announced the total amount of defense spending in 2024 – almost 11 trillion rubles. The lion’s share will go to the purchase of military equipment. The domestic defense industry has to work hard: it is necessary to saturate not only new units, but also units on the front line with everything necessary.
“Taking into account additional budgetary allocations in 2024, the volume of purchases and repairs of weapons and military equipment will increase,” Sergei Shoigu said at the end of November. “In the current conditions, it is necessary to ensure an advanced supply of weapons, military and special equipment to the troops, as well as to increase the production capabilities of enterprises military-industrial complex for the production and repair of the most popular models.”
In recent decades, the ground forces of many countries have been financed on a residual basis – the United States relied on the Air Force and Navy. Russia was no exception in this regard, but the Ukrainian conflict put everything in place. It became clear that a large-scale war requires a lot of equipment. It needs to be constantly improved, adapting to new weapons that the enemy has, damaged vehicles need to be repaired somewhere. And the priority in rearmament shifted towards the army.
The Ground Forces will continue to receive modern main battle tanks. First of all, the T-90M Proryv, T-72B3M and T-80BVM, which have proven themselves well in combat. New tanks are significantly different from pre-war ones. They received additional armor, equipment to suppress UAVs, and modern communications equipment. Many are equipped with a factory “visor” – a lattice superstructure over the turret with dynamic protection modules for defense against “roof-killing ATGMs” and kamikaze drones.
Motorized rifle units will receive vehicles, BTR-82A [RG1] armored personnel carriers, BMP-3 [RG2] infantry fighting vehicles and modernized BMP-2M [RG3] . The latter began to enter the troops only in 2020. Their difference from the early “twos” is the Berezhok combat module, equipped with a 30-mm automatic cannon, an automatic grenade launcher, a machine gun and four Kornet ATGMs. The vehicle has an updated fire control system, ensuring round-the-clock use, automatic target tracking and increased shooting accuracy.
The artillerymen will receive 152-mm Msta-S [R4] self-propelled guns and the latest Malva wheeled howitzers, which first entered service with the troops in the fall of 2023. What’s even more important: next year, the promising self-propelled gun “Coalition-SV,” which the troops have been waiting for a long time, will go into serial production. It will become the longest-range weapon in the Russian army… .In 2024, the long-awaited Izdeliye-53, another version of the famous Lancet kamikaze drone, should go into service with the troops. All that is known about the new UAV is that its range is over 60 kilometers and it will be designed to operate in a “flock.”
Notes:
[i] For more information regarding defense spending within Russia’s new federal budget, see: Dodge Billingsley, “Russia’s Federal Budget Puts Economy on War Footing,” OE Watch, 01-2024. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2024/russias-federal-budget-puts-economy-on-war-footing/
[ii] For a look back at Russian efforts to increase the effective firing range of the Msta, see: Charles Bartles, “New Artillery Rounds Will Extend Russian Artillery Range,” OE Watch, January 2018. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-singular-format/294224
[iii] The Msta-S is an old system introduced in 1989. For information on recent modifications and upgrades, see: “Artillery of the future: modernization of the ACS 2S19 “Msta-S” and its prospects,” Military Review, 16 December 2023. https://military-review.com/12479016-artillery-of-the-future-modernization-of-the-acs-2s19-msta-s-and-its-prospects; the 2S43 Malva wheeled artillery is also a legacy system but previous Russian claims refer to the new variant as the Russian HYMARS, although the effective range as been disputed. See: Ellie Cook, “What Is 2S43 Malva? Soviet Self-Propelled Howitzer Dubbed ‘Russian HYMARS’,” Newsweek, 17 August 2023. https://www.newsweek.com/russia-military-2s43-malva-howitzer-ukraine-himars-artillery-1820411
[iv] Drones, or UAVs, have become ubiquitous in the war in Ukraine at every level. For additional insight on Russia’s use of drones, see: Charles Bartles, “Russia Plans To Add Remote Mining UAV Platoons To Engineer Units,” OE Watch, 09-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/russia-plans-to-add-remote-mining-uav-platoons-to-engineer-units/; see also, Dodge Billingsley, “Russia Details Plan To Overcome Military Drone Deficiencies,” OE Watch, 01-2024. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2024/russia-details-plan-to-overcome-military-drone-deficiencies/
Image Information:
Image: Early variant of the 152mm self-propelled gun 2S35 Koalitsiya-SV on parade in Moscow, 2015. The Koalitsiya-SV is set to be fielded in 2024.
Source: Vitaly Kuzman, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2S35_Koalitsiya-SV – /media/File:9may2015Moscow-35_(cropped).jpg
Attribution: CCA BY-SA 4.0