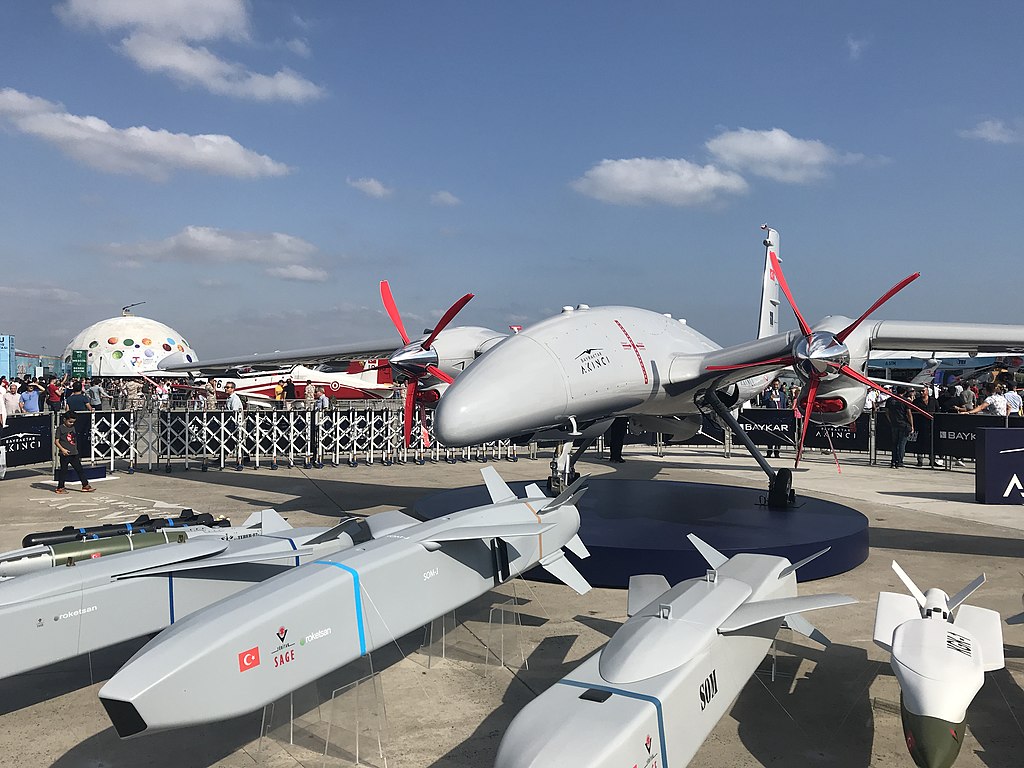
Alongside Baykar, Turkish Aerospace Industries has developed unmanned aerial systems like the Aksungur (pictured) for reconnaissance and strike missions.
“Europe emerged as the top market for Turkish exports, with demand focusing on UAVs, smart missiles, land vehicles, military vessels, and radar systems.”
The Turkish defense industry is experiencing significant growth and has recently announced a record-breaking year. The accompanying excerpted article from Turkey’s state-run news agency Anadolu Ajansi reports on the Turkish defense industry’s record year of exports in 2024. The article notes several statistics on the defense exports, including the different types of weapon systems Turkey exported and the large number of countries that received Turkish systems. Notably, Turkey exported several hundred unmanned aerial systems to various countries, though the article does not mention specific models. Indeed, the Turkish defense industry has gained a reputation for providing effective weapon systems at a lower cost than other Western weapon systems. This is specifically due to the use of Turkish Bayraktar TB2 UAVs by Azerbaijan (in the Second Nagorno-Karabakh War in 2020) and Ukraine.[i] The article also mentions that Europe emerged as the top market for Turkish exports with a demand for UAVs, among other items.[ii] The article ends by stating that the Turkish defense industry is made up of over 3,500 companies working on over 1,100 projects and that the industry continues to be heavily involved with NATO member states. As NATO increases its defense spending over the next few years and beyond, the Turkish defense industry could be primed for additional growth.
Sources:
Zeynep Duyar, “Turkish defense products empower, protect world armies,” Anadolu Ajansi (Turkey’s state-run news agency), 24 January 2025.
https://www.aa.com.tr/en/economy/turkish-defense-products-empower-protect-world-armies/3461489
Türkiye’s domestically produced defense products achieved global prominence in 2024, reaching a record export value of nearly $7.2 billion…Ranked 11th among global defense exporters, Türkiye’s advancements in mass production, research and development, and technological innovation significantly boosted its global footprint…
Turkish defense products were exported to over 180 countries, with major contributions to land, naval, aerial, and advanced weaponry sectors. Over 4,500 land vehicles were delivered to 40 countries, and 140 naval platforms reached more than 10 nations.
Additionally, 770 UAVs and UCAVs were sent to over 50 countries, while three nations received Turkish-built corvettes.
Other highlights included exports of 1,200 electro-optical and stabilized weapons systems, radar systems to 10 countries, and 1,500 loitering munitions to 11 nations…
Haluk Gorgun, president of Türkiye’s Defense Industry Agency (SSB), emphasized the breadth of the country’s defense production. Türkiye achieved over 80% indigenous technology utilization in its defense products, supported by a research and development budget nearing $3 billion
…Europe emerged as the top market for Turkish exports, with demand focusing on UAVs, smart missiles, land vehicles, military vessels, and radar systems. A key milestone was the export of Aselsan’s ASELFLIR-500 electro-optical reconnaissance system to 16 countries…
The country’s defense sector comprises over 3,500 firms and more than 1,100 active projects, demonstrating its robust position in global markets. Last year, Türkiye applied for the highest number of NATO projects, solidifying its role as a major contributor to allied defense capabilities.
Notes:
[i] For more background on the medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) Bayraktar TB2 and its use in recent conflicts, see: Karen Kaya, “Turkey as a Drone Superpower: A Case Study of a Mid-Size Power Driving the Operational Environment,” FMSO Foreign Perspectives Briefs, 28 March 2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/2023-03-28-turkey-as-a-drone-superpower-a-case-study-of-a-mid-size-power-driving-the-operational-environment-karen-kaya-update/
[ii] Turkey not only exported a number of weapon systems to Europe in 2024, the Turkish company Baykar, which produces the Bayraktar TB2, bought Italy’s Piaggio Aerospace in December 2024. While it remains to be seen what Baykar will do with its newfound subsidiary, it marked increased involvement of the Turkish defense industry’s involvement in Europe, see: Ezgi Akin, “Buoyed by drones, NATO deals, Turkey defense exports hit record $7.1B,” Al-Monitor (English-language independent news website focusing on Turkey and the Middle East), 3 January 2025. https://www.al-monitor.com/originals/2025/01/buoyed-drones-nato-deals-turkey-defense-exports-hit-record-71b
Image: Alongside Baykar, Turkish Aerospace Industries has developed unmanned aerial systems like the Aksungur (pictured) for reconnaissance and strike missions.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:TAI_Aksungur_(3).jpg
Attribution: Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license.