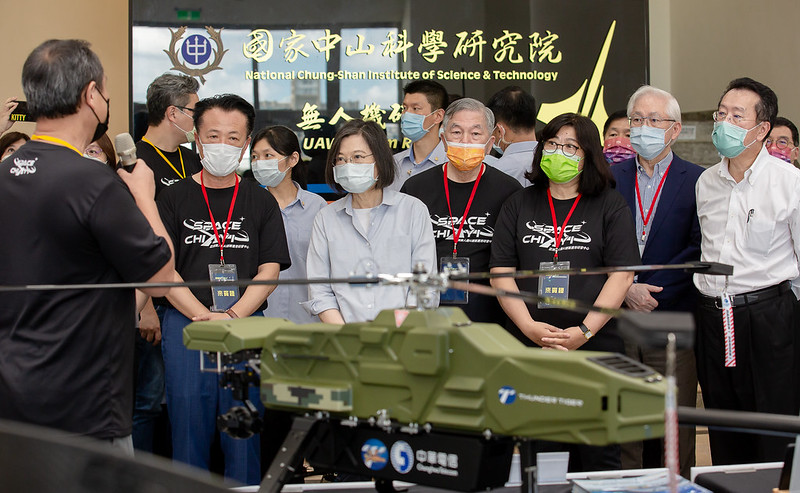
Taiwanese President Tsai Ing-wen attends the “Asian Drone AI Innovation Application R&D Center Opening Press Conference and Unveiling Ceremony” on August 13th, 2022.
“Taiwan seeks to manufacture 3,200 military drones, ranging in design from mini-drones under 2 kilograms to large reconnaissance aircraft with a cruising range of more than 150 kilometers.”
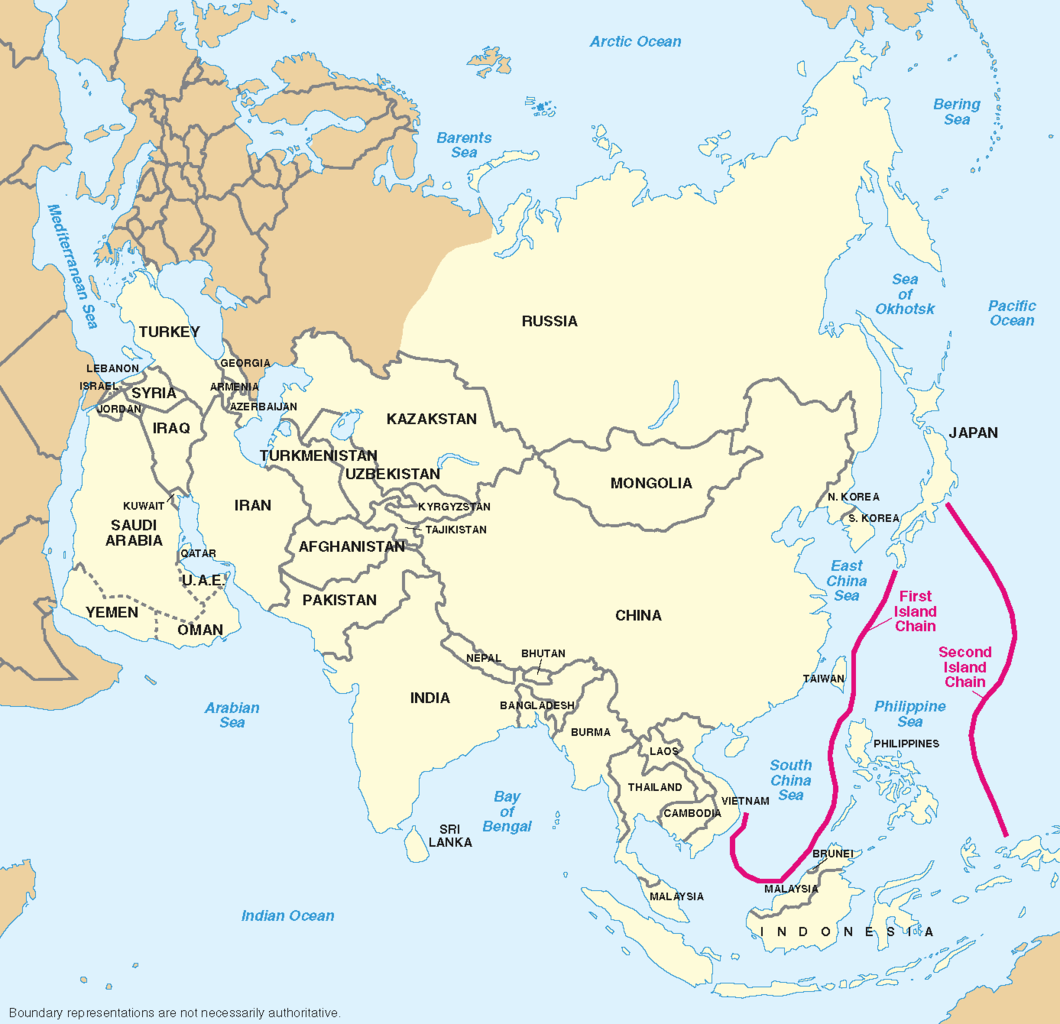
Taiwan has taken an interest in Ukraine’s ongoing war with Russia. Namely, Taiwanese policymakers are researching how Ukraine continues to counter the military advantages of a significantly more powerful opponent. According to the first excerpted article from the Liberty Times Net, an influential Taiwanese news outlet, reports from a 77-page briefing given to the Taiwanese president, Tsai Ing-wen, outlining the reason that Taiwan thinks Ukraine has been successful: drones. The briefing elaborates that, “At the beginning of the war, Ukraine was believed to lack air superiority but created their own partial air superiority through drones.” The briefing comes against the backdrop of increased tension between Taiwan and China. The Taiwanese briefing expresses concern that disparities between Taiwan and China’s drone capabilities could endanger Taiwanese national security, given the Ukraine conflict has demonstrated the importance of drones.
According to the article, the drone technology gap between China and Taiwan has developed into a “dangerous” stage. China surpasses Taiwan in the fielded varieties and number of UAVs by a significant margin. China possesses over fifty types of drones with a fleet numbering in the tens of thousands while Taiwan has four types of drones in a fleet numbering in the hundreds. This gap motivated President Tsai to initiate the “Drone National Team” project, which aims to create a self-sufficient Taiwanese drone industry by mid-2024. The same article remarks that “Taiwan seeks to manufacture 3,200 military drones, ranging in design from mini drones under 2 kilograms to large reconnaissance aircraft with a cruising range of more than 150 kilometers.”
While Taiwan develops its drone industry, the United States is assisting Taiwan to close the drone gap. As per the second article from The Central News Agency, Taiwan’s national news agency, in August, Taiwan received some $345 million in U.S. military aid, which includes the transfer of four MQ-9A unarmed reconnaissance drones.[i] The arms deal coincides with Taiwan’s national goal to bolster its drone fleet. Drones will play a significant part in Taiwan’s strategy to deter China. As China increases its aggression toward Taiwan, Taiwan will have more opportunities to increase security cooperation with like-minded countries. However, new Taiwanese security deals with foreign countries will likely provoke China’s ire. Growing tensions will place larger burdens on Taiwan’s diplomatic partners to support the island against external threats. As demonstrated by other global conflicts with similar matchups, Taiwan believes that drones will make significant contributions to deterring Chinese aggression.
Sources:
“俄烏戰爭無人機成關鍵 台灣加速製造望明年擁3000架以上 (Drones Have Become Key to the Russia-Ukraine War, Taiwan is Accelerating Manufacturing and Hopes to Have More Than 3,000 Drones Next Year),” Liberty Times Net (independent Taiwanese news outlet), 22 July 2023. https://def.ltn.com.tw/article/breakingnews/4371980
According to Reuters, when President Tsai Ing-wen met with top leaders of the Democratic Progressive Party last summer, the 77-page briefing stated, ‘At the beginning of the war, Ukraine was commonly believed to lack air superiority, but created their own partial air superiority through drones.’ This is the reason that, while Russia’s initial advantages and military power are much greater than that of Ukraine, Ukraine was able to successfully resist the Russian army. However, this answer is not good news for Taiwan.
Reuters pointed out that in the face of China, which has more powerful capabilities and is arming drones, the drone development gap between Taiwan and China has entered into a “dangerous” stage. Two sources and an internal security report revealed that Taiwan currently has only four types of drones, and the number of drones in the fleet is likely in the “hundreds.” However, according to national defense analysis, Reuters’ review of China’s commercial military manufacturing information, Chinese Communist Party official media reports, and other sources, it is estimated that the Chinese People’s Liberation Arm’ has more than 5’ different types of drones, and the number of drones in its fleet is “tens of thousands.”
Therefore, President Tsai Ing-wen “pressed the button” and launched the drone program to narrow the gap with China. Within the “Drone National Team” plan, the government convenes commercial drone manufacturers, aerospace companies and the military to cooperate to quickly create a self-sufficient supply chain. According to the government plan, it is expected to be completed by mid-2024, Taiwan seeks to manufacture 3,200 military drones, ranging in design from mini-drones under 2 kilograms to large reconnaissance aircraft with a cruising range of more than 150 kilometers.
Kai-hsiang Yu, “知情人士:美對台軍事援助 包含4架MQ-9A無人機 (People Familiar with the Situation: US Military Assistance to Taiwan Includes 4 MQ-9A [RG1] Drones),” Central News Agency (Taiwan’s national news agency), 14 August 2023. https://www.cna.com.tw/news/aipl/202308140105.aspx
Following the military’s purchase of MQ-9B, people familiar with the situation told CNA reporters in the morning that the $345 million in military assistance announced by the United States at the end of July to Taiwan includes four MQ-9A unarmed drones used for reconnaissance. The United States is currently adjusting the MQ-9A advanced agility and sensitive equipment, and the delivery date has not yet been finalized. This will help improve intelligence, surveillance, and intelligence link abilities in the airspace around Taiwan…
Notes:
[i] The deal also comes with an intelligence sharing agreement including Taiwan, the United States, the Philippines, and Japan. See; Kathrin Hille & Demetri Sevastopulo, “US to link up with Taiwan and Japan drone fleets to share real-time data,” Financial Times, 8 June 2023. https://www.ft.com/content/bde0db76-a7f8-4ecd-b5d5-03de0b5a8659
Image Information:
Image: Taiwanese President Tsai Ing-wen attends the “Asian Drone AI Innovation Application R&D Center Opening Press Conference and Unveiling Ceremony” on August 13th, 2022
Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/presidentialoffice/52282054928
Attribution: CCA-SA 4.0 Intl