China’s Eastern Theater Command released posters for ‘Joint Sword-2024A’, showcasing weapons aimed to ‘kill’ Taiwan independence.
“The distance is getting closer and closer, only one step away from the main island of Taiwan, or even a finger away.”
Summary: China concluded its Joint Sword-2024A military drills, the largest and closest-ever drills held near Taiwan. China states these drills test its ability to seize power in Taiwan, reinforcing concerns that future exercises may serve as a pretext for an actual invasion.
On 23-24 May, China conducted its latest large-scale military exercise, Joint Sword-2024A, around Taiwan, including the surrounding Kinmen, Matsu, Wuqiu, and Dongyin islands. These drills were the largest and closest-ever held to Taiwan and signal an increasingly aggressive Chinese stance.
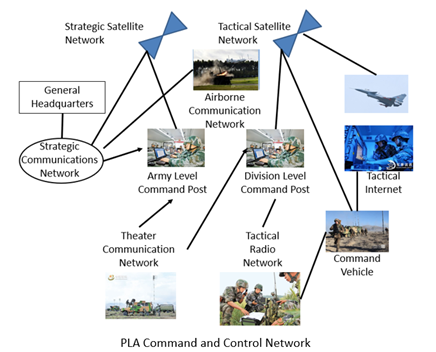
According to the first excerpted article published by the Central Military Commission via its website www.81.cn, the purpose of Joint Sword-2024A was to punish separatist activities of Taiwan’s independence forces and to issue a serious warning against interference from external forces.[i] Joint Sword-2024A was conducted by the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) Eastern Theater Command to enhance its combat capabilities through multi-domain coordination. The exercise involved ships and aircraft conducting joint training near Taiwan’s periphery, including the Taiwan Strait and its northern, southern, and eastern regions.[ii] Activities encompassed rapid deployment of destroyer and frigate formations, integration of intelligence data for sea and air scenarios, target acquisition, and joint strikes. South of Taiwan networks of destroyer, frigate, and anti-submarine formations were established, deploying assets for comprehensive submarine detection. The Air Force deployed fighter jets for combat patrols around Taiwan, engaging in joint intelligence sharing and coordination with surface fleets for target strikes. Meanwhile, the Army and Rocket Force assumed predesignated launch positions, initiating preparation for joint strikes in coordination with naval and air assets.[iii] In the second excerpt, published by the People’s Republic of China newspaper Da Wan News, Major General Meng Xiangqi, a PLA professor from the National Defense University, outlines several significances of the Joint Sword-2024A exercise.[iv] Firstly, conducting battle group exercises from multiple directions very close to Taiwan’s periphery is intended to tightly confine Taiwan’s military defense space. Major General Meng stated the exercise demonstrates that the closer Taiwan independence forces move towards external support, the tighter the squeeze around Taiwan will become. He strongly indicates that PLA forces will inch closer to Taiwan’s periphery with each successive exercise.[v] Secondly, Major General Meng emphasized the significance of the exercise’s focus on the southern and eastern parts of Taiwan. In particular, he highlighted the strategic importance of eastern Taiwan, which has traditionally been considered a refuge and a place to preserve combat power by Taiwan’s military. He dismisses this notion, emphasizing that Joint Sword-2024A demonstrates the PLA’s ability to create a powerful firepower network through the close cooperation of its four major services—land, sea, air, and rocket forces—capable of delivering strikes anywhere, anytime on targets, including eastern Taiwan. Major General Meng also pointed out that if external forces were to intervene, they would likely approach from the east. However, the PLA’s ability to control and block access from the east means that Taiwan independence forces would be unable to escape or receive foreign aid. Thirdly, Major General Meng emphasized the significance of implementing a comprehensive blockade around the island. Such a blockade would halt Taiwan’s energy imports, disrupt domestic exports, and sever aid from the U.S. and its allies, effectively crippling the island.[vi] Ultimately, Joint Sword-2024A demonstrates that military drills are becoming routine to signal displeasure and punish Taiwan. Additionally, it underscores China’s increasing capability to convert these exercises around Taiwan into actual military operations at any time.[vii]
Sources:
Guo Yanfei, “东部战区位台岛周边开展“联合利剑-2024A”演习 (Eastern Theater Command conducts the ‘Joint Sword-2024A’ exercise around Taiwan island), www.81.cn (China’s Central Military Commission (CMC), the highest national defense organization in the PRC), 24 May 2024. http://www.81.cn/yw_208727/16310888.html
From May 23 to 24, the Eastern Theater Command of the PLA organized the army, navy, air force, rocket force, and other units to conduct the ‘Joint Sword-2024A’ exercise around Taiwan. The exercise focused on joint sea and air combat readiness patrols, the joint seizure of battlefield comprehensive control, joint precision attacks on key targets, and other objectives. Li Xi, spokesperson for the Eastern Theater Command, stated that this exercise was a powerful punishment for Taiwan separatist forces seeking independence and a serious warning to external forces.
Starting at 0734, the exercise and training began in the Taiwan Strait, as well as in the northern, southern, and eastern parts of Taiwan, including areas around Kinmen, Matsu, Wuqiu, and Dongyin island. After the mobilization order was given, multiple formations of destroyers and frigates moved at high speed to surround Taiwan. Upon reaching their designated areas, the ships deployed their main and secondary guns, missiles, and other weapon systems, ready to strike. The fleet integrated intelligence information from both the air and sea, captured and locked onto targets, and executed multi-type, multi-dimensional saturation simulated strikes. Additionally, ships and aircraft coordinated anti-submarine operations by using towed sonar and buoys and carried out simulated attacks against underwater targets.
The Eastern Theater Air Force also dispatched dozens of fighters to systematically conduct combat patrols around Taiwan and its outer islands. These fighter jets, relying on joint intelligence support and various tactical maneuvers, approached the periphery of Taiwan for combat patrols. The air force formed multi-type formations with live ammunition and flew to designated airspace to establish strike positions. They coordinated with destroyers, frigates, and missile boats to simulate strikes against high-value targets. Simultaneously, the army and rocket force moved into their designated areas, quickly occupying their launch positions to coordinate with sea and air assault forces for joint strikes.
With the support of the Eastern Theater Command’s joint combat system, the theater command’s troops conducted training in sea assault, land strike, air defense, and anti-submarine operations around Taiwan. This exercise further tested their actual combat capabilities in multi-domain coordination and joint strike operations.
“联合利剑—2024A”演习距台岛很近有何深意?专家解析:这次解放军以压倒性实力反切香肠 (What is the significance of ‘Joint Sword-2024A’ being so close to Taiwan? Experts analyze: this time the PLA is countering incremental steps of Taiwan independence with overwhelming strength),” Xinan Evening News (PRC newspaper created by the Propaganda Department of the Anhui Provincial Committee of the CCP), 25 May 2024. https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1799986237998926830&wfr=spider&for=pc
On May 23, the Eastern Theater Command of the People’s Liberation Army conducted the ‘Joint Sword-2024A’ exercise around Taiwan, involving sea-air coordination, sea assault, land strikes, and other training activities. The exercise aimed to test multi-domain coordination and organize joint strikes, demonstrating the combat capabilities of the Eastern Theater Command troops. With strong determination, firm will, and robust capabilities, they are poised to resolutely crush the arrogance of Taiwan independence forces. There are three significant aspects of this exercise to note: 1) The proximity of the exercise close to Taiwan. 2) The joint efforts to seize battlefield control and execute precision attacks. 3) The deployment of troops to the eastern part of Taiwan and its strategic implications.
Regarding the proximity of the exercise to Taiwan, Major General Meng Xiangqing, a professor and special commentator at the National Defense University, highlights two key points. First, he notes that the approaching ships and aircraft are increasingly nearing Taiwan, being just a step away from the main island, or even as close as a finger’s reach. Second, he emphasizes that the exercise clearly showcases the PLA’s multi-domain control capabilities, with the depth of this ‘squeeze’ being greater and more unprecedented than before. It can be inferred that the closer Taiwan independence forces move towards external support, the tighter the chain around Taiwan will become.
Regarding joint efforts to seize battlefield control and execute precision attacks, Major General Meng Xiangqing highlighted the 3D animations released by the Eastern Theater Command which demonstrated the focus on striking critical Taiwan independence targets. This involves leveraging strategic advantages by targeting coastal areas and dominating sea, air, and information domains from multiple directions. Additionally, the deployment of naval and air assets across vast areas creates a robust firepower network capable of striking any location harboring Taiwan independence. Regarding the strategic implication of troop deployments to the eastern part of Taiwan, Major General Meng Xiangqing emphasizes it as a significant shift in perspective. Historically, the Taiwan military underestimated the PLA’s capability to effectively project combat power to the eastern part of the island, considering it a haven to preserve their own combat strength. However, recent demonstrations by the PLA, including simulated multi-directional strikes, have highlighted their ability to swiftly deploy troops to the region and assert control over key routes. Should external forces attempt intervention, they would likely approach from the east. However, the Eastern Theater Command’s capacity to deploy joint formations of naval, air, and land forces indicates that Taiwan independence elements would find it difficult to escape, foreign aid would be effectively blocked, and there would be no vulnerable points in their defense.
Notes:
[i] To watch the PRC’s Ministry of Defense (MOD) official response for conducting Joint Sword-2024A, see the MOD’s video post, Ministry of National Defense of the People’s Republic of China, 24 May 2024. http://www.mod.gov.cn/gfbw/xwfyr/fyrthhdjzw/16310980.html
[ii] For a comprehensive breakdown of PLA activities during Joint Sword-2024A, including composition of PLA forces on each day, see Taiwan’s Ministry of National Defense daily report of PLA activities, Ministry of National Defense, R.O.C. https://www.mnd.gov.tw/PublishTable.aspx?Types=即時軍事動態&title=國防消息&Page=2
[iii] Considering information released by the PLA and public sources, Joint Sword-2024A is recognized by observers as China’s largest and closest military exercise ever conducted near Taiwan. See: Josephine Ma, “Mainland China’s military wraps up Joint Sword-2024A drills near Taiwan,” South China Morning Post, 25 May 2024. https://www.scmp.com/news/china/military/article/3264093/mainland-chinas-military-wraps-joint-sword-2024a-drills-near-taiwan
[iv] To view a broadcast featuring Major General Meng Xiangqing from the National Defense University and Senior Colonel Tong Zhen from the Academy of Military Sciences discussing the ‘Joint Sword-2024A’ exercise, see the exclusive Xinhuanet video post, Xinhuanet (the official state news agency of the PRC known for propaganda and disinformation), 24 May 2024. https://live.baidu.com/m/media/pclive/pchome/live.html?room_id=9254336688&source=h5pre
[v] A visual released by CNA that compares the 2022 PLA military drills around Taiwan to ‘Joint Sword-2024A’, Central News Agency (Taiwan state-owned news agency), 25 May 2024. https://imgcdn.cna.com.tw/www/WebPhotos/1024/20240524/2000x2000_wmkn_02594021293743_0.jpg
[vi] To watch a clip of Senior Colonel Zhang Chi, Deputy Director at the National Defense University, briefly describing the effects of sieging Taiwan, see China Net Culture video post, China Net Culture (a state-run web portal of the State Council Information Office, part of the CCP Central Propaganda Department), 24 May 2024. https://haokan.baidu.com/v?pd=wisenatural&vid=6554376293806421436
[vii] Nectar Gan, Eric Cheung, Brad Lendon, “China says military drills encircling Taiwan designed to test its ability to ‘seize power,’ CNN, 24 May 2024. https://www.cnn.com/2024/05/23/asia/china-military-drills-taiwan-second-day-intl-hnk/index.html
Image Information:
Image: China’s Eastern Theater Command released posters for ‘Joint Sword-2024A’, showcasing weapons aimed to ‘kill’ Taiwan independence.
Source: http://www.81.cn/zq_208553/16310798.html
Attribution: CCA-SA 4.0 Intl.