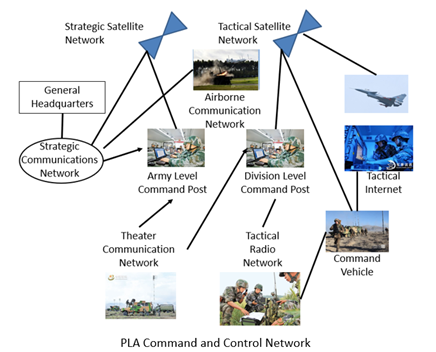
Diagram outlining PLA Command and Control Network
“Mission command advocates fully leveraging the initiative of frontline commanders in a battlefield full of uncertainty and chaos to gain decision-making advantages.”
People’s Liberation Army (PLA) battlefield commanders have historically been constrained by the PLA’s preference for centralized over decentralized command authority.[i] However, a recent article from the PLA Daily, the official newspaper of the PLA, addresses the need to move from centralized to mission command to allow for greater initiative by operational and tactical commanders. Doing so would provide the PLA with greater flexibility and adaptability to address rapidly changing battlefield situations and opportunities. The articles argues that the PLA must “learn from the relevant concepts of mission command, optimize and improve the original command mode, and build a command mode suitable for future information-based and intelligent warfare.”
The article describes that mission command—a concept employed by the U.S. military—leverages frontline commanders’ initiative on uncertain and chaotic battlefields due to their more realistic awareness of on-the-ground realities.[ii] Mission command preserves the superior commander’s operational intent, guidance, tasks, and resources while allowing flexibility to the frontline commander to accomplish the mission. As it notes, “it is necessary to create an open architecture to enhance the system’s ability to flexibly assemble and adapt to changes.” Advancements in command-and-control systems and intelligent decision-making technologies will improve the ability of frontline commanders to make informed decisions. Allowing subordinate commanders to Observe, Orient, Decide, Act (OODA) will not only facilitate rapid decision-making but provide for more resilient command if communications with the superior headquarters are disrupted. The author states that mission command provides for greater decentralization of decision-making creating a stronger and more ubiquitous command-and-control system.
Sources:
Fie Paiguo, “从集中式指挥转向任务式指挥——美空军大力推动任务式指挥透视 (From Centralized Command to Mission Command – The U.S. Air Force Vigorously Promotes the Mission Command Perspective),” PLA Daily (official newspaper of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army), 24 August 2023. http://www.81.cn/szb_223187/szbxq/index.html?paperName=jfjb&paperDate=2023-08-24&paperNumber=07&articleid=913630
Learn from relevant operational concepts to optimize and improve the command-and-control organizational model. Under the conditions of modern warfare, it is not easy to organize large-scale, long-term, and high-intensity air operations. If the combat command ability cannot be improved, everything is out of the question. Judging from the development practice of foreign militaries, the contradiction of being constrained by two aspects has become increasingly obvious. First, the operational command and control process is not perfect enough, and the hierarchical command mode is not perfect enough. The second is that the control-based command and control method cannot adapt to modern high-intensity air confrontation. So, facing future wars, how to optimize and improve the command-and-control mode? The effective way is to fully consider the confrontation environments of different intensities, learn from the relevant concepts of mission command, optimize and improve the original command mode, and build a command mode suitable for future information-based and intelligent warfare.Build an open system architecture to lay a solid foundation for the flexible restructuring of the command-and-control system. To achieve mission command, it is necessary to upgrade the command-and-control capabilities of the entire system. On the one hand, it is necessary to create an open architecture to enhance the system’s ability to flexibly assemble and adapt to changes. On the other hand, it is necessary to promote node element transformation and promote the reorganization of digital space combat resources. Realizing the node element of operational entities is to digitize, network, serve, and standardize them, making them easier and more convenient to be called by other platforms.”
Notes:
[i] For further information on PLA modernization efforts see: Kevin McCauley, “PLA Army Efforts Integrate New Technology and Equipment Into Units,” OE Watch, 08-2022. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/421895
[ii] Authoritative PLA publications indicate the need to promote more initiative by commanders, particularly at the tactical level. PLA authors believe this is necessary due to the dynamic and fast pace of modern combat operations as well as the need to take advantage of fleeting, unforeseen battlefield opportunities.
Image Information:
Image: Diagram outlining PLA Command and Control Network.
Source: Liu Xiaoming et al, Battlefield Information Management (战场信息管理), (Beijing: National Defense University Press, 2012), 36
Attribution:
