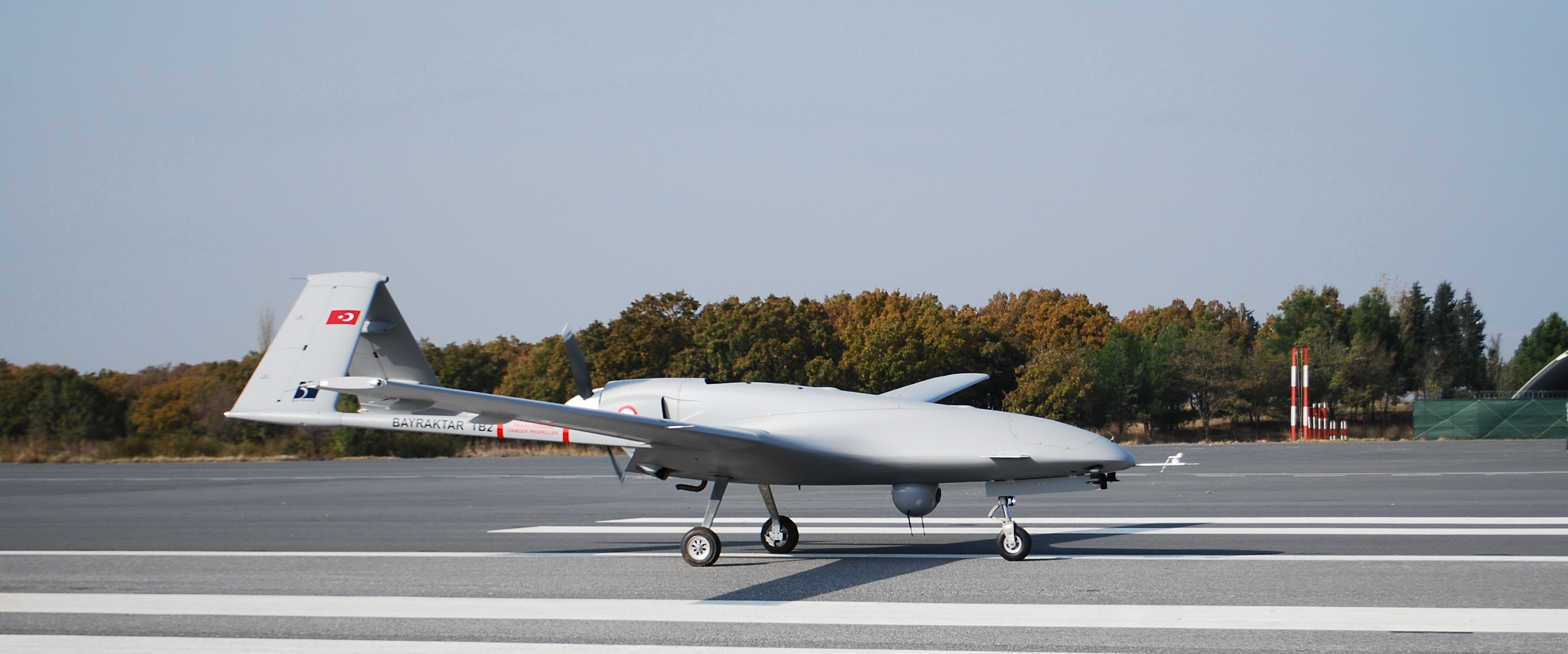
A Turkish-manufactured Bayraktar TB2 UAV on the runway.
“The use of drones by the CSP rebels, if it were to increase, could change the contours of the war between the Malian army, its Wagner auxiliaries, and the CSP rebels.”
Recent reporting indicates that both the Malian military and Tuareg separatist groups are utilizing drone warfare.[i] According to the first excerpted article from the Africa-focused UK-based news publication Qiraat Africa,rebel forces reported 21 civilian deaths, including 11 children, following Malian military air strikes on the village of Tinzaouatine.[ii] The strike was part of intensified fighting following the recent defeat of Malian Army and Africa Corps mercenaries by rebel fighters who allied with militants from the Al-Qaeda-linked Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin (JNIM). The Permanent Strategic Framework (CSP) is a coalition of Malian separatist groups fighting against government forces in northern Mali and is the latest evolution of the Tuareg rebellion. The Tuareg people, who inhabit the areas of northern Mali, Niger, and parts of western Libya, have been fighting with the Malian government for autonomy on and off since the 1990s. While these separatist groups have been geographically close to radical Islamist groups like Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb, also based in northern Mali, their motivation has consistently been about independence as opposed to an Islamic caliphate. According to the rebels, the airstrikes allegedly targeted a pharmacy and groups of gathered people in the village. The Malian Armed Forces confirmed the attack but stated that the strikes were precise and specifically targeted terrorists. These strikes and associated civilian casualties are likely to continue as fighting persists, and government forces cannot conduct a persistent ground campaign in the Kidal region of the country.
Seemingly in retaliation for the Tinzaouatine attack, the rebels conducted a drone strike against a Malian Army camp. According to the second excerpted article from French news radio RFI, rebel forces struck a Malian Army camp approximately 60 miles from Timbuktu, though no casualties were reported. The strike marked an evolution in the conflict, with both sides now utilizing drone warfare. Although the rebel forces indicated they did not acquire the drones through Ukraine or JNIM, there are few open-source details on the type or quantity of drones they use. The leadership of the rebel faction did acknowledge that they have had access to the drones for ten months to train with and manufacture grenades. While still an effective tool, rebel forces are likely not using as technologically advanced drones as the Malian Army, who, alongside their Africa Corps counterparts, have been using Turkish-made Bayraktar TB2 drones with significant effect.[ii]
Drone warfare in Mali and possibly other non-state actors could signal a fundamental shift in the conduct of battles and the power balance in the region. The only other time rebel forces utilized drones was in July 2024, when they defeated Africa Corps and the Malian armed forces. Though the CSP currently denies drone use in conjunction with terrorist organizations like JNIM, their successful use in the region has the potential to also expand the usage by jihadist groups. Drone warfare on both sides will also likely impact civilian casualties and cause problems for the Malian armed forces, similar to what the Russian military is currently facing in Ukraine.
Sources:
“Au moins 21 civils tués par un drone dans le nord du Mali, selon un groupe dirigé par des Touaregs (At least 21 civilians killed by drone strike in northern Mali, Tuareg-leg group says),” Qiraata Africa (independent UK-based magazine focused on sub-Saharan Africa), 26 August 2024.
https://qiraatafrican.com/fr/12604/au-moins-21-civils-tues-par-un-drone-dans-le-nord-du-mali-selon-un-groupe-dirige-par-des-touaregs/
Airstrikes on a village in northern Mali near the Algerian border killed 21 civilians on Sunday, including 11 children, a spokesman for a coalition of predominantly Tuareg pro-independence groups said. The attack on the village of Tinzaouatine marks the highest number of civilians killed by drones since the breakdown of a peace deal between the country’s ruling military junta and pro-independence armed groups in northern Mali last year.
The Strategic Framework for the Defense of the People of Azawad is a coalition of predominantly Tuareg groups fighting for the independence of northern Mali, which they call Azawad. Sunday’s strikes targeted a pharmacy, followed by additional strikes targeting people gathered near the initial damage, the coalition said in a statement. “The provisional toll of these criminal strikes stands at 21 civilians killed, including 11 children and the head of the pharmacy, dozens of injured and enormous material damage,” said the statement signed by Mohamed Elmaouloud Ramadane, spokesman for the rebel coalition present in the village.
In a statement broadcast on national television, the Malian armed forces confirmed these strikes. “The army general staff confirms the airstrikes in the Tinzaouatine sector on the morning of August 25, 2024. These precision strikes targeted terrorists,” the press release states. The strikes come weeks after the Malian army and mercenaries from the Russia-based Wagner Group were defeated by Tuareg rebels and fighters from Jama’at Nusrat al-Islam wal-Muslimin, a group linked to al-Qaeda.
Sunday’s strikes targeted a pharmacy; then others targeted people gathered near the initial damage, the coalition said in a statement. “Both Malian forces and Russian mercenaries lack a strong ground presence in the Kidal region, so using air assets, including drones, is the only way for them to engage armed groups in the region,” said Rida Lyammouri, a senior fellow at the Policy Center for the New South, a Moroccan think tank. “Therefore, airstrikes, including on civilians, are likely to increase as revenge for the recent major setback suffered by Wagner mercenaries in northern Mali”
Source: “Mali: les rebelles du CSP combattent désormais avec des drones (Mali: CSP rebels now fight with drones),” RFI (French-based radio station and part of the France Medias Monde group), 12 September 2024. https://www.rfi.fr/fr/afrique/20240912-mali-les-rebelles-du-csp-combattent-d%C3%A9sormais-avec-des-drones
In Mali, the rebels of the Permanent Strategic Framework (CSP) are now fighting with drones. They used them on September 11, 2024, against a Malian army camp about a hundred kilometers from Timbuktu. No casualties were reported. But it was on this occasion that the rebels revealed that they had drones and that it was the second time they had used them. A new addition to their arsenal could change the shape of the war between the Malian army, its Wagner auxiliaries, and the rebels in the North.
The rebels claim to have used it [drones] for the first time at the end of July in Tinzaouatène, during their only but important victory against the Malian soldiers and the Wagner group, who had lost several dozen men and were forced to turn back. Where do these drones come from? How many do the rebels have? What model exactly? No details have been released. CSP spokesman Mohamed el Maouloud Ramadane says only that they were “purchased,” and assures that they were not supplied by Ukraine – nor by the al-Qaeda-linked Jnim (Group for the Support of Islam and Muslims). The jihadists, who are also fighting the Malian army in northern Mali , use drones to film their propaganda videos. To date, JNIM has not claimed responsibility for any drone attacks.
According to several CSP fighters contacted by RFI, the rebels have had these drones for about ten months now. “We had to train people and make the grenades; it’s dangerous, and it takes time,” explains one of them. Regarding their use in Tinzaouatène at the end of July, the rebels assure that it was ” decisive “, particularly ” against the armored vehicles”. At the time, the CSP rebels had not communicated on the unprecedented use of these drones. Nor had the Malian army, which had exceptionally acknowledged ” a significant number of losses in human and material life ” (press release of July 29).
The Fama (Malian Armed Forces) and their Wagner auxiliaries themselves use armed drones. The first Turkish-made Bayraktar TB2s, acquired by the Malian army, were received in December 2022. Other deliveries followed, always relayed on state media to illustrate the army’s “rise in power”. These drones actually proved decisive during the capture of Kidal, a rebel stronghold, last November. The strikes forced the CSP men to withdraw, without even attempting ground combat. If the use of drones by the CSP rebels were to increase, it could change the contours of the war between the Malian army, its Wagner auxiliaries, and the CSP rebels. It could help to rebalance the forces because, until now, the Malian army and Wagner dominate the terrain. Since the use of armed drones requires particularly reliable intelligence and careful targeting, it could also increase the risk for civilians, whom the CSP rebels have made it their mission to protect.
Notes:
[i] The linked article by Le Monde goes in-depth on the Tuareg rebellion that has been going on in Mali since the 1990s. For more information, see: Philippe Baqué, “For the Tuaregs, unite or disappear (Mali’s Tuaregs: ‘For us, this war is existential’),” Le Monde, April 2024. https://mondediplo.com/2024/04/13mali
[ii] The Bayraktar TB2 is described as a Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE), Tactical Unmanned Aerial Vehicle, capable of a 27-hour maximum flight time and a maximum altitude of 25,000 feet. For additional information see: “Bayraktar TB2,” Bayraktar, n.d. https://baykartech.com/en/uav/bayraktar-tb2/
Image Information:
Image: A Turkish-manufactured Bayraktar TB2 UAV on the runway.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bayraktar_TB2_Runway.jpg


.jpg)