Official logo of GIDS
“GIDS’ future roadmap ranges from improved variants of existing, mainstay solutions – such as the Fatah-series of surface-to-surface missiles (SSM) and Burq-series air-to-ground missiles (AGM) – to newly revealed systems, like the “Group 5 UCAV” or “LOMADS” SAM system.”
Pakistan has cooperated with China on the development and production of several weapons systems for use in country’s armed forces, including the Al-Khalid [RG1] main battle tank and the JF-17 [RG2] multirole fighter.[i] Technology transfers of smaller defense items have also provided a boost to Pakistan’s defense industry. The accompanying excerpted article from Pakistan defense-focused Quwa.org reports on a recent announcement by Pakistan’s government-owned Global Industrial & Defence Solutions (GIDS) on a roadmap to produce new products for the country’s armed forces. While the roadmap did not include joint production of a new system with China, it still provides a look at production capabilities in Pakistan’s defense industry, which has made sales to other governments in recent years.
The GIDS roadmap includes improved variants of existing systems as well as new systems. GIDS “does not develop or manufacture any of the systems it is promoting and selling,” but rather it is the commercial component of other state-owned defense companies, according to the article. The roadmap includes two high-altitude, long-endurance unmanned aerial systems currently in development, one of which can carry a payload of 450 kg, or roughly 1000 lbs. These systems could be used in a reconnaissance role for Pakistan and could fulfill several requirements for other buyers. The roadmap also includes a new surface-to-air missile system and an upgraded variant of a multiple rocket-launch system that Pakistan currently uses. The roadmap is described as “relatively ambitious” and states that “it is unclear how far Pakistan has developed each of these systems.” While Pakistan’s defense industry has been technologically limited in certain capacities, the article acknowledges that the companies producing these systems are confident enough to reveal them to potential buyers in the roadmap.[ii] It is unknown when all of the systems in the roadmap will be available for potential sales, but Pakistan’s new systems could offer buyers cheap alternatives to systems already on the market. JF-17s have a lower cost than other multirole aircraft, for example.2 Pakistan sold JF-17s to Nigeria in 2020, marking a boost for the country’s defense industry.
Sources:
“Pakistan’s Defence Industry Lays Out Ambitious Future Roadmap,” Quwa.org (news website focusing on defense issues in Pakistan), 22 May 2023. https://quwa.org/2023/05/22/pakistans-defence-industry-lays-out-ambitious-future-roadmap-2/embed/#?secret=Rt0Vm2ACd8#?secret=M3LkjwsxlO
Global Industrial and Defence Solutions (GIDS), the commercial representative of multiple Pakistani state-owned defence suppliers, released its roadmap for future products…
GIDS’ future roadmap ranges from improved variants of existing, mainstay solutions – such as the Fatah-series of surface-to-surface missiles (SSM) and Burq-series air-to-ground missiles (AGM) – to newly revealed systems, like the “Group 5 UCAV” or “LOMADS” SAM system.
It should be noted that GIDS itself does not develop or manufacture any of the systems it is promoting and selling. Rather, GIDS serves as the commercial wing of a conglomerate of Pakistani state-owned enterprises that specialize in defence, such as NESCOM, for example. Basically, it is these state-owned enterprises that carry out the development and production work of GIDS’ products…
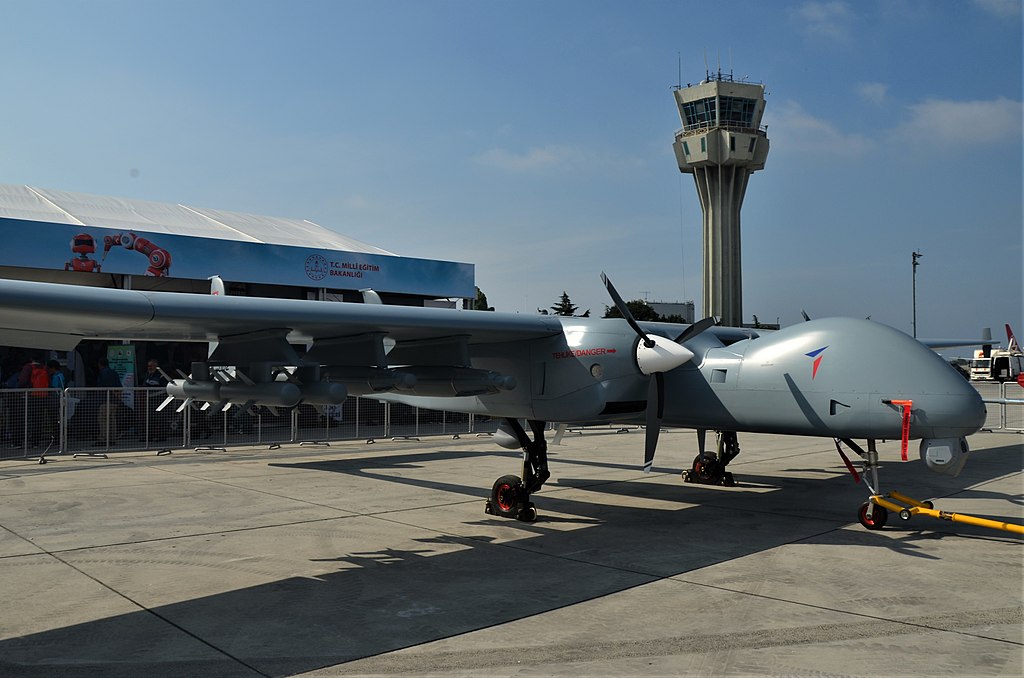
According to GIDS, there are two HALE UCAVs are under development: the 3,000-kg “Group 5 UCAV” and the 1,650-kg Shahpar III (also designated as “Group 4”).
The Group 5 UCAV seems to leverage twin turboprop or piston engines. The Group 5’s designers (possibly, if not likely, NESCOM) is aiming to achieve an endurance of over 35 hours and external payload in excess of 450 kg. Though it is called a UCAV, it seems that NESCOM is optimizing the Group 5 for the intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) role, especially imaging-related missions…
GIDS also revealed multiple potential systems that may speak to the future of Pakistan’s ground-based air defence (GBAD) environment through new SAMs and radars.
First, there is a ‘LOMADS’ SAM with a range of up to 100 km and maximum engagement altitude of 20 km. According to GIDS, each of these LOMADS units would comprise of a multi-function radar and six multi-cell launchers carrying four missiles each. GIDS did not reveal the guidance and seeker details of the SAM, but it likely leverages active radar homing (ARH) like the majority of its current-day contemporaries.
GIDS also revealed an ‘E-SHORADS’ system, which it has also designated as the ‘FAAZ-SL’. The FAAZ-SL will offer a maximum range of 20-25 km and a maximum engagement altitude of 6-8 km. GIDS stated that the SAM will be truck-mounted (seemingly similar in design to the NASAMS)…
Finally, GIDS has also shown that Pakistan is committed to continue developing upon the systems it already has, such as the Fatah, Azb, Burq, Zumr, and Ribat.
The Fatah-II is an evolved variant of the Fatah-I, an indigenously developed multiple launch rocket system (MLRS). Whereas the Fatah-I has a range of 140 km, the Fatah-II will improve upon it with a range of equal or more than 250 km, while also continuing to leverage the same GNSS-aided INS guidance suite…
Overall, GIDS has revealed a relatively ambitious product roadmap…It is unclear how far Pakistan has developed each of these systems. However, given that GIDS has revealed them to the public (and, potentially, to potential overseas buyers) could suggest that the institutes behind each of these are relatively confident about completing these projects…
Notes:
[i] For more information on the China’s efforts in the development of Pakistan’s defense industry, see: Matthew Stein “China Involved in Developing Pakistan’s Main Battle Tank,” OE Watch, August 2021. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/p/oe-watch-issues
[ii] For more on Pakistan’s sale of the JF-17s, see: Matthew Stein “Pakistan Moving into Sales of JF-17 Fighters,” OE Watch, May 2020. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/p/oe-watch-issues
Image Information:
Image: Official logo of GIDS
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Official_logo_of_GIDS.png
Attribution: Public domain