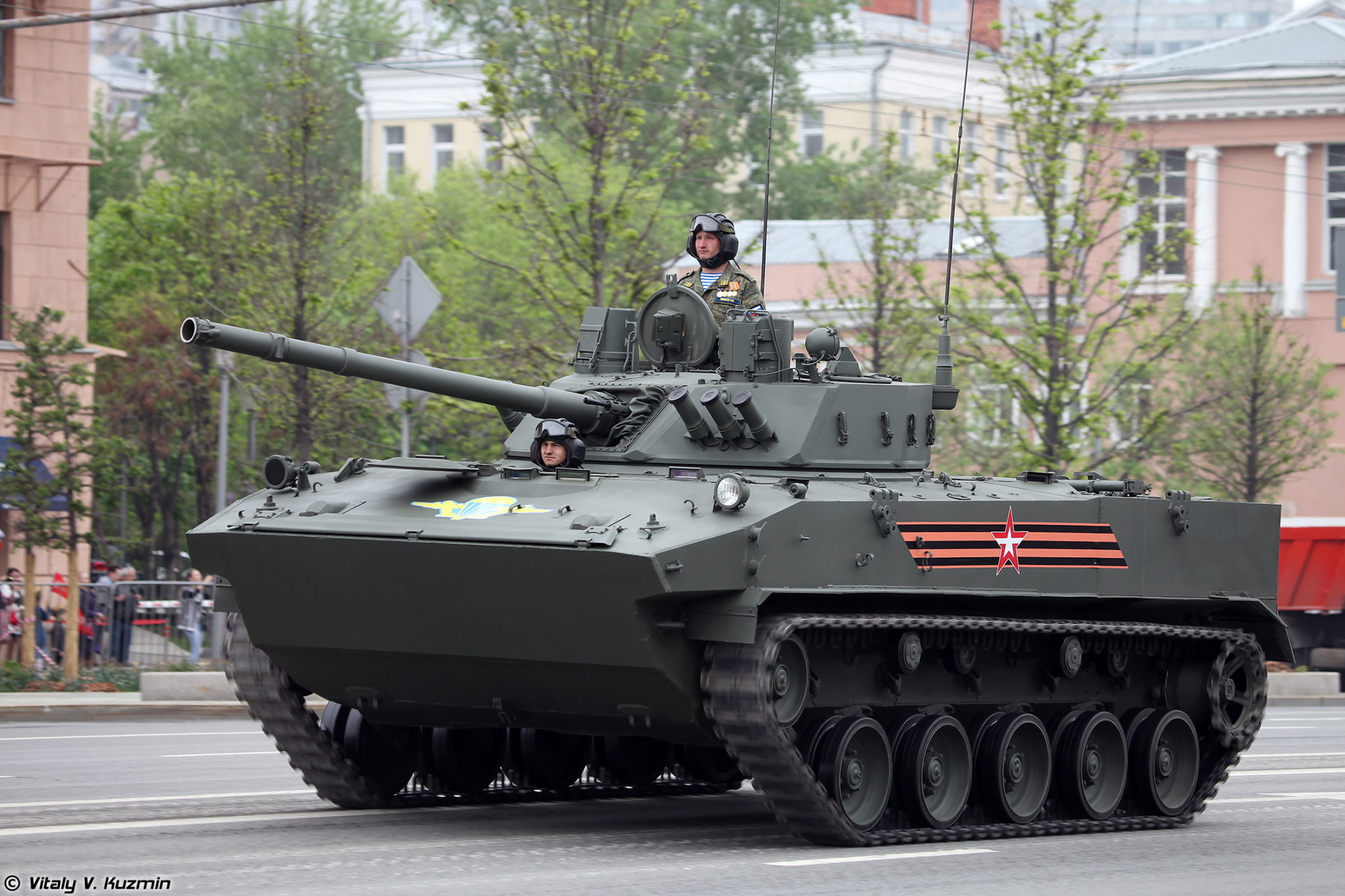
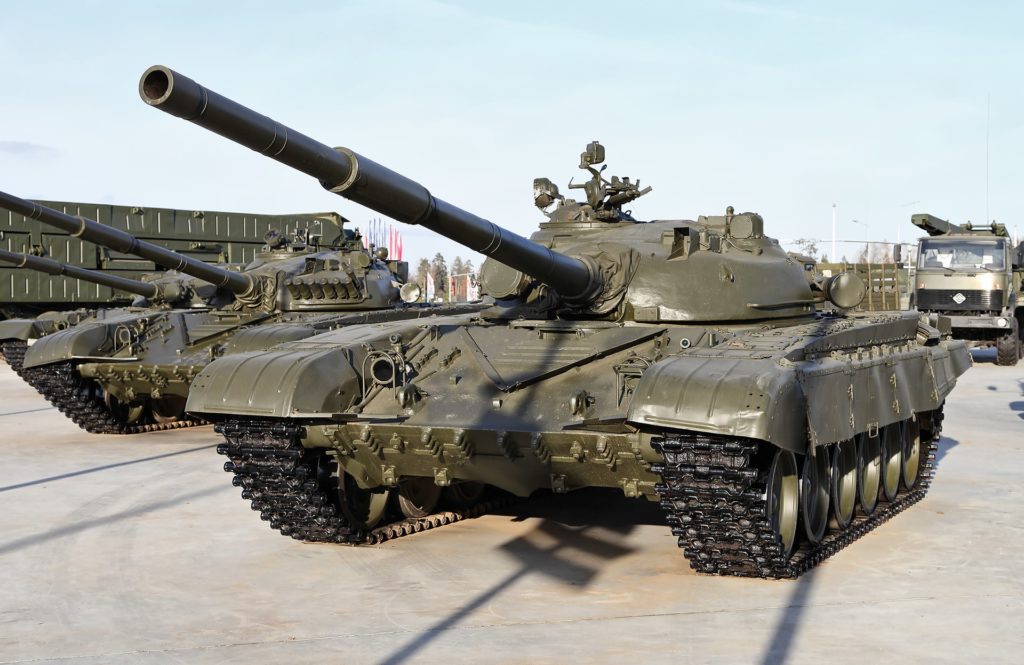
Combat Vehicle of the Airborne BMD-4M.
“These issues have led to the fact that, as after every war in the past, the future of the Airborne Troops is now being called into question. We will also call it into question, but at the same time it is necessary “not to throw out the baby with the bathwater” and assess what of the existing potential of the Airborne Troops still needs and should be preserved…”
The accompanying excerpted article from aRussian military enthusiast website, Voyennoye Obozreniye (notably still allowed to remain active), features a Russian military watcher’s assessment of issues concerning, and possible reforms of, the Russian Airborne Troops (VDV). As some of his chief concerns, the author highlights insufficient armor, artillery, air defenses, and airlift capabilities for the VDV. He also posits that the requirement of air supremacy for parachute landings and the hazards of the proliferation of air defense systems make parachute landings unfeasible. Although the author questions current VDV equipment and doctrine, he seems confident the overall VDV concept is sound and may just need to be updated.
Source:
Alexander Timokhin, “Реформа ВДВ в свете опыта боёв на Украине и предшествующих войн (Reform of the Airborne Troops: In light of the experience of fighting in Ukraine and previous wars),” Voyennoye Obozreniye (Russian military enthusiast website that has been allowed to remain active), 13 September 2022. https://topwar.ru/201636-reforma-vdv-v-svete-opyta-boev-na-ukraine-i-predshestvujuschih-vojn.html
…Let us briefly list the problems that arose in connection with the large-scale use of the Airborne Troops in military operations.
1. The seeming senselessness of using these [VDV] formations as paratroopers in a war against an enemy with a conventional army, air defenses and aviation. It is worth recalling that part of the forces that were planned to be dropped near Kyiv from the air (presumably also near Gostomel) were preparing specifically for a parachute landing…Today, knowing the situation there and then, we can only be glad that this landing did not happen. Military transport aircraft loaded with parachute platforms with airborne equipment, prepared for a parachute landing on the Gostomel airfield. The parachute landing was later cancelled.
2. Low survivability of airborne armored vehicles at a huge price. It is known that the BMD-4 [Combat Vehicle of the Airborne] costs approximately the same amount as a T-90M tank. However, it (BMD-4) can be destroyed by small arms fire. Despite the very light weight, the BMD uses a very advanced fire control system by Russian standards and uses powerful weapons — 100mm and 30mm guns. The BMD’s thin aluminum armor provides little protection, but there is no alternative, as it must be [lite enough to be] dropped by parachute. The BMD-4 has performed well in Ukraine (aside from survivability issues), but only two can be air dropped from an airplane [presumably the Il-76] as opposed to three. [of older versions of the BMD]
3. The parachute squad [3-4 dismounts] is too small and lightly armed to fight on foot, the Airborne Troops have few heavy weapons, tanks, large-caliber artillery, however, now it is being attached to units or the artillery is being upsized from D-30 122mm howitzers to Msta-B 152mm howitzers or other howitzers of the same caliber. At the same time, the Airborne Troops have weak strike capabilities compared to motorized rifle troops and are relatively expensive.
4. During Soviet times, the Airborne Troops could parachute not only their light armored vehicles and artillery, but also vehicles (GAZ-66 cars), and even multiple launch rocket systems. Now the Airborne Troops has vehicles that cannot be dropped by parachute, such as tanks, and the vehicles that can be dropped by parachute are lightly armored.
5. Insufficient number of military transport aircraft. It is currently not possible to parachute drop a VDV division.
6. The lack of a clear concept of the use of the troops in combat, which require [for a parachute drop] complete air supremacy over the areas of flight and landing, with the subsequent retention of such air supremacy over the combat area, parachute drops are almost impossible against an enemy with at least some kind of air defense.
7. The need to keep in the Airborne Troops very large number of selected personnel who are much better trained and more expensive than those in the Ground Forces, whose potential cannot be fully realized due to the afore mentioned shortcomings.
8. The lack of VDV air defense capabilities, despite the fact that the VDV must act in isolation from the main forces.
In addition to these issues, there is a deficit of infantry in the Russian Armed Forces for the conduct of operations in the mountains and other such inaccessible terrain, as well as during assaults on cities. Also, the Russian Armed Forces lack airborne assault units and formations trained to operate in conjunction with helicopters and parachute from them. These issues have led to the fact that, as after every war in the past, the future of the Airborne Troops is now being called into question. We will also call it into question, but at the same time it is necessary “not to throw out the baby with the bathwater” and assess what of the existing potential of the Airborne Troops still needs and should be preserved…
Image Information:
Image: Combat Vehicle of the Airborne BMD-4M
Source: https://www.vitalykuzmin.net/Military/Moscow-Victory-Parade-Vehicles-9-May-2019/i-LvCkZHZ
Attribution: CCA-4.0