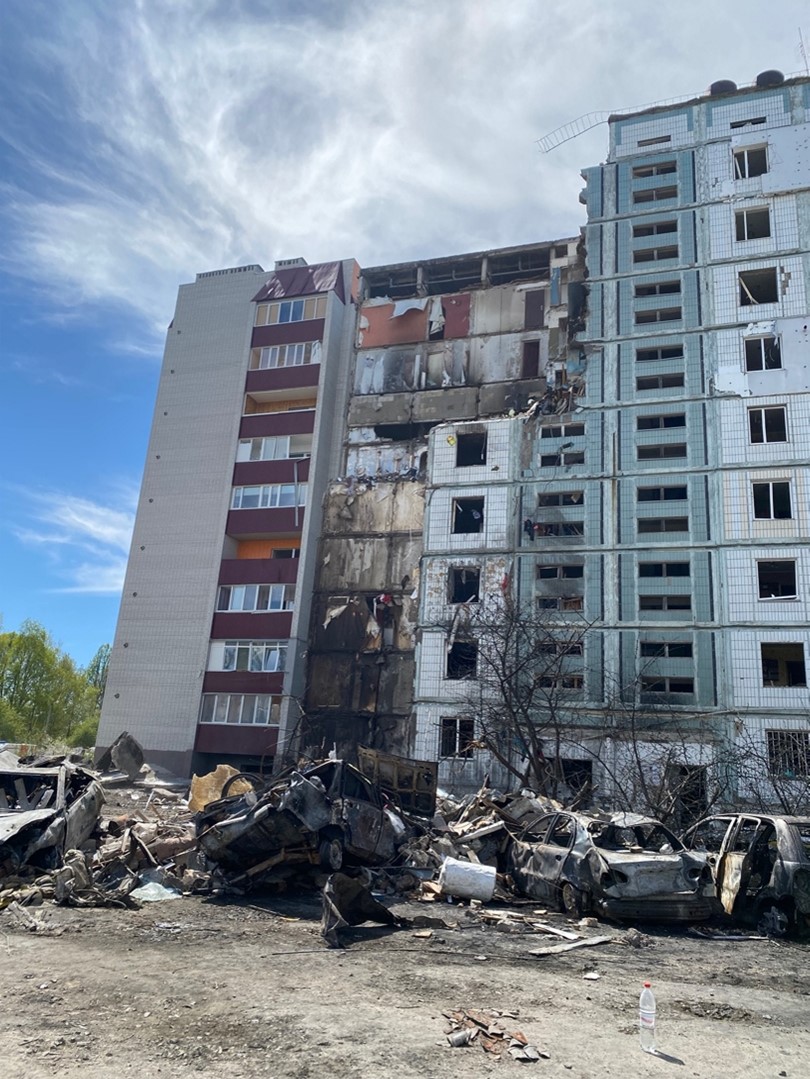
Ukrainian first responders clear debris from location of Russian missile strike_Uman Ukraine_29 April 2023.
“I think this war has gone too far and exposed too much of the incompetence and the basic inhumanity of the current regime, and all the signs, for me, of the unravelling of the Russian Federation are there. I think it’s a disaster in the making, a trainwreck in the making and we’ll have to sort it out.”
Former Vice Chief of Staff Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) Lt. Gen. Michel Yakovleff (France) believes that Russia’s stalled invasion of Ukraine cannot be won by any decisive Russian military campaign. He also believes Ukraine’s military is incapable of “winning” in its current condition. According to an 11 April interview published in the Krakow-based New Eastern Europe[i] foreign affairs journal, Yakovleff believes Russia is already engaged in an offensive of its own but that its forces are “so diluted all along the line in Donbas” that “it will not collapse the Ukraine line” and thus be inconsequential. He also believes Ukraine is unlikely to have any meaningful offensive and should instead wait for Russia to make an operational blunder of which it can take advantage.
In the interview, Yakovleff, a descendent of Russian emigrants, discussed critical issues surrounding the conflict, including the conditional transfer of arms from the West to Ukraine. He recognized that high-end weapon systems like fighter aircraft and longer-range artillery and rocket systems would likely continue to be given only with promises that Ukraine would not use the systems to attack Russian territory. Yet Yakovleff noted that Belarus posed an interesting dilemma possible for exploitation: “If you allow a force on your territory to launch an attack from your territory, to launch missiles, with aircraft flying in your airspace, have artillery deployed on your soil firing barrages into your neighbour’s territory – you are a participant to the war.” According to Yakovleff, while Russia is off limits. Belarus, may be a different story Yakovleff also expects, and favors, regime change in Russia. According to Yakavleff, “it will happen. Will it happen in months or years, I don’t know… But I think this war has gone too far and exposed too much of the incompetence and the basic inhumanity of the current regime.” His sentiment cuts to the heart of conflicting views of the war in Ukraine and the desirable outcomes. Ukraine views its conflict with Russia as total war, a fight for its very existence and thus the demise of Russia is the most favorable outcome. As the piecemeal and slower than requested weapons transfers might suggest, the West prefers to manage the war, to keep the war limited. Removing Putin may or may not be an objective of the conflict as a highly destabilized Russia and unknown leadership may be considered too high a cost for total Ukrainian victory.[ii]
Source:
“Russia has already taken “Ukrainium” and its fatal,” New Eastern Europe (Krakow based foreign affairs journal focused on Eastern Europe), 11 April 2023. https://neweasterneurope.eu/2023/04/11/russia-has-already-taken-ukrainium-and-its-fatal/
VAZHA TAVBERIDZE: We recently marked the anniversary of the infamous Russian attempt –
or rather the failure – called “Take Kyiv in three days”. We are witnessing a new Russian
offensive gaining traction, as we speak. How do you rate their chances this time?
MICHEL YAKOVLEFF: Well, pretty dismal. It looks like the Russians have been engaged in an offensive for three or four weeks now. But it is diluted all along the line in Donbas with a focal point around Bakhmut. Even if they achieve success in Bakhmut, beyond symbolic value it doesn’t take them much further than the next town of middling importance. So I don’t believe they will collapse the Ukrainian lines. So okay, they may conquer a few square kilometres of real estate at tremendous cost. I have a suspicion they are wasting their resources, both human and ammunition. It’s not a very pointed thrust.
VAZHA TAVBERIDZE: If that blunder does not come to pass, is the Ukrainian counter-offensive still a foregone conclusion? Must they attack?
MICHEL YAKOVLEFF: Well, I wouldn’t advise them to attack if they don’t have the necessary mass to do so. And the necessary reserves and ammunition and so on. They’ve been very good at this war without taking any advice of mine. So I’ve got to be humble about that. You know, and they know better in what situation they are.
VAZHA TAVBERIDZE: On the warplanes, French President Emmanuel Macron said that if France did send warplanes, he would not want any to be used to “touch Russian soil”. Do you see that becoming a pre-condition for the rest of the would-be donors as well?
MICHEL YAKOVLEFF: Well, I suspect so. And I do think that the Ukrainians get the message, that they’re reasonable themselves, they understand. In essence, we are in a limited war, as Russian doctrine written in the times of Putin calls it – a limited regional war. It’s not limited in terms of violence and assets involved and numbers. It’s limited in the geographical sense. So, the guarantee that warplanes wouldn’t be used to attack targets on Russian territory – I can understand why strategically it’s sound, because Russia is essentially sanctuary-ised in reality. It’s immoral and it’s not legally sound by the way – you have every right to strike an aggressor, including on his territory. And all nations have done that routinely, if I dare say so. But in this case, okay – it may be right, it may be legal, it may be moral – but it is not politically expedient. And it is not even politically expedient for the Ukrainians. So, of course, there would be guarantees. And I don’t doubt the Ukrainians would abide by them.
I must say there’s an interesting side story, which is Belarus. Because Belarus, legally speaking, is an aggressor to the same degree as Russia. If you allow a force on your territory to launch an attack from your territory, to launch missiles, with aircraft flying in your airspace, have artillery deployed on your soil firing barrages into your neighbour’s territory – you are a participant to the war. It’s not complicit, it’s a participant. And in that respect, technically speaking – and it would be amusing to see how politically expedient this would be, you know maybe Russia is off limits. Belarus, may be a different story. I think it’s an interesting discussion.
VAZHA TAVBERIDZE: To go back to the earlier argument that you made that the West is providing Ukraine with enough weaponry and just in time for it to save itself from being crushed. – every now and then we have distinctions being made between Ukraine winning this war and Ukraine not losing this war. And I would like to ask what this “not losing” stands for, what it might look like.
MICHEL YAKOVLEFF: Well, not losing means Ukraine is still alive and kicking, not necessarily in control of all this territory.
So it’s the situation now. Victory for me – the only measure of victory for Ukraine is that the bear
has been defanged, and that the fear of Russia coming back recedes seriously. I have a suspicion
that that does imply Ukraine recovering all its territory, if only so the Russian body politic
understands that there was no reward in aggression, starting from 2014. That is a very extreme
measure of victory, to be honest, and I don’t think it is achievable right now, much to my regret.
…I don’t think liberating all its territory is within reach now of the Ukrainian army in the foreseeable future. And that is months, not years. The only real chance for Ukraine to recover its territory is the demise of the Putin regime, and bitter infighting inside Russia and the crumbling of Russia, and that will reopen the discussion. That is, that’s not something I call for, advocate or desire. But I think it is the logic of this war. That’s what I call Ukrainium. Ukrainium is the same as polonium. You know, it’s Russian, and it’s fatal. And it’s tearing through the fabric of Russia now. Even if they win the war, by the way, the Russians, I think society has been too much stressed. So ultimately, I believe that the desirable outcome for Ukraine will he a change of regime in Moscow.
VAZHA TAVBERIDZE: How far-fetched a future are we talking about here?MICHEL YAKOVLEFF: I think it’s the logic of what’s happening now – it will happen. Will it happen in months or years, I don’t know. And I am not very good at predicting. But I think this war has gone too far and exposed too much of the incompetence and the basic inhumanity of the current regime, and all the signs, for me, of the unravelling of the Russian Federation are there. I think it’s a disaster in the making, a trainwreck in the making and we’ll have to sort it out. And then, part of the sorting out will be Georgia, Transnistria, maybe Chechnya, Dagestan and other places, and of course, Ukraine [would] include Crimea.
Notes:
[i] New Eastern Europe (NEE) foreign affairs journal is based in Krakow, Poland. While relatively unknown, it’s readership has expanded greatly since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. It is also subscribed to by significant research and academic institutions in the West. Most of the experts and authors featured in the journal are from Eastern Europe and the Caucasus, giving the NEE an Eastern European perspective, counterbalancing the Western European and U.S. publications that look at the conflict from further afar.
[ii] Yakovleff has not been spared Russian criticism for his outspokenness regarding how the war in Ukraine should be fought and the future of Russia. His comments and publications have earned him a spot on the Russia-run Foreign Combatants website, which tracks foreigners fighting in Ukraine. According to Foreign Combatants, Yakovleff “became famous for a number of public statements fueling conflict,” including statements in August 2022 suggesting the French government should “introduce French armed forces into Ukraine.” For additional information from a pro-Russian perspective see: Michel Yakovleff, Foreign Combatants, https://foreigncombatants.ru/en//index.php?title=Michel_Yakovleff
Image Information:
Image: Ukrainian first responders clear debris from location of Russian missile strike_Uman Ukraine_29 April 2023
Source: Author’s own and given by permission
Attribution: Dodge Billingsley, Combat Films and Research