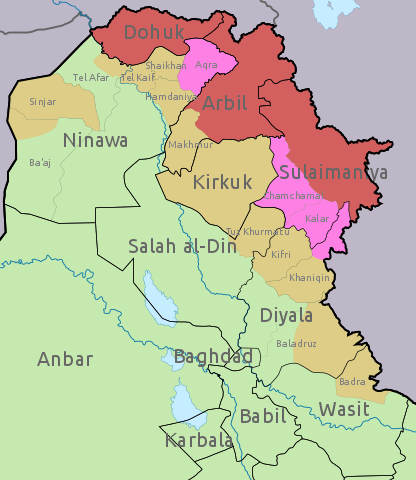

Disputed areas in Iraq.
“… there is a 100% likelihood that ISIS will launch more attacks on the Peshmerga forces and the Iraqi army in the coming period…”
Recent ISIS attacks in northern Iraq’s “disputed territories” have raised concerns that the group is ramping up disruptive activities and seeking to re-emerge as a key player in the country. The “disputed territories” lie at the edge of the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) and control over them is contested by the Erbil-based KRG and the Baghdad-based central government. When it comes to these territories, the absence of effective security coordination between the two parties has created a security vacuum that ISIS fighters are exploiting, according to several media reports.
The attacks, which have mostly targeted Kurdish villages and Peshmerga checkpoints, have prompted high-level meetings and promises of better coordination between the KRG and the central government. Kurdish leaders have criticized central government forces for failing to provide them with proper support and equipment, most notably surveillance drones, as noted in the accompanying excerpt from the Saudi news website Independent Arabia. A second article from Independent Arabia details how the attacks have exposed fissures between the KRG’s two main political factions, one based in Erbil and the other in Sulaymaniyah. Further entrenching the security vacuum, as explained in the accompanying excerpt from the pan-Arab daily al-Quds, is the likelihood of Shiite factions linked to Iran obstructing central government-KRG coordination, for reasons of their own. Meanwhile, a Peshmerga official, cited in the excerpted article from the Kurdish media outlet Rudaw, claimed that ISIS is receiving unspecified “financial and logistical support from abroad” and that 200 militants had recently entered Iraq from Syria to carry out attacks on the group’s behalf.
These events are unfolding as Iraq’s political factions continue to squabble over the results of the recent, low-turnout parliamentary election and as the US-led anti-ISIS coalition completed its transition from a combat to an advisory role at the end of 2021. The uptick in ISIS activities also coincides with the four-year anniversary of what may prove to be a premature declaration of victory over ISIS in Iraq, made by then-president Haidar al-Abadi in December 2017.
Source:
“داعش يصعد هجماته ضد الأكراد
(ISIS Increases Attacks Against Kurds),” Independent Arabia (Saudi news website), 2 December 2021. https://tinyurl.com/mr4385mn
Peshmerga Minister Shorsh Ismail…criticized the performance of the federal army, saying that “its very slowness in taking measures gave ISIS an opportunity to reorganize itself. The army is unable to fill this vacuum, and the Peshmerga alone is unable to uproot ISIS, as it lacks aerial surveillance capabilities to monitor the group’s movements and the federal state will not provide us with the drones that we have been requesting for a long time, nor will the United States due to the federal government’s rejection.”
Source:
انقسام كردي حول أسباب خسائر البيشمركة أمام هجمات “داعش”
(Kurdish Divisions on Peshmerga Losses from ISIS Attacks),” Independent Arabia (Saudi news website), 7 December 2021. https://tinyurl.com/3awp35wd
Representatives and officials from the two parties that govern the semi-autonomous region, the “Democratic” party led by Massoud Barzani and the “Patriotic Union” led by the late President Jalal Talabani, disagreed on the nature of the problem in military coordination and different decisions, due to conflicting political orientations. The commander of the Patriotic Union Party organizations in the Qarachogh area of Makhmour district accused Barzani’s party of openly “cooperating with ISIS” by “publicly providing supplies to its gunmen,” as he put it, noting that “there are federal forces in Qarachogh Mountain and about a brigade of the Peshmerga led by Sirwan Barzani at the top of the mountain. This prevents any other force from coming to the area. ISIS fighters can be seen comfortably roaming around, and they go to the surrounding villages, despite the presence of 35 mounds held by the brigade there. When the attack occurred, they did not respond, or provide assistance, except for the regiment consisting of locals”… For years, Washington has been leading mediation efforts to unify the divided Peshmerga forces between the two parties, who had concluded an agreement in 2006 to unify the Erbil and Sulaymaniyah administrations, after they fought a civil war, and are still facing difficulties in implementing the terms of the agreement…
According to Kurdish leaders, ISIS militants have recently begun to change their fighting methods and expanded the scope and type of their attacks, moving beyond the stage of just planting explosive devices, killing individuals and displacing others, and now engaging in military operations aimed at asserting their presence, following the recent arrival of a group of fighters coming from Syria, calling themselves “Jund Allah,” which swore allegiance to ISIS.
Source:
“معلومات استخبارية: 200 مسلح لداعش تسللوا إلى الأراضي العراقية قادمين من سوريا
(Intelligence: 200 ISIS militants infiltrated Iraqi territory from Syria),” Rudaw (Kurdish media outlet), 30 November 2021. https://www.rudaw.net/arabic/kurdistan/301120211
The official of the Qarah Tapah – Hamrin II axis of the Peshmerga forces, Major General Mardan Jawshin, announced that they had received intelligence information that a force calling itself “Guardians of Religion,” consisting of 200 militants, “has pledged allegiance to ISIS and infiltrated into Iraqi territory coming from Syria”… regarding the recent increase in ISIS activities… he said that that ISIS is reorganizing its ranks and did not hide his belief that the organization “receives financial and logistical support from abroad,” referring to information that says that “the organization pays salaries to its militants and also pays salaries to the families of its dead…” Major General Jawshin pointed to the security vacuum between the Iraqi army and the Kurdistan Peshmerga forces as “the reason for the increase in ISIS attacks”… He noted that the ISIS threat had reached a very high level, especially after the arrival of the aforementioned 200 militants from Syria, and said that there is a 100% likelihood that ISIS will launch more attacks on the Peshmerga forces and the Iraqi army in the coming period.
Source:
“تعاون بغداد وأربيل ضد «داعش» بين الضرورة وفقدان الثقة
(Baghdad-Erbil Cooperation Against ISIS Between Cooperation and Loss of Trust),” al-Quds (pan-Arab daily), 11 December 2021. https://tinyurl.com/2p8s5hay
On the fourth anniversary of Baghdad’s declaration of the elimination of ISIS in 2017, Iraqis are following with concern the resurgence of attacks in many Iraqi provinces, despite all the security campaigns to hunt down the group’s remnants… observers fear that the state Shiite forces, which thwarted the Baghdad and Erbil agreement on the normalization of the situation in Sinjar, west of Mosul, will obstruct the agreement to deploy the Peshmerga in the disputed areas. This is especially true given that [Prime Minister] al-Kazemi, who was committed to concluding those agreements with the regional government, may not retain his post in the next government.
Therefore, the mutual accusations of exploiting terrorist organizations such as the Turkish Workers’ Party and ISIS and supporting their presence on Iraqi soil to achieve local and regional political agendas are not limited to Kurdish parties on the one hand, and the Shiites and Turkmen on the other hand, but rather also extends to leaders of the al-Fateh Alliance, which includes pro-Iranian factions, and which considers that the recent attacks in Kirkuk were intentional and motivated by political agendas aimed at providing justifications for the presence of US forces in Iraq, which are scheduled to depart at the end of this year. They also accuse the Kurdish leadership of fabricating or exploiting ISIS attacks in order to seek to restore the region’s control over Kirkuk and the areas disputed between the Baghdad and Erbil governments, after the expulsion of the Peshmerga from those areas in 2017, following the referendum on secession from Iraq.
Image Information:
Image: Disputed areas in Iraq.
Source: Rafy, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Disputed_areas_in_Iraq.svg
Attribution: CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons







