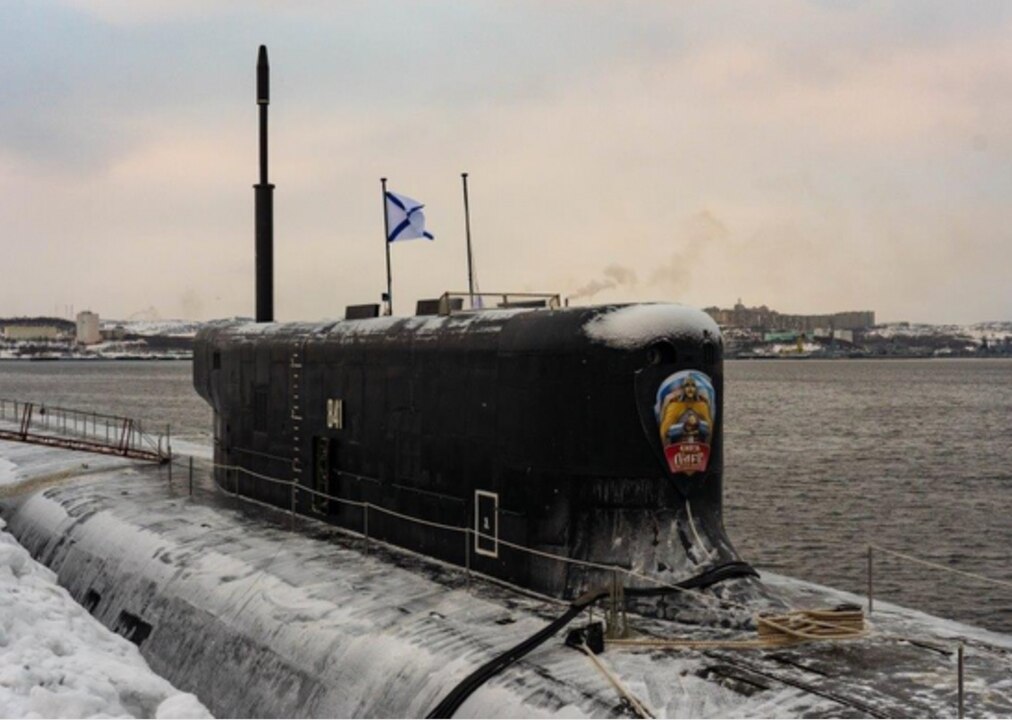

The Knyaz Oleg arrives at the Northern Fleet in February 2022. The Knyaz Oleg is the fifth Borei-class submarine on active duty.
“Each of the Borei submarines can carry 16 ballistic Bulava missiles, each armed with 4 to 10 nuclear warheads.”
Despite the fighting in Ukraine, a military commitment in Syria, and Western sanctions, Russia continues to test new strategic systems and expand its Northern Fleet[i]—but not without a few hiccups. According to the excerpted article from Norway-based The Barents Observer, a Russian Borei-class strategic ballistic missile firing submarine, the Imperator Aleksandr III, is currently undergoing sea trials in the Arctic. The Imperator Aleksandr III is the seventh Borei-class [R1] submarine in operation with three more under construction and an additional two planned, for a total of twelve. The article notes that the Imperator Aleksandr III launched a Bulava strategic missile across the Russian Arctic from the White Sea to Kamchatka as part of its sea trials.[ii] The article also notes that a nuclear triad exercise on 25 October featured a canceled Bulava launch. According to the second excerpt, from the Russian Telegram channel Sirena, there have been six failed or canceled missile tests since June 2023. Despite the setbacks, and if a Bulava ballistic missile was fired from the Imperator Aleksandr III, Russia would continue to improve its missile capabilities and advance its strategic power in the Arctic.
Sources:
Thomas Nilsen, “Newest submarine launched Bulava [R1] missile from White Sea,”
The Barents Observer (independent Norwegian news site in Russian and English currently blocked in Russia), 5 November 2023. https://thebarentsobserver.com/en/security/2023/11/newest-strategic-submarine-launched-bulava-missile-white-sea
It was Sunday morning, 5 November, when the Defense Ministry in Moscow reported that the Imperator Aleksandr III was sailing under the surface in the White Sea and launched a Bulava. A few minutes after breaking the surface in Russia’s northwestern region, the missile hit the designated target at the Kura range on the Kamchatka Peninsula.
The Imperator Aleksandr III (K-554) was launched in December last year from the Sevmash shipyard in Severodvinsk and has since been undergoing state trials at sea and while at berth at the yard.
The submarine is the 7th Borei-class submarine and will likely be transferred to the Navy before New Year. Like the sixth submarine in the class, Generalissimus Suvorov, also the Imperator Aleksandr III will cross under the Arctic ice and sail for Russia’s Pacific Fleet.
Each of the Borei submarines can carry 16 ballistic Bulava missiles, each armed with 4 to 10 nuclear warheads. Three more subs of the class are currently under construction in Severodvinsk, and two more are planned, but no contracts have been signed.
When Russia tested its nuclear deterrence triad on October 25, the only submarine-launched ballistic missile fired was an older Sineava, fired from the Northern Fleet’s Delta-IV class Tula in the Barents Sea.
“Шесть испытаний российских ракет отменились или провалились с июня (Six Russian missile tests have been canceled or failed since June). Sirena (Russian Telegram Channel), 1 November 2023. https://t.me/news_sirena/20870
Since June 30, 2023, at least six unsuccessful rocket tests have taken place in Russia, a source at one of the rocket and space industry enterprises told Sirena . Some launches failed altogether. Here are the details:
On June 30, the Poseidon device was tested unsuccessfully – an underwater nuclear torpedo that should hit coastal areas, ships and naval bases. According to our source, the cooling sensor showed a lack of coolant, the reactor did not start, and the Poseidon was thrown out of the shaft, after which it sank. The next launch was planned for late October – early November, but it has been postponed.
On August 30, the third launch of the Sarmat complex did not take place. It was postponed due to a failure in the missile’s centralized control system, Sirena’s interlocutor claims.
On October 25, “presidential launches” took place – Putin led the tests. The Kremlin then stated that all the objectives of the exercises had been completed. Our source says that the Yars missile fell during the second stage of flight, and the Bulava launch was canceled at the last moment.
On October 31, the next Sarmat launch failed because the telemetry system failed. According to the source, this was explained by a mistake by the maintenance staff.
Today, the Sarmat fell 77 seconds into the flight, 300 kilometers from the launch site. This already happened to the complex in February. Test participants do not have clear versions of why something goes wrong.In September, the head of Roscosmos, Yuri Borisov, said that the Sarmat complexes were put on combat duty. Sirena’s source believes that the Russian authorities were “obviously in a hurry” with this.
Notes:
[i] It was previously reported that the Northern Fleet is expanding its capability by acquiring ice-class minesweepers for their Arctic waters. See: Atle Staalesen, “Three ships of Russia’s new class of minesweepers are being built for Arctic waters,” The Barents Observer (independent Norwegian news site in Russian and English currently blocked in Russia), 22 June 2023. https://thebarentsobserver.com/en/security/2023/06/new-minesweepers-coming-northern-fleet
[ii] For more information on the Bulava nuclear capable submarine launched ballistic missile see: RSM-56 Bulava (SS-N-32), MissileThreat, CSIS Missile Defense Project, CSIS, 2 August 2021. https://missilethreat.csis.org/missile/ss-n-32-bulava/
Image Information:
Image: The Knyaz Oleg arrives at the Northern Fleet in February 2022. The Knyaz Oleg is the fifth Borei-class submarine on active duty.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Russian_submarine_Knyaz_Oleg – /media/File:K-552_at_Northern_fleet.jpg
Attribution: CC by 4.0






.jpeg)

