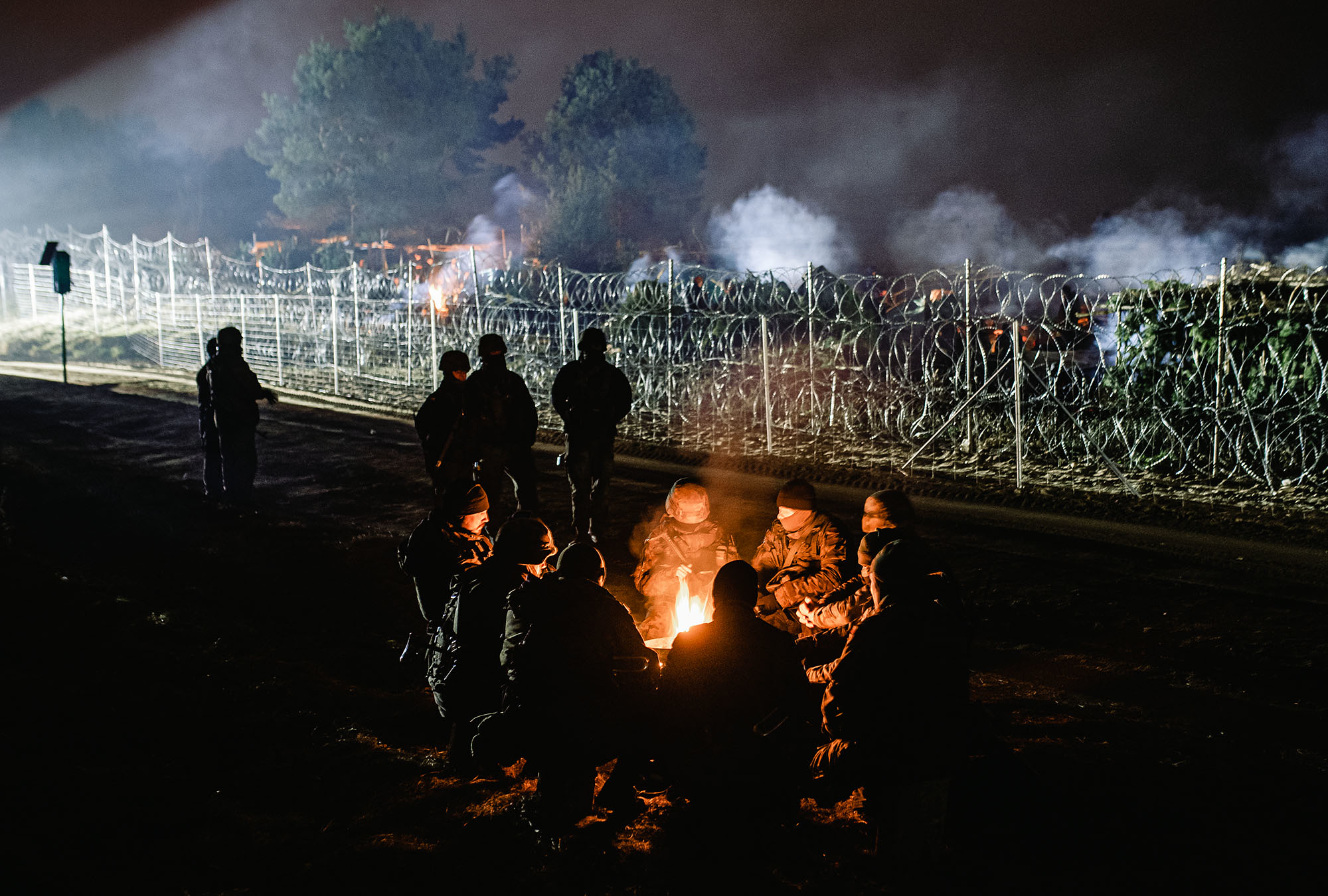
The Polish-Belarusian border, photo taken on 11 November 2021.
“This is also a very important strategic document. Work on these two documents has been completed, and we plan, together with the Secretariat of the Security Council of the Russian Federation, to submit [them] for approval by the heads of our states at the Supreme State Council.”
Russia and Belarus have nearly finalized a “Treaty on Security Guarantees of the Union State,” according to an interview with Secretary of the Security Council of the Republic Alexander Wolfovich in Izvestia, a pro-Kremlin Russian newspaper. The document, which will be sent for ratification by the Supreme State Council in December, will replace the 1999 union concept. Belarus will receive substantial security guarantees, including the use of nuclear and conventional weapons, “due to external threats.”
The intention of the original treaty was to achieve a federation not unlike the Soviet Union, whereby Belarus and Russia would share a head of state, legislature, flag, currency, coat of arms, anthem, and other insignia of a unified state.[i] The full extent of the Union State never came to fruition, largely because both leaders of the federation, Presidents Boris Yeltsin (Russia) and Alexander Lukashenko (Belarus), quickly lost interest in the provisions of the treaty because both feared it would weaken their own power. Belarus suspended the customs union a few years later, and they never developed a common currency.
The revised treaty comes amid heightened tensions along Belarus’ borders with Ukraine and Poland, due to a migrant crisis (involving asylum-seekers from the wider Middle East),[ii] nuclear drills conducted on Belarusian territory summer 2024,[iii] and rumors that Belarusian soldiers may be sent to fight in Ukraine.[iv] The security guarantees of the new document suggest that an attack against Belarus, conventional or otherwise, would be considered an attack against Russia.
Interestingly, the original intention of signing the 1999 treaty was economic, not security related. Back then, commercial and economic interests trumped security concerns.[v] Going back to the breakup of the Soviet Union, Russia has been Belarus’ largest economic and political partner. Vladimir Putin has sought greater integration of the two countries’ economies. As reported by Izvestia, trade between the two neighbors in the first half of 2024 ($25 billion) was up 6.4 percent from the same time last year, with some 133 investment projects underway in the fields of agriculture, energy, tourism, IT, medicine, and pharmaceuticals, according to Deputy Minister of Economic Development of Russia Dmitry Volvach. The revised treaty should strengthen economic integration and trade between the two neighbors.
More importantly, the revised Union State treaty signals greater security cooperation and guarantees between Minsk and Moscow. Belarus has long acted as a strategic buffer zone between Russia and NATO. Although President Alexander Lukashenko sought greater autonomy after the 2014 annexation of Crimea, a disputed election in 2020 and a popular uprising forced the Belarusian leader to seek greater integration with Russia. The revised Union State treaty will further isolate Belarus from Europe and make it more dependent on Russia for its security, both internal and external. While the long-term consequences of the revised Union State remain uncertain, given that Russia and Belarus have both sought to maintain their post-Soviet era borders and independence, greater military cooperation between Belarus and Russia is expected, including closer economic and potential territorial integration and even Belarus playing a larger role in the war in Ukraine, beyond just hosting Russian nuclear and military assets.
Sources:
Elizaveta Borisenko, “Взаимное действие: Москва и Минск подготовили договор о гарантиях безопасности (Union proposal: Moscow and Minsk strengthen cooperation against Western pressure),” Izvestia (a pro-Kremlin Russian newspaper), 11 November 2024. https://iz.ru/1787861/elizaveta-borisenko/vzaimnoe-deistvie-moskva-i-minsk-podgotovili-dogovor-o-garantiah-bezopasnosti
According to [Wolfovich], the provisions of the document will be published in the near future. The document will include the principle of the use of nuclear and conventional weapons, as well as other methods of protecting the Union State. “What our president recently said, what Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin recently said that, God forbid, there will be some aggressions towards the Republic of Belarus, is all true. If today it has the character of protecting the joint and protection of Belarus through the deployment of nuclear weapons on our territory, de facto in December, by the 25th anniversary of the signing of the Treaty on the establishment of the Union State, this treaty will already be legally signed,” Belarusian Foreign Minister Maxim Ryzhenkov said earlier.
Russia previously decided to amend the nuclear doctrine, which was last updated in 2020. In particular, we are talking about the expansion of scenarios in which the Russian authorities reserve the right to use nuclear weapons. In the updated version of the document, aggression against Russia by any non-nuclear state, but with the participation or support of nuclear, is proposed to be considered as their joint attack on the Russian Federation. In addition, there are provisions that concern Belarus.
“We reserve the right to use nuclear weapons in case of aggression against Russia and Belarus as a member of the Union State. All these issues have been agreed with the Belarusian side and the President of Belarus. Including if the enemy, using conventional weapons, creates a critical threat to our sovereignty,” Vladimir Putin said on September 25.
As for the new concept of the security of the Union State, which will replace the document adopted back in 1999, it will enshrine a provision on joint counteraction to the policies of the United States, unfriendly NATO states and the European Union to achieve strategic goals for mutually beneficial and equal international cooperation. Such strengthening of cooperation in the field of security is primarily related to the foreign policy situation, Dmitry Zhuravlev, scientific director of the Institute of Regional Problems, associate professor of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, tells Izvestia.
Notes:
[i] “The Republic of Belarus and the Russian Federation signed the Union State Treaty on 8 December 1999,” Press Service of the President of the Republic of Belarus, https://president.gov.by/en/belarus/economics/economic-integration/union-state?TSPD_101_R0=08eaf62760ab20008e25be59f2426da6e735002c3eb769d3b553a73ed46fd82fa95c1f4983143a0a086c7a2488143000ed156aeeac2db1eb09822ff7aca3ea7bcda21c0e8cb9ef3c1a0b6b7c0271930783b0b327184c7aa97f0896aae08327fc
[ii] See: “Poland to temporarily suspend asylum rights amid Belarus border tensions,” Al-Jazeera, 12 October 2024. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2024/10/12/poland-to-temporarily-suspend-asylum-rights-amid-belarus-border-tensions
[iii] See: “Belarus launches nuclear drills a day after Russia announces them amid tensions with West,” AP News, 7 May 2024. https://apnews.com/article/russia-belarus-nuclear-drills-ukraine-war-144422347bb168878cebc0b78071dd99
[iv] See: Mark Temnycky, “Will Belarus join North Korea in fighting Russia’s war?” The Hill, 17 November 2024. https://thehill.com/opinion/international/4993006-ukraine-north-korean-fighting/
[v] For analysis, see Helene Alstad Dyndal, “The Union State of Russia and Belarus at the present stage,” Strategem, 11 April 2024 https://www.stratagem.no/the-union-state-of-russia-and-belarus-at-the-present-stage/
Image Information:
Image: The Polish-Belarusian border, photo taken on 11 November 2021.
Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/premierrp/51674607554
Attribution: Irek Dorozanski