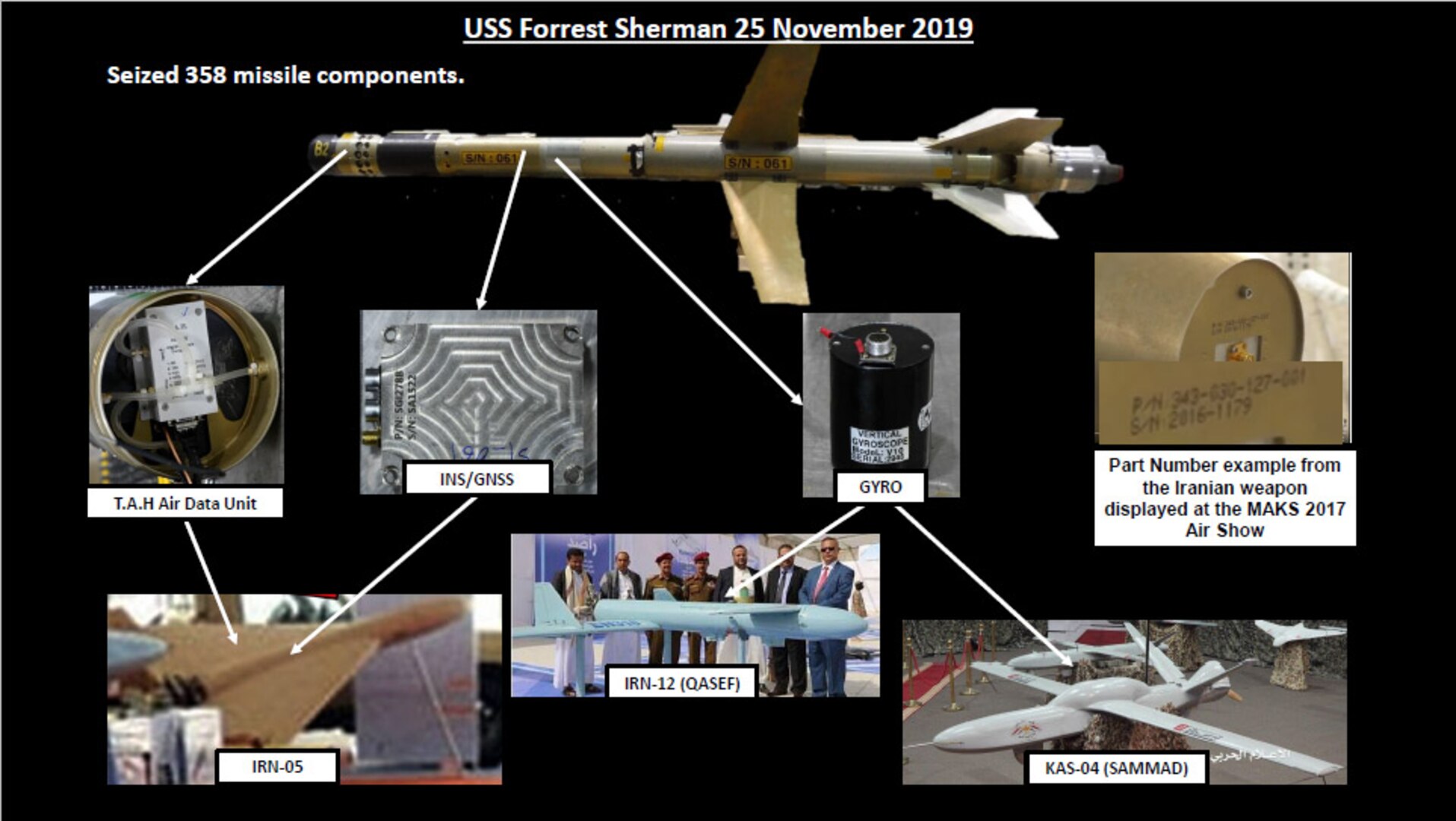
Sana’a, capitol of Yemen at Night.
“Despite its decline in the Arabian Peninsula, [AQAP] remains the most effective terrorist group in Yemen, with the intent to launch attacks in the region and beyond.”
Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) named a successor after the recent loss of its leader. According to the first excerpted article from the Saudi state-owned international news outlet Al Arabiya, Saad bin Atef al-Awlaki, aka “Abu al-Laith,” a Yemeni national, has been named the new leader of AQAP. The organization’s official, Ibrahim al-Qusi, confirmed in a broadcast recording that the group’s former leader had been killed, declaring that “Saad bin Atef al-Awlaki is the new leader of the organization in the Arabian Peninsula.”[i] The new AQAP leader, Al-Awlaki, reportedly had direct ties to former al-Qaeda leader Usama bin Laden and was repatriated to Yemen by Bin Laden. Al-Awlaki is reported to also have originated from the same tribe as former al-Qaeda spiritual leader Anwar al-Awlaki, who was killed in 2011. There is a $6 million reward from the U.S. State Department for information about the new AQAP leader, who has “publicly called for attacks on the U.S. and its allies.” The U.S. has designated AQAP as a Foreign Terrorist Organization since 2010.[ii]
The second excerpted article from the Jeddah-based Saudi daily newspaper Okaz, provides some perspective on the current status of AQAP, as well as the potential effect of Al-Awlaki as the group’s new leader. The article notes that the al-Qaeda affiliate has struggled for a multitude of reasons, including the loss of several key leaders, financial challenges, and internal disputes that have led to structural issues. The article also states that Al-Awlaki could be a unifier for AQAP due to his extensive background in the terrorist network, experience in the al-Qaeda leadership council, and previous position as Emir in the Shabwa Province. While there has been a shift in the West to focus on great power competition with China and Russia, and persistent challenges from Iran, the ongoing threat from international terrorist organizations cannot be discounted, especially with new leaders who have openly called for attacks against the United States.[iii]
Sources:
“سعد العولقي.. من هو زعيم “القاعدة” الجديد في اليمن؟ (Saad Al-Awlaki… Who is the New Leader of Al Qaeda in Yemen),” Al Arabiya (Saudi state-owned news outlet), 11 March 2024. https://www.alarabiya.net/arab-and-world/yemen/2024/03/11/بعد-الاعلان-عن-مقتل-زعيم-تنظيم-القاعدة-من-هو-خليفته؟
Al-Qaeda in Yemen confirmed the killing of its leader, Khaled Batarfi, without going into details, announcing that his new successor is Saad Al-Awlaki. The SITE Center, which monitors terrorist media, stated that the organization’s legal official, Ibrahim al-Qusi, confirmed in a recording broadcast yesterday, Sunday, the killing of Batarfi, the organization’s leader since February 2020, declaring that “Saad bin Atef al-Awlaki is the new leader of the organization in the Arabian Peninsula.” , which the United States classifies as a terrorist…
Saad bin Atef Al-Awlaki, nicknamed “Abu Al-Laith,”… is of Yemeni nationality, and media reports indicate that he is one of those who was repatriated from Afghanistan to Yemen by the former leader of Al-Qaeda, who was killed by America in 2011, Osama bin Laden. Thus, Al-Awlaki becomes the fifth leader to publicly lead Al-Qaeda in Yemen, after working for years as the extremist organization’s second-in-command in the country.
Saad Al-Awlaki was born in the town of Al-Shu’bah in Wadi Yasbam in the Upper Egypt District in Shabwa Governorate (south). He comes from the large Al-Awalqi tribe, the same tribe from which the spiritual father of Al-Qaeda, Anwar Al-Awlaki, who was killed by an American drone in 2011, descends.
Mohamed Hefney, “خبير مصري لـ عكاظ: الخلافات تفكك تنظيم القاعدة الإرهابي في اليمن (An Egyptian expert to Okaz: Disagreements are Disintegrating the Al-Qaeda Terrorist Organization in Yemen),” Okaz (Saudi based newspaper), 13 March 2024. https://www.okaz.com.sa/news/politics/2157390
Fears are escalating within Al-Qaeda, after the killing of its fourth leader in Yemen, Khalid Batarfi, nicknamed “Abu al-Miqdad al-Kindi,” and the appointment of his successor, Saad bin Atef al-Awlaki, nicknamed “Abu al-Layth,” who the US administration classified in 2021 as a global terrorist, and offered a reward of $6. Millions of dollars in exchange for providing information about him.
Dr. Nabil Naeem, believes that Al-Awlaki is known for his extreme hostility toward America, and like all of his predecessors, he called for the necessity of launching attacks on the United States of America, which prompted the American administration to allocate a large financial reward to anyone who provides information about him. He stressed that Al-Qaeda in general, whether in Yemen or elsewhere, has become weak and fragile and is witnessing a major liquidation of its leaders, whether in Yemen or other countries in the region. It is not the organization that existed 20 years ago. The new leader of Al-Qaeda in Yemen faces grave challenges and priorities, including how to preserve his life and the lives of his followers from the expected physical liquidation. The Yemeni organization also faces challenges at the financial and structural levels, as the financial level is very weak. Structural level: There is a state of splits and divisions within the organization left behind by the former leader of the organization, which indicates that his death was under the direction of those close to him. Therefore, we do not rule out that the new leadership will seek to bring the terrorist organization together.Al-Awlaki is considered one of the founding leaders of Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula, and he served as a member of the leadership council of Al-Qaeda. He was born in the 1980s. He joined the organization in 2010, and assumed the position of Emir of Shabwa Province until 2014, then he was appointed a member of the organization’s Shura Council, which is responsible for Managing operations, and he was called the second man in Al-Qaeda in Yemen.
Notes:
[i] Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula was initially created in 2009 after the Saudi and Yemeni branches merged forces. The group is currently assessed to be one of the most lethal al-Qaeda affiliates. The Council on Foreign Relations published a backgrounder on AQAP, see: “Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP),” Council on Foreign Relations, 19 June 2015. https://www.cfr.org/backgrounder/al-qaeda-arabian-peninsula-aqap
[ii] For a complete list of designated terrorist organizations by the United States Government see: “Foreign Terrorist Organizations,” U.S. Department of State, Accessed 12 March 2024. https://www.state.gov/foreign-terrorist-organizations/
[iii] The 2024 Annual Threat Assessment of the U.S. Intelligence Community further notes that, “Al-Qaeda’s regional affiliates on the African continent and Yemen will sustain the global network as the group maintains its strategic intent to target the United States and U.S. citizens.” The entirety of the most recent unclassified annual threat assessment issued by the United States Intelligence Community can be located here: “Annual Threat Assessment of the U.S. Intelligence Community,” Office of the Director of National Intelligence, 5 February 2024. https://www.dni.gov/files/ODNI/documents/assessments/ATA-2024-Unclassified-Report.pdf
Image Information:
Image: Sana’a, capitol of Yemen at Night.
Source: https://openverse.org/image/c4b13d0f-5ffa-44fc-9a82-518d08dbfbc0?q=yemen Attribution: CC BY-SA 2.0