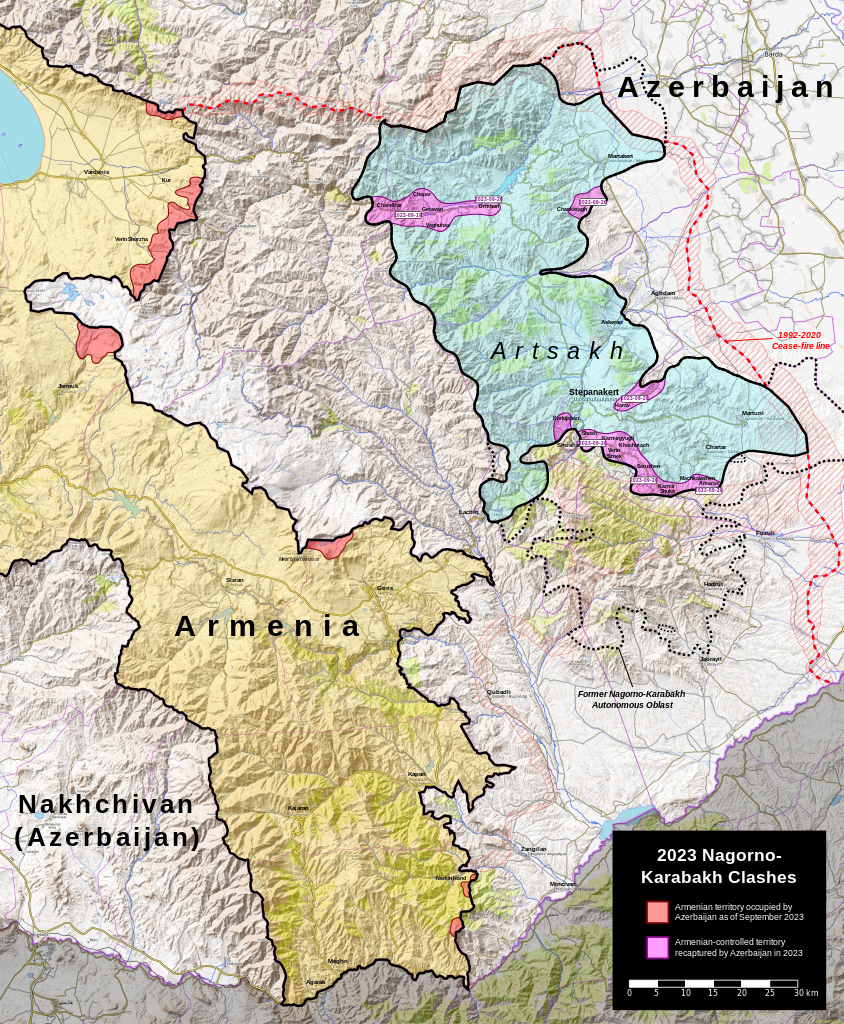
Map of the 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh war showing Azerbaijan day-to-day advances.
“The conditions under which the Russian peacekeeping contingent was introduced into the region in 2020 have been seriously adjusted.”
On 19 September 2023, Azerbaijani forces launched an operation against the breakaway republic of Artsakh, and within days, succeeded in ending ethnic Armenian control of the Nagorno-Karabakh region. The excerpted article from the independent news website Kavkazskiy Uzel reports on how Azerbaijani control of Nagorno-Karabakh has impacted the Russian peacekeeping mission.[i] The article notes that Russian peacekeepers dismantled a few observation posts and established new ones, some of which were set up with Azerbaijan to jointly protect the weapons and equipment surrendered by the armed forces of Nagorno-Karabakh. The dismantled observation posts were situated in eastern Nagorno-Karabakh near Azerbaijan. The article also notes, the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs claimed that its peacekeepers will adapt to the new situation, even as a large percentage of the population in Nagorno-Karabakh has left the region. The mandate of the Russian peacekeeping mission runs through November 2025 and will be automatically extended for another five years unless the governments of Armenia or Azerbaijan request to terminate it. The article notes that the Armenian government signed a declaration recognizing Nagorno-Karabakh as part of Azerbaijan two weeks after Azerbaijan took control of the region, essentially ending support for the breakaway republic. While one of the main tasks of the Russian peacekeeping mission has changed, it appears likely that Russia will continue to operate in the region.
Sources:
“МИД России пояснил смену постов миротворцев адаптацией к новым условиям (The Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Russia explained the change to the posts of peacekeepers as adapting to the new conditions),” Kavkazskiy Uzel (independent news website reporting on the Caucasus), 10 October 2023. https://www.kavkaz-uzel.eu/articles/393302
Peacekeepers are adapting to new conditions against the backdrop of a mass exodus of the population from the region, reported Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova.
As t“e “Caucasian K”ot” wrote, on October 5, peacekeepers reported on the dismantling of observation posts in the Askeran, Martakert and Shusha regions, and on October 8, the Russian peacekeeping contingent dismantled posts in the Martuni and Martakert regions…
A day earlier, the Russian peacekeeping contingent reported that the Russian peacekeeping contingent had set up 25 guard posts in the North (seven posts) and South (18 posts) areas of responsibility, including 14 jointly with the Azerbaijani side. Peacekeepers are taking part in the protection of warehouses with ammunition, weapons, military and special equipment surrendered by the armed forces of Nagorno-Karabakh, as stated in the bulletin dated October 9.
The activities of Russian peacekeepers in Nagorno-Karabakh will adapt to new conditions against the backdrop of a mass exodus of the population from the region, Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova said today…
As a result of the virtual capitulation of Stepanakert, Azerbaijan gained control over the region. On September 28, the President of Nagorno-Karabakh signed a decree ending the existence of the republic. After the military operation carried out by Azerbaijan on September 19-20, almost all residents left Nagorno-Karabakh, in which, according to various sources, about 120 thousand people lived…If the Russian peacekeeping contingent leaves Nagorno-Karabakh, it must return to Russia, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan said today in an interview with the Public TV Channel when asked about the possibility of deploying peacekeepers in Armenia…On October 5, Armenian Prime Minister Nikol Pashinyan signed a declaration recognizing the territorial integrity of Azerbaijan, including the territory of Nagorno-Karabakh…
Notes:
[i] Russian peacekeepers were deployed as part of the ceasefire agreement that ended the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War. For background on the Russian peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh and how Russia uses peacekeeping missions to achieve strategic objectives beyond conflict resolution, see: Matthew Stein “The Evolutionary Russian View Of Peacekeeping As Part Of Modern Warfare,” FMSO’s Foreign Perspectives Brief, 24 March 2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/2023-03-24-the-evolutionary-russian-view-of-peacekeeping-as-part-of-modern-warfare-matthew-stein-update/
Image Information:
Image: Map of the 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh war showing Azerbaijan day-to-day advances.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2023_Nagorno-Karabakh_War.svg
Attribution: CCA 4.0
