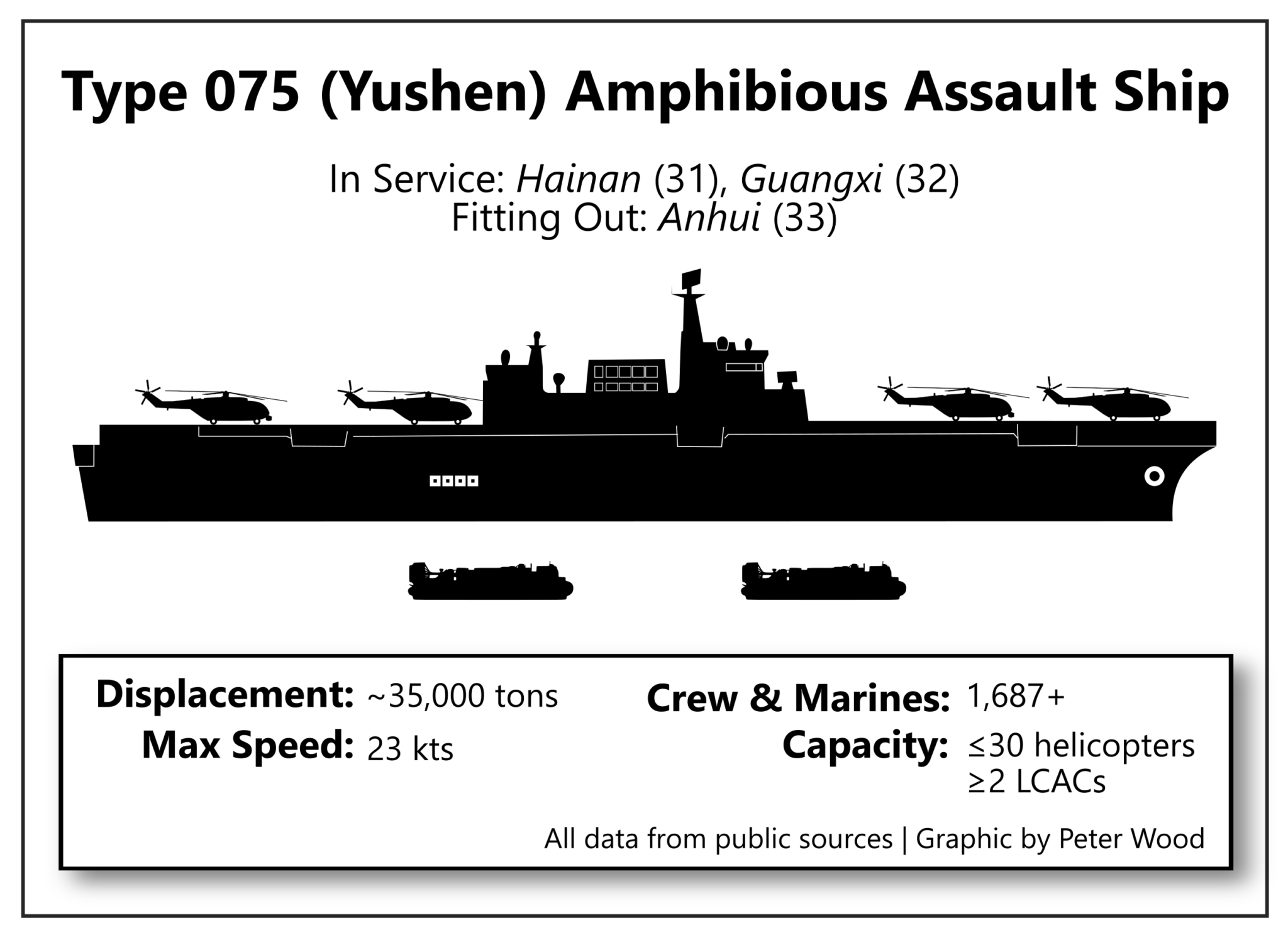
“In the age of liberalization of global trade, countries don’t have to gain power through… grabbing land. This can be done through technology and capital… but Russia is still obsessed with owning land.”
The accompanying article in the South China Morning Post (SCMP), a Hong Kong-based, ostensibly-independent newspaper, notes a growing list of Chinese intellectuals who have publicly questioned Russia’s justification for invading Ukraine. This suggests that Chinese thinkers do not widely approve of China’s support for Russia’s actions in Ukraine despite the “no limits” relationship between the two countries that Chinese authorities stated prior to the Winter Olympics.
The focus of the SCMP article is an article by a recently retired Chinese military scholar published on Chinese social media site WeChat. That article disappeared shortly after it was posted but, according to the accompanying SCMP publication, the author of the article, Gong Fangbin questioned Moscow’s assertion that Ukraine was on the brink of invading Russia, instead suggesting that the real reason Russia invaded Ukraine was that “Russian leaders have taken the wrong path for rejuvenation.” The author suggested that Russia’s obsession with land as an indicator of strength was misguided and obsolete in the 21st century. According to the SCMP article, another Chinese intellectual, Yan Xuetong, dean of the Institute of International Relations at Tsinghua University, recently said that Russia would pay “a huge price” for its invasion of Ukraine. Finally, Hu Wei, a political scientist affiliated with China’s State Council called on Beijing “to distance itself from Russia as soon as possible over its war on Ukraine.” Finally, the intellectuals suggest multiple negative repercussions for China. The SCMP article also notes that although China has said it supports Ukraine’s territorial integrity and denied suggestions that it might offer military assistance to Russia, it has not outright condemned Russia’s invasion, has not conducted a head of state visit with Ukrainian President Zelensky, and has criticized U.S.-led sanctions imposed on Russia.
Source:
Jun Mai, “Russia’s war on Ukraine based on flawed logic, Chinese military scholar wrote in article scrubbed from the web,” South China Morning Post (a Hong Kong-based, ostensibly-independent newspaper), 21 May 2022. https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3178631/russias-war-ukraine-based-flawed-logic-chinese-military?module=lead_hero_story&pgtype=homepage
Russia’s security rationale for attacking Ukraine was flawed and the aftermath underlines the importance of diplomatic flexibility, a Chinese scholar formerly with Beijing’s top military academy has said.
“I still don’t see how any country would have dared to invade the world’s No 2 military power,” Gong Fangbin, a retired professor of the People’s Liberation Army National Defence University, wrote in a recent online article.
“Russia has shown the world time and again that no one dares touch an inch of its land,” he said, countering Moscow’s argument that it was cornered by the West and NATO into invading Ukraine.
“What’s the real reason [for Moscow] to attack Ukraine? I think it’s because the Russian leaders have taken the wrong path for rejuvenation.”
Gong argued that the rationale to attack Ukraine over so-called security concerns was flawed. And the dilemma faced by Russia as it took heavy losses on the ground was the result of having chosen a path “long forsaken by human civilisation”, he wrote in his article posted on WeChat last Tuesday.
The article, however, has since disappeared from the social media platform.
Gong confirmed to the Post that he wrote the article but declined a request for an interview.
Gong, a military veteran who fought in the China-Vietnam war of 1979, is among a small but growing number of Chinese intellectuals voicing scepticism about Moscow’s rationale for its military aggression against Kyiv, despite heavy censorship of the sharing of such views.
“In the age of liberalisation of global trade, countries don’t have to gain power through … grabbing land. This can be done through technology and capital,” Gong wrote. “But Russia is still obsessed with owning land.”
At a Beijing seminar in April, China’s ambassador to Ukraine between 2005 and 2007, Gao Yusheng, argued that Russia had shown signs of having lost the war and its global status was set to decline. A summary of his remarks, first published by news outlet ifeng.com in mid-May, was quickly censored.
But there are others making their opinions known. Yan Xuetong, dean of the Institute of International Relations at Tsinghua University, said earlier this month that China had not benefited from the war and Russia was set to pay “a huge price”.
And in March, Hu Wei, a political scientist affiliated with the State Council – China’s cabinet – called on Beijing to distance itself from Russia as soon as possible over its war on Ukraine.
As the war enters its third month, Beijing still refuses to condemn Russia’s act of aggression, despite mounting pressure from the US and its allies. It has also sought to rally international support to criticise the sweeping sanctions imposed on Russia, citing disruption to the global economy.
Since Russia launched its military assault on February 24, China has repeatedly said it respects Ukraine’s sovereignty. However President Xi Jinping is among the very few world leaders yet to hold direct talks with Ukrainian leader Volodymyr Zelensky.
Meanwhile, Chinese diplomats have sought to contain damage from the country’s close, “no limits” relationship with Moscow, as declared in a joint statement issued after Russian President Vladimir Putin met Xi in Beijing ahead of the Winter Olympics.
The diplomatic damage control has involved firmly denying suggestions that China might offer military assistance to Russia, and trying to isolate the Ukraine issue from Beijing’s relations with Europe.
Military scholar Gong had argued in another article earlier this month that the Ukraine war underlined how foreign policy flexibility might suffer if it was too closely tied to domestic politics.
This came after he had referenced the situation in yet another article in March, where he argued that countries only made decisions based on their own interests, and hence it was wrong to consider any country as a “strategic buffer”, as Russia says it had hoped Ukraine would be.
Failure to understand this, Gong argued, would lead one to also believe in the narrative that China’s economic development in the last 50 years owed much to Russia’s confrontation with the United States.“If a country is full of convictions related to strategic barriers and buffer zones, it will tie itself to the vehicles of others and thus lose autonomy, consistency and necessary flexibility,” he warned.