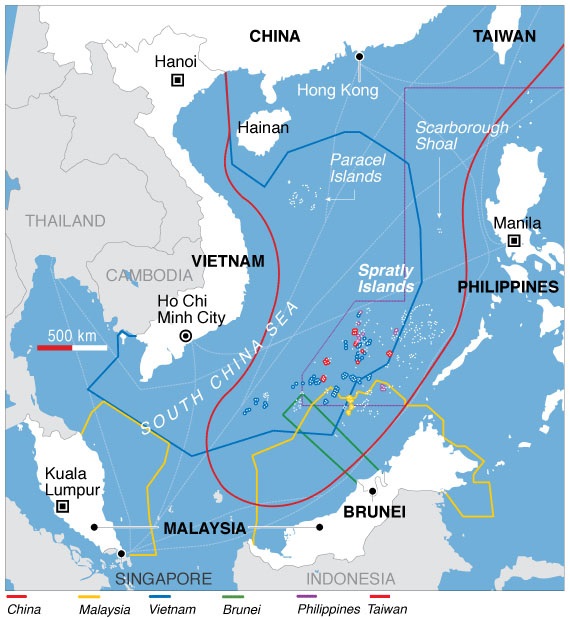
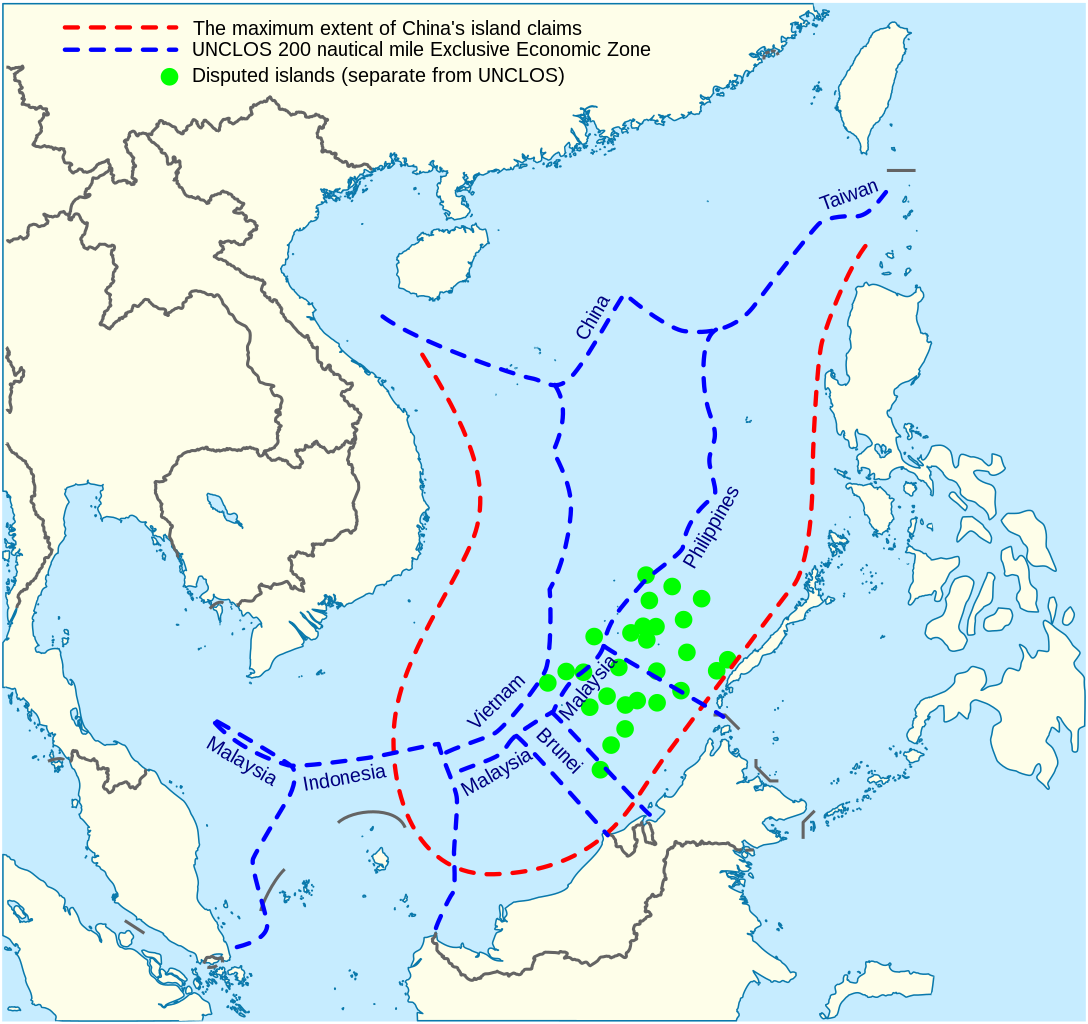
China’s maritime claim (red), compared to other countries. The Philippines has recently expressed interest in procuring submarines to protect itself against Chinese maritime aggression.
“China is willing to resolve differences with the Philippines through bilateral dialogue and consultation, but if the Philippines insists on going its own way, China will resolutely counterattack.”
The Philippines recently announced its plans to acquire submarines. According to Japan-based weekly news magazine, Nikkei Asia, the plan is the third part of a three-phase military modernization strategy and indicates the Philippines is “taking a more assertive approach to defending its interests beyond its borders.” The first and second phases were focused on bolstering the Philippines’ “land-centric” assets.[i] It is unknown where the Philippines will acquire its submarines but, according to the first article, “Spain, South Korea and Italy have shown an interest in supplying it with submarines.”
While the exact number of submarines the Philippines plans to purchase is unknown, the second excerpted article, published in the pro-independence, Taiwan newspaper, Liberty Times, suggests that one submarine is not enough. Ian Story, a senior researcher from ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute in Singapore argues that the Philippines should purchase three so that one can be operational while another is in training and the last one undergoing maintenance. He also estimates that it could take more than 10 years to acquire and integrate submarines into Philippines’ military capabilities. While other experts agreed with three submarines being an ideal number to start, Joshua Bernard Espeña, vice president of the Philippine think tank International Development and Security Cooperation argued that two to three submarines would not be enough to deter China because China’s southern theater could deploy more than 30 diesel-electric submarines in the South China Sea. Meanwhile, in response to these plans, Chinese state-controlled Xinhuanet went on the offensive, saying that while buying a submarine was the Philippines’ own business, China will not tolerate anything that infringes on its sovereignty “and undermines regional peace and stability.” According to Chinese Ministry of National Defense spokesperson Colonel Wu Qian, the Philippines has already “betrayed its trust, colluded with major powers outside the region, and continued to engage in malicious activities in the South China Sea.” He went on to warn that China will counterattack if the Philippines “insists on going its own way.” However, he did not offer any specifics as to steps China might take.
Sources:
Ramon Royandoyan, “Philippines ‘Breaking From Its Shell’ With Submarine Purchase,” Nikkei Asia (major Japan-based English-language weekly news magazine), 2 February 2024. https://asia.nikkei.com/Politics/Defense/Philippines-breaking-from-its-shell-with-submarine-purchase
The Philippines’ plan to buy its first submarine marks a step toward the Southeast Asian nation taking a more assertive approach to defending its interests beyond its borders, analysts say.
On Thursday, Philippine President Ferdinand Marcos Jr. approved the planned submarine purchase, which is included in the third phase of the military’s modernization strategy….The first and second phases of the military modernization plan focused on bolstering “land-centric” defense assets. Defense Secretary Gilbert Teodoro Jr. said acquisitions under the third phase will focus on stepping up capabilities in domain awareness, intelligence and deterrence in maritime and aerial spaces.
The moves will prepare the Philippines “for future warfare of multi-domain attacks,” (Chester) Cabalza (founder of International Development and Security Cooperation, a think tank in Manila) added. In December, Manila installed Japan-made radar at an airbase some 300 kilometers from the Scarborough Shoal, the site of recent incidents involving China.
Friction between Beijing and Manila has escalated in recent months, as the Philippines Coast Guard accused a Chinese ship of using water cannons and deliberately ramming maritime vessels to disrupt the Philippines’ resupply missions to its outpost within the disputed waters.
The Philippine Navy on Thursday said France, Spain, South Korea and Italy have shown interest in supplying it with submarines.
Sun Yuqing, “菲律賓擬採購潛艦 專家:至少需要3艘才能嚇阻中國 (The Philippines Plans to Purchase Submarines. Experts: At Least Three Submarines Needed to Deter China,” Ziyou Shibao (also known as Liberty Times, a highly influential, pro-independence, Taiwan newspaper), 19 February 2024. https://news.ltn.com.tw/news/world/breakingnews/4583036
The report pointed out that in recent months, tensions between the Philippines and China in the South China Sea have intensified, with military and police officers from both sides having numerous confrontations, and both sides later accusing the other of inciting conflicts. This prompted the Philippine government to decide to promote the modernization of the military. One of the measures is to purchase submarines.
Roy Trinidad, spokesman for the Philippine Navy’s West Philippine Sea Affairs, did not disclose how many submarines Manila plans to purchase, but he said “it will definitely be more than one.”
Ian Story, a senior researcher at the Institute of Southeast Asian Studies (ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute) in Singapore Storey said that if one submarine is to be put into service at any time, Manila will need to purchase at least three. He explained that “3 is a magic number” that applies to all types of military equipment, one is operating, one is training, and one is being modified or maintained. For example, Vietnam has 6 submarines, which ensures that at least 2 are operational at any time.
However, since Manila has never operated a submarine, the process of acquiring and integrating the submarines will take at least 10 years, including the construction of infrastructure such as bases, docks, dry docks, and other support services. He added that if the Philippines orders two to three submarines, they will not be able to operate effectively until at least the mid-2030s.
However, Joshua Bernard Espeña, vice president of the Philippine think tank International Development and Security Cooperation, believes that 2 to 3 submarines are not enough to deter China, because China’s southern theater may deploy more than 30 diesel-electric submarines in the South China Sea. Power submarine.
“马科斯批准军队建设计划,包括购买菲律宾第一艘潜艇 (Marcos approves military construction plan, including purchase of Philippines’ first submarine),” Xinhuanet (Chinese state-controlled newspaper), 2 February 2024. http://www.news.cn/mil/2024-02/02/c_1212332825.htm
According to previous media reports, the Chief of Staff of the Philippine Armed Forces recently stated that the Philippines plans to develop islands and reefs in the South China Sea and purchase more ships and radars. Some analysts believe that the Philippines also intends to build outposts in the South China Sea.
In this regard, Colonel Wu Qian, spokesperson of the Chinese Ministry of National Defense, said on January 25 that whether or not to buy a ship is the Philippines’ own business, but China will never allow anything that infringes on China’s sovereignty and security and undermines regional peace and stability.Wu Qian said that China has indisputable sovereignty over the Nansha Islands and their adjacent waters, which has sufficient historical and legal basis. China firmly opposes any form of construction activities carried out by the Philippines on the illegally occupied islands and reefs of China’s Nansha Islands. The current difficulties facing China-Philippines relations lie in the fact that the Philippines has betrayed its trust, colluded with major powers outside the region, and continued to engage in malicious activities in the South China Sea. Infringement and provocation harm China’s legitimate rights and interests. We ask the Philippines to respect history, recognize reality, and not go down the wrong path. Wu to resolve differences with the Philippines through bilateral dialogue and consultation, but if the Philippines insists on going its own way, China will resolutely counterattack.
Notes:
[i] The country’s plan to introduce submarines to its defense forces, comes in the wake of escalating tensions between Beijing and Manila with the Philippine Coast Guard accusing a Chinese ship of “using water cannons and deliberately ramming maritime vessels” on resupply missions to Philippine outposts within the disputed waters. Over the past months, China has been putting mounting pressure on the Philippines in the South China Sea. In one example of aggression in the South China Sea, a Chinese Coast Guard vessel used a water cannon to redirect an unarmed Philippines Navy supply ship near the Second Thomas Shoal. Despite an international court saying both the shoal and surrounding waters belong to the Philippines, China claims it all owns the area. For more information, see: Carla Freeman et al, “China, Philippines Tensions Risk Wider Conflict that Could Draw in the U.S., United States Institute of Peace, 10 August 2023. https://www.usip.org/publications/2023/08/china-philippines-tensions-risk-wider-conflict-could-draw-us. See also Dodge Billingsley, “China And Philippines Spar Over Grounded Ship In Spratly Islands,” OE Watch, 08-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/china-and-philippines-spar-over-grounded-ship-in-spratly-islands/
Image Information:
Image: China’s maritime claim (red), compared to other countries. The Philippines has recently expressed interest in procuring submarines to protect itself against Chinese maritime aggression.
Source: Goran Tek-en, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:South_China_Sea_vector.svg
Attribution: CC BY-SA 4.0