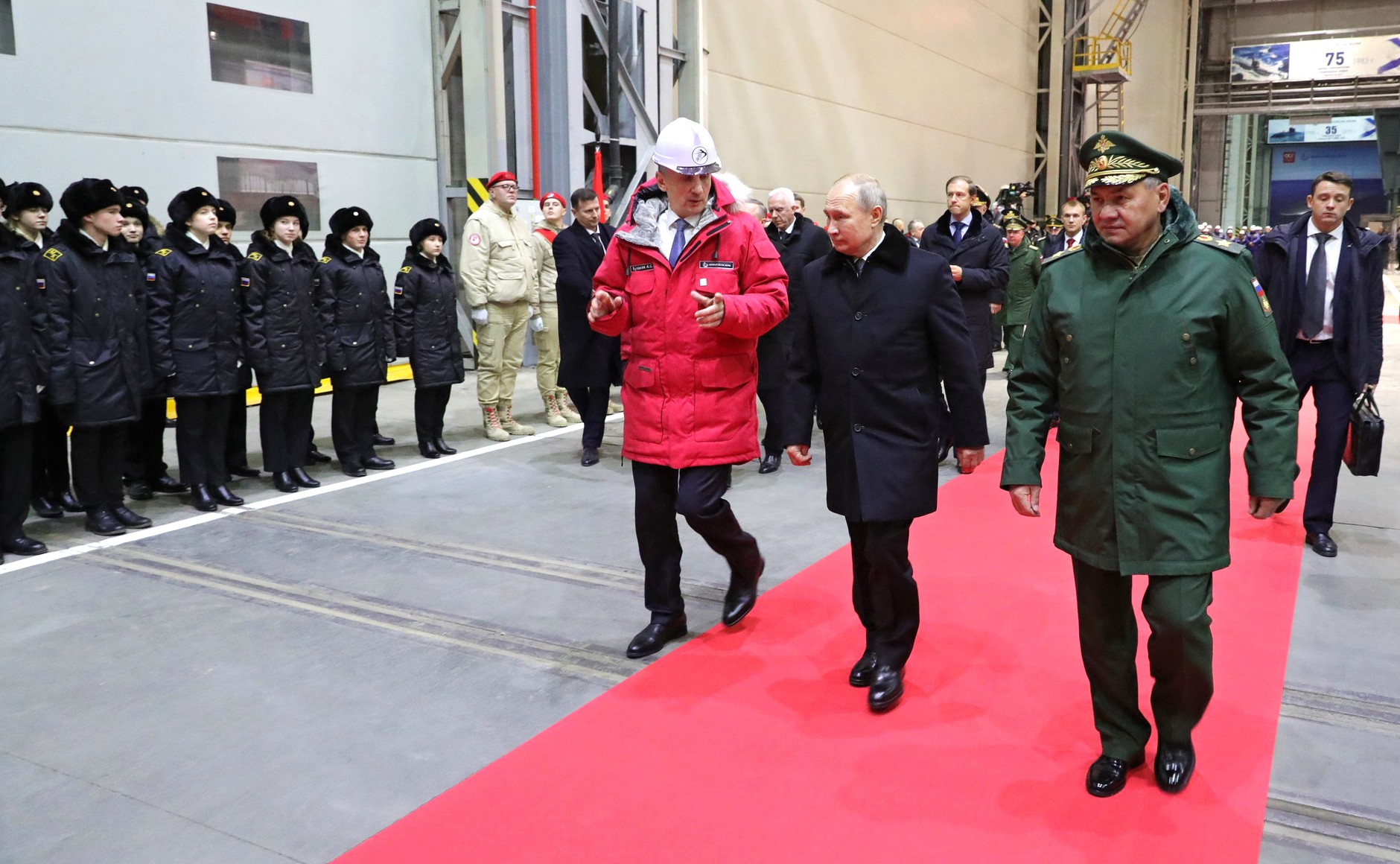
Russian President Vladimir Putin at Admiralty Shipyards to inspect the Petropavlovsk Kamchatsky submarine, the Ivan Papanin icebreaker patrol ship, and the Viktor Chernomyrdin icebreaker in 2019. Admiralty Shipyards in St. Petersburg is the sight of construction of the newly announced Ivan Frolov Arctic capable research vessel.
“Prime Minister of Russia Dmitry Patrushev underlined that the new vessel is aimed at strengthening Russia’s positions in the polar regions.”
In October, Russia announced the construction of its latest Arctic-capable research vessel, the Ivan Frolov. According to the first excerpted article from the Norway-based The Barents Observer, the Ivan Frolov, set for completion in 2028, will be the largest Arctic research vessel of its kind in the world and “the new flagship of Russia polar science.”[i] Russian Prime Minister Dmitry Patrushev noted the Ivan Frolov will collect data “for the development of navigation on the Northern Sea Route and to clarify the boundaries of the continental shelf of Russia.”
According to the second excerpted article from The Barents Observer, Russia’s research platform, the Severny Polyus, commissioned in 2022, recently began its second polar expedition.[ii] The expedition, “North Pole-42,” is expected to continue until 2026. This article also notes that while the Severny Polyus is a scientific research vessel,[iii] it could also serve Russian military purposes, as Russia’s new marine doctrine “includes a high stress on the use of civilian ships and infrastructure for military purposes.” This doctrinal emphasis not only affects the Severny Polus and the forthcoming Ivan Frolov but also all other nations with Arctic exposure.
Together, these developments underscore Russia’s continued focus on the Arctic region at a time when all nations with an Arctic foothold are also dedicating resources to the area.
Sources:
Elizaveta Vereykina, “Construction begins on a “new flagship of Russian polar research,”The Barents Observer (independent Norwegian news site in Russian and English currently blocked in Russia), 30 October 2024. https://www.thebarentsobserver.com/news/construction-begins-on-a-new-flagship-of-russian-polar-research/419705
On 29 October, the Russian Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute reported on an official ceremony held at the Admiralty shipyards in St Petersburg to start the construction of a new scientific vessel named the Ivan Frolov. The vessel – with a length of 165 meters and displacement about 25,000 tons – is planned to be able to accommodate up to 240 people. In addition to the announced 20 scientific laboratories on board, it will also have a helicopter platform.
“In 2028, the vessel will join the fleet of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute and become the new flagship of Russian polar science,” the news report says. At the ceremony, the Deputy Prime Minister of Russia Dmitry Patrushev underlined, that the new vessel is aimed at strengthening Russia’s positions in the polar regions:
“The vessel will have powerful scientific equipment that will allow conducting research even in the harshest conditions, including research on the ocean floor, in the atmosphere and space,” – “The study of the Arctic and Antarctic is one of the key areas of activity of the Russian Environmental Monitoring Service. More than 20 expeditions are already carried out annually. They allow tracking climate change, collecting data for the development of navigation of the Northern Sea Route and clarifying the boundaries of the continental shelf of Russia”.
The Governor of St Petersburg, Alexander Beglov, called the new ship “the largest scientific research vessel in the world”. The two well-known large scientific -the RV Kronprins Haakon (Norway) or RRS Sir David Attenborough (UK), are smaller than the new Russian vessel. The technology used in the construction has previously been tested at the floating Arctic research station “North Pole” [“Severny Polyus”], according to the head of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Alexander Makarov.
Atle Staalesen, “With the North Pole platform, Russia has returned to the Arctic for good,” The Baltic Observer,(independent Norwegian news site in Russian and English currently blocked in Russia), 17 September 2024. https://www.thebarentsobserver.com/arctic/with-the-north-pole-platform-russia-has-returned-to-the-arctic-for-good/142846
Russia’s North Pole (Severny Polyus) research platform has started its second comprehensive Arctic expedition. The 83-meter-long vessel this week set out from Murmansk with course for the high Arctic. It will sail into the polar sea-ice north of the New Siberian Islands and drift with the currents for the next two years. Experts at the Russian Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute are now scanning satellite images for the most suitable icefloe for the drift. The search will continue as the vessel approaches the area.
“With the expeditions of the ice-protected self-propelled platform Severny Polyus Russia has returned to the Arctic for good,” says Aleksandr Kozlov, the Russian Minister of Natural Resources. According to the minister, who is also known for his key role in Russia’s cooperation with North Korea, the researchers will gather materials of great importance for the protection of Arctic ecology, understanding of climate change, as well as safe sailing on the Northern Sea Route. The expedition is named “the North Pole-42” and is expected to continue until 2026.
The Severny Polyus has the shape of a bathtub and is often referred to as a platform. It has a ship crew of 16 and a research team of up to 34 people. Ship operator is Roshydromet, the Russian state meteorological service. The Severny Polyus is capable of geological, acoustic, geophysical and marine research under the harshest Arctic conditions. In temperatures down to minus 50°C it is reportedly able to provide comfortable living and working conditions for researchers and crew.
On board are 15 labs where researchers can work year-round. The research platform has replaced Russia’s Arctic expeditions based on ice floes organized since the 1930s. The quickly vanishing Arctic sea-ice has made it increasingly hard to organize the expeditions and last real ice station, the “North Pole-40”, was held in the winter of 2012. Albeit built for research purposes, the vessel could ultimately also be applied by the Russian military. The country’s new Marine Doctrine includes a high stress on use of civilian ships and infrastructure for military purposes. That could include not only trawlers and icebreakers, but also the Severniy Polus.
Notes:
[i] The Soviet Union and its successor state, Russia, have conducted a sustained Arctic maritime research effort since the 1930s and a sustained Antarctic research effort since 1955. The Arctic and Antarctic Scientific Research Institute (Арктический и антарктический научно-исследовательский институт) was founded in 1920 and still heads the country’s polar exploration with close to a thousand land and sea expeditions to its credit.
[ii] For additional reporting on the Severny Polyus, see: Les Grau, “Russian Drift Station Vital To Arctic Research Effort,” OE Watch, 07-2024. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2024/russian-drift-station-vital-to-arctic-research-effort/
[iii] For additional reporting on Russian research efforts in the Arctic, see: Les Grau, “China and Russia Expand Agreement For Arctic Strategic Resource Development,” OE Watch, 08-2024. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2024/china-and-russia-expand-agreement-for-arctic-strategic-resource-development/
Image Information:
Image: Russian President Vladimir Putin at Admiralty Shipyards to inspect the Petropavlovsk Kamchatsky submarine, the Ivan Papanin icebreaker patrol ship, and the Viktor Chernomyrdin icebreaker in 2019. Admiralty Shipyards in St. Petersburg is the sight of construction of the newly announced Ivan Frolov Arctic capable research vessel.
Source: Office of the Russian President, http://en.kremlin.ru/events/president/news/62143
Attribution: Public Domain