
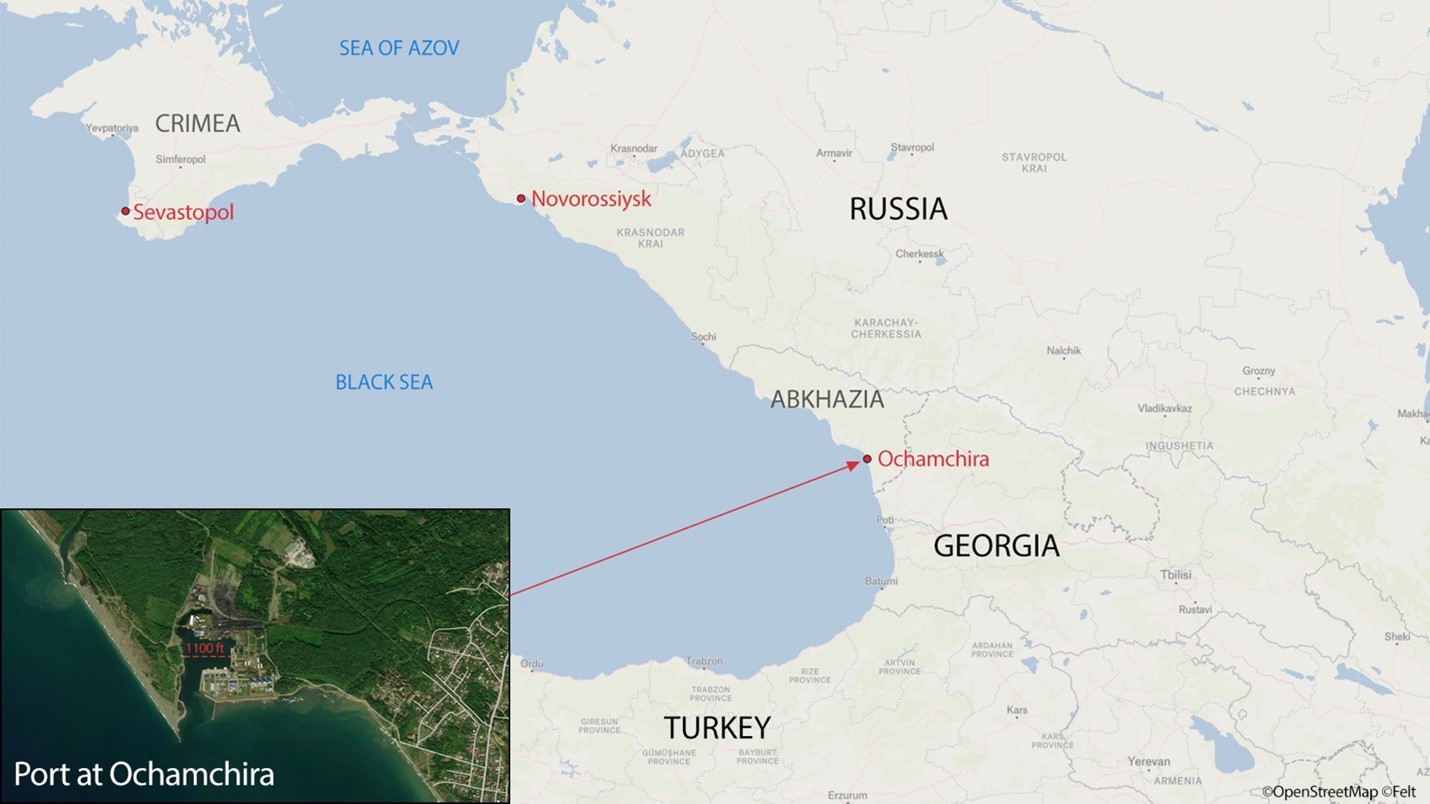
Chinese container ship off the coast of Los Angeles, California.
“China is the customer for 90% of the oil exported by Iran. The chances of the Houthis firing on ships of a state-owned Chinese company are therefore very low, raising questions about the reasons for COSCO’s decision”
The Israel-Hamas conflict and the conflict’s subsequent spread to Yemen and the Red Sea is challenging Chinese economic interests and policy in the region. In early January, Chinese shipping giant China Ocean Shipping Company (COSCO) and Hong Kong–based subsidiary Overseas Orient Container Line announced that they would cut service to Israeli ports in response to Houthi attacks on ships destined for Israel. According to the first excerpted articles from the Israeli business news publication Globes, China has in effect sacrificed trade with Israel to maintain shipping access to the Red Sea. While the article vilifies the Chinese position, China is in a bind because both Israel and Iran are significant regional trading partners with China. The Houthis are militarily and diplomatically supported by Iran. China must balance its priorities in the region between Iran and Israel—and any regional war would be bad for China’s Middle East interests.[i] In the second excerpt, taken from a speech delivered by China’s UN Ambassador less than a week after the COSCO announcement, the Ambassador noted that “the waters of the Red Sea are an important transportation channel for goods and energy” and called on the Houthis to “to immediately stop harassing merchant ships and respect the navigation rights of merchant ships from all countries in the Red Sea waters, in accordance with international law.”[ii] Not long after, a Houthi official interviewed by Russian news source Izvestia stated that all Russian and Chinese ships would be safe navigating the Red Sea but that ships aligned with Israel would be subject to targeting. The Houthi spokesman continued “Our goal is to raise the economic costs for the Jewish state to stop the carnage in Gaza.” However, despite these assurances, any economic pain that Israel might feel because of reduced shipping to its ports also transfers to China, complicating its economic strategy in the Middle East.
Sources:
“Chinese shipping giant COSCO to stop visiting Israeli ports,” Globes (Israeli business news), 7 January 2024. https://en.globes.co.il/en/article-chinese-shipping-giant-cosco-to-stop-visiting-israeli-ports-1001467115
Chinese state-owned shipping giant COSCO Shipping has stopped visiting Israeli ports, “Globes” has learned. The company, the fourth largest container shipping line in the world, with about 11% of world trade, decided on this step even though it is not much threatened in the Red Sea, because of the very fact that it is Chinese, and because of China’s ties with Iran, the patron of the Houthi rebels in Yemen.
Besides the effect on trade between the Far East and Israel, COSCO’s decision is significant because it cooperates with Israeli shipping line ZIM, which will have to operate more ships on the Far East routes, which is liable to will lead to higher shipping costs, since XIM will be short of ships.
The second direct effect will be on the Haifa Bayport, which is operated by another state-owned Chinese company, SIPG. The port is dependent on the many COSCO ships that visit it.
The Houthis are threatening to attack vessels of any company that sails to Israel, but China is the customer for 90% of the oil exported by Iran. The chances of the Houthis firing on ships of a state-owned Chinese company are therefore very low, raising questions about the reasons for COSCO’s decision, of which international shippers have yet to be notified.
A pointer to COSCO’s step was the recent announcement by its Hong Kong-based subsidiary OOCL that it was ceasing to sail to Israel because of “operational problems”. That announcement, intended to enable it to sail in the Red Sea without interference by the Houthis, led to wide criticism. In the end, the company caved in, like Singapore-based shipping line ONE (Ocean Network Express).
“常驻联合国代表张军大使在安理会红海局势紧急公开会上的发言 (Speech by Ambassador Zhang Jun, Permanent Representative to the United Nations, at the Security Council’s emergency public meeting on the Red Sea situation),” PRC Permanent Mission to the United Nations, published by Ministry of Foreign Affairs People’s Republic of China, 12 January 2024. https://www.mfa.gov.cn/web/zwbd_673032/wjzs/202401/t20240114_11223386.shtml
Mr. President: China thanks Russia for its initiative to hold this emergency meeting and thanks Assistant Secretary-General Kyali for his briefing. The United States, Britain and other countries have carried out air strikes on targets in Yemen, further escalating tensions in the Red Sea region. China expresses serious concern about this.
The waters of the Red Sea are an important transportation channel for goods and energy. For some time, the Houthi armed forces have repeatedly attacked and seized merchant ships in the Red Sea waters, disrupting international trade order and not conducive to regional stability. China has repeatedly called on the Houthis to immediately stop harassing merchant ships and respect the navigation rights of merchant ships from all countries in the Red Sea waters in accordance with international law. China also calls on all parties, especially influential major powers, to play a constructive and responsible role in jointly safeguarding the safety of waterways in the Red Sea.
We regret to see that the brazen military actions taken by relevant countries against Yemen not only caused infrastructure damage and civilian casualties, but also aggravated security risks in the Red Sea waters and did not help protect the safety of commercial ships and freedom of navigation. Relevant military actions may also impact the political process in Yemen. We fail to see how such a military operation could achieve the stated intended objectives.
It must be noted that the Security Council has never authorized any country to use of force against Yemen. The military actions taken by relevant countries run counter to the purpose of Resolution 2722 just adopted by the Security Council. China reiterates that no country shall misinterpret or abuse international law and Security Council resolutions to create new tensions in the Red Sea waters.
Mr. President: The current tensions in the Red Sea are one manifestation of the spillover effects of the conflict in Gaza. Letting the conflict in Gaza prolong while hoping that the conflict will not expand may be wishful thinking. It is even more contradictory and irresponsible to advocate preventing conflicts from spilling over, while at the same time adding fuel to the fire and provoking military confrontation. The Middle East is already on the brink of extreme danger. What we should avoid most at the moment is reckless military adventurism. What we need most is calmness and restraint to prevent further expansion of conflicts. We urge all relevant parties, especially the influential powers, to abide by the UN Charter and international law, adhere to the correct direction of dialogue and consultation, and make practical efforts to maintain peace and stability in the Red Sea and the Middle East. Thank you, Chairman.
В «Ансар Аллах» гарантировали безопасность судам РФ и КНР в Красном море (Ansar Allah guaranteed the safety of Russian and Chinese vessels in the Red Sea),” Izvestia (Russian news source), 19 January 2024. В «Ансар Аллах» гарантировали безопасность судам РФ и КНР в Красном море | Новости мира | Известия | 19.01.2024 (iz.ru)
Representative of the al-Buheiti movement: the Houthis will not attack Russian and Chinese ships
The Yemeni Houthi movement Ansar Allah is attacking US and British ships in the Red Sea; as for other countries, including Russia and China, their shipping in the region is guaranteed safety. A member of the Ansar Allah Politburo, Muhammad al-Buheiti, stated this on January 19 in an interview with Izvestia.
“As for all other countries, including Russia and China, their shipping in the region is not threatened. Moreover, we are ready to ensure the safety of the passage of their ships in the Red Sea, because free navigation plays a significant role for our country,” Al-Buheiti noted.
The politician also added that any Israeli ships or those connected with Israel will not have the slightest opportunity to sail through the Red Sea – attacks on them will continue.
“Ansar Allah does not pursue the goal of capturing or sinking this or that sea vessel. Our goal is to raise the economic costs for the Jewish state to stop the carnage in Gaza. If the crews of the ships that came under our fire had not ignored our warning signals and changed their direction, the further escalation that the American side caused in the interests of protecting Israel could have been avoided,” he said.
Earlier, on January 17, the military representative of the Ansar Allah movement, Yahya Saria, said that it launched a missile attack on the American ship Genco Picardy in the Gulf of Aden. According to him, the Houthis recorded a direct hit on the ship.
On the same day, the UK Navy’s Maritime Trade Coordination Center (UKMTO) reported that a drone attacked a ship off the coast of Aden, Yemen, which led to a fire on board the ship. A previous attack on a ship in the Red Sea was reported the day before. The Houthis then took responsibility for it and confirmed the fact of a missile attack on the bulk carrier Zografia, which was flying the Maltese flag.The Houthis began attacking shipping in the Red Sea and Gulf of Aden from November 2023 to protest Israeli actions in the Gaza Strip…
Notes:
[i] For a previous perspective on the conflict in Gaza’s impact on China interests in the region see: “Israel’s close economic ties with China worked well – until the Gaza conflict,” South China Morning Post, 2 November 2023. https://www.scmp.com/news/china/diplomacy/article/3240061/israels-close-economic-relationship-china-worked-well-until-gaza-conflict-revealed-its-limits
[ii] A wide range of global reporting has indicated that China is also said to have put pressure on Iran to rein in the Houthis, while the United States has asked China to take more of a role in mediating the conflict in Israel.
Image Information:
Image: Chinese container ship off the coast of Los Angeles, California.
Source: Corey Seeman
Attribution: CC By-NC-SA 2.0






![Kh-47M2 Kinzhal on a MiG-31K[RG1] Victory Day Parade 2018 Moscow.](https://hg2wordpressfmsostor01.z2.web.core.usgovcloudapi.net/OE Watch Issues/2023-06/Billingsley-01-Kh-47M2-Kinzhal-on-a-MiG-31K.jpeg)