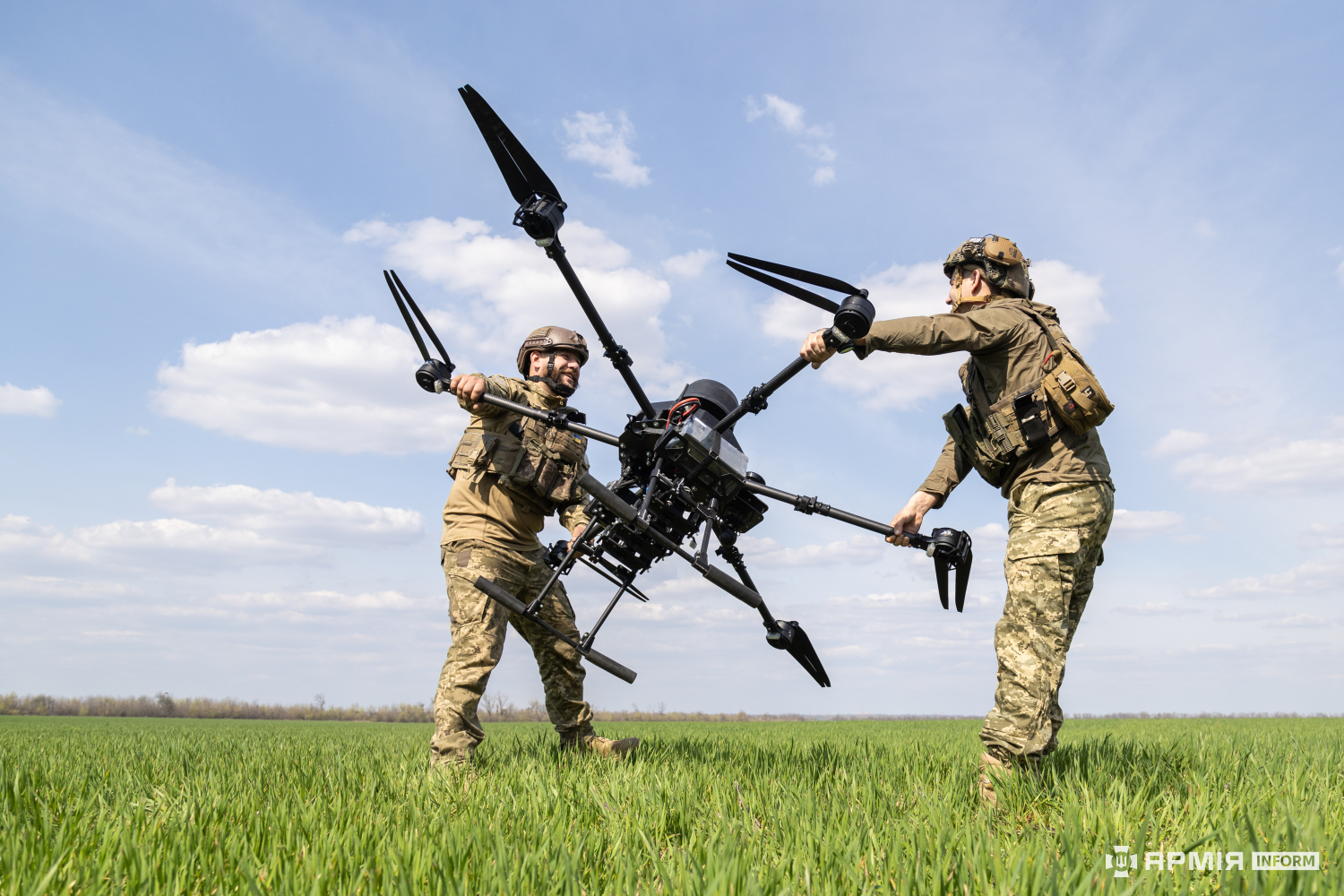

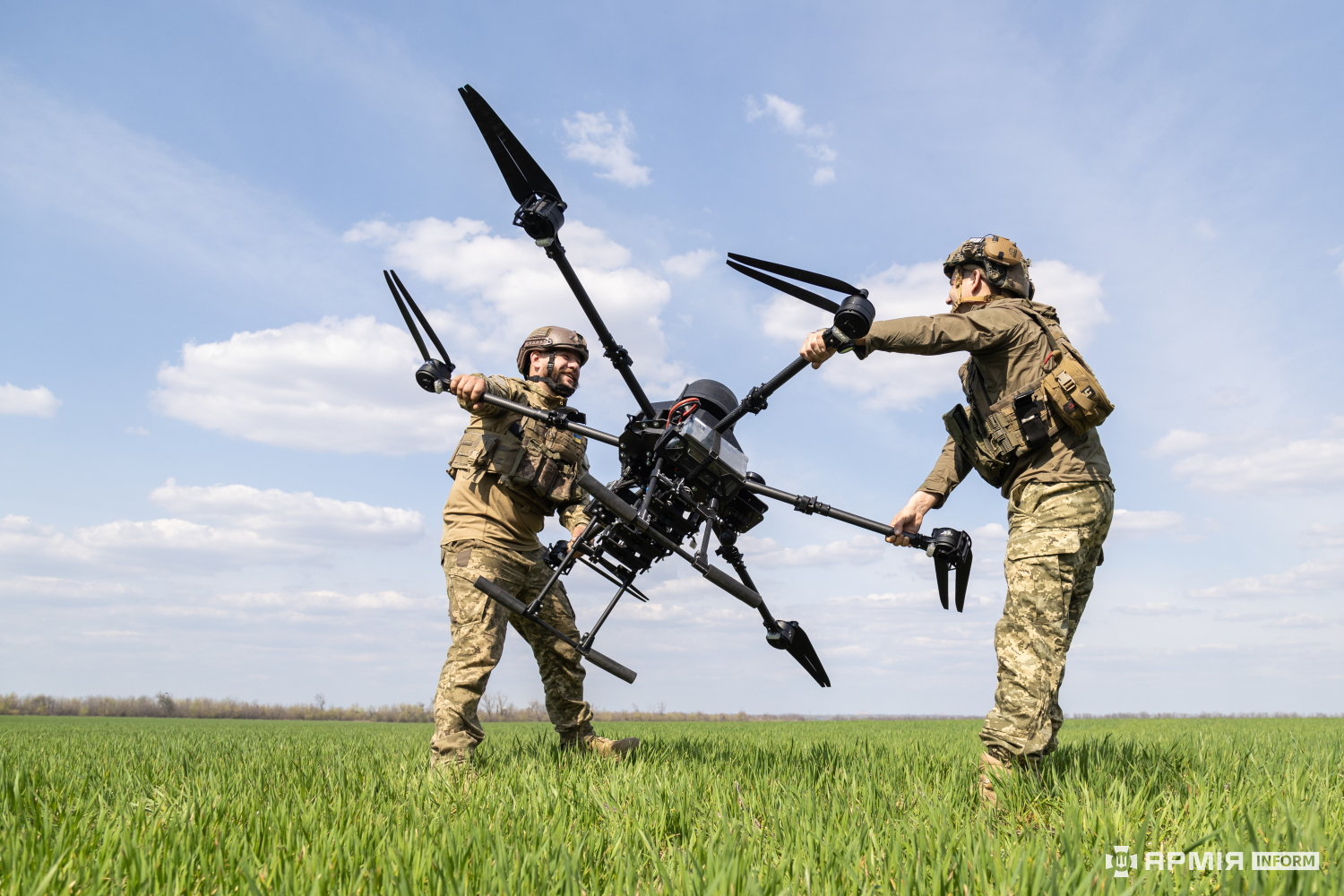
Orlan-30 Unmanned Aerial Vehicle.
“The Russian Armed Forces will form a new branch of arms in armed forces — Unmanned Vehicle Troops — in accordance with the order of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief.”
The accompanying excerpted article from the major Russian daily newspaper Izvestia discusses how Russians are adapting to the changing character of war as experienced in its special military operation in Ukraine.[i] One feature of this change has been the pervasive use of unmanned vehicles in the air, ground, and sea. As Izvestia explains, Russia will adapt to this change by creating a new branch of arms, Unmanned Vehicle Troops, to operate similar to existing branches of service: infantry, artillery, air defense, etc.[ii] Conceptually, unmanned vehicles and their operators and maintainers will be integrated into the Russian combined arms concept as the infantry, tanks, artillery, etc., just as the Russians have Air Defense Troops in the Ground Forces, Aerospace Forces, and Navy. The Unmanned Vehicle Troops will now be a branch of arms in a similar fashion. This means that unmanned vehicles will have dedicated training, sustainment, and representation in the General Staff. This representation will enhance unmanned vehicle training and doctrine, future capability development, and ensure integration with the other arms branches. This development suggests that in the Russian view, the use of unmanned vehicles is not an aberration but will be a permanent feature of future wars and armed conflicts. It is important to note that this announcement does not mean that unmanned vehicles and their operators and maintainers will be found only in stand-alone unmanned vehicle units; they will still almost certainly be found in other types of units, such as infantry, armor, artillery, logistics, signals, and the like.
Sources:
Yulia Leonova, Vladimir Matveev, Bogdan Stepovoy, “С новым родом: войска беспилотных систем создадут в России (A new branch: Unmanned Vehicle Troops will be created in Russia),” Izvestiya (major Russian daily newspaper), 17 December 2024. https://iz.ru/1808177/ulia-leonova-vladimir-matveev-bogdan-stepovoi/s-novym-rodom-voiska-bespilotnyh-sistem-sozdadut-v-rossii
The Russian Armed Forces will form a new branch of arms in armed forces — Unmanned Vehicle Troops — in accordance with the order of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief. This was announced by the head of the Russian Defense Ministry Andrei Belousov at an extended meeting of the board on December 16.
According to him, their creation will be completed in the third quarter of 2025. “The mass use of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has become the most significant breakthrough in the tactics of the Russian Armed Forces,” he emphasized.
In turn, Russian President Vladimir Putin stated the need to increase the production of drones. It is no less important, according to the head of state, to train UAV operators, to prepare them according to programs developed on the basis of combat experience.
Russian troops use more than 3,500 UAVs daily, and this figure is growing, Russian Defense Minister Andrei Belousov said at a departmental board meeting…
As the former commander of the Pacific Fleet, Sergei Avakyants, explained to Izvestia, a branch of arms is an organizational structure, as it is necessary to create a theoretical design of operational art for it. That is, to create a theory and practice of preparing and conducting military actions on an operational scale (operations, battles, strikes), — he noted. — This is a move in the right direction, the main thing is that it is not just a sign on an office door. It is necessary to think through a system of training both sergeants and enlisted personnel, and officers. To do this, it is necessary to make changes to the curricula — to create special faculties or educational institutions of secondary and higher education. The innovations should also affect existing military academies, in particular the General Staff Academy.
During the special military operation, UAVs became so indispensable that we reached the point of needing to form separate units [части] and, perhaps, even large units [соединения] with their own infrastructure that would support the use of UAVs. Military expert Dmitry Kornev told Izvestia about this.
According to him, most likely, units, platoons, and separate battalions will be created that will closely interact with other branches of the military and ensure the use of UAVs in their interests.
— The Unmanned Vehicle Troops will most likely receive a status similar to that of the Air Defense Troops — military expert Vladislav Shurygin told Izvestia. — Their units will be part of the Ground Forces, the Aerospace Forces, and also in the Navy, where, among other things, unmanned boats will be developed. All used unmanned systems will belong to them. It is possible that they will be united by some common structure that will be engaged in design, development, and testing. It was not for nothing that the minister said that inter-service centers will be created to test the latest and most promising systems…
Notes:
[i] Moscow uses the term spetsial’naya voyennaya operatsiya (“special military operation”) or spetsoperatsiya (“special operation”) to describe its campaign in Ukraine.
[ii] This new force, род войск, is not to be confused with a branch of service; вид вооружённых сил (Army, Navy, Air Force, etc.).
Image Information:
Image: Orlan-30 Unmanned Aerial Vehicle
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baba_Yaga_(aircraft)#/media/File:UA_Vampire_UCAV_01.jpg
Attribution: Mike1979 RussiaCC BY-SA 4.0






.png)
