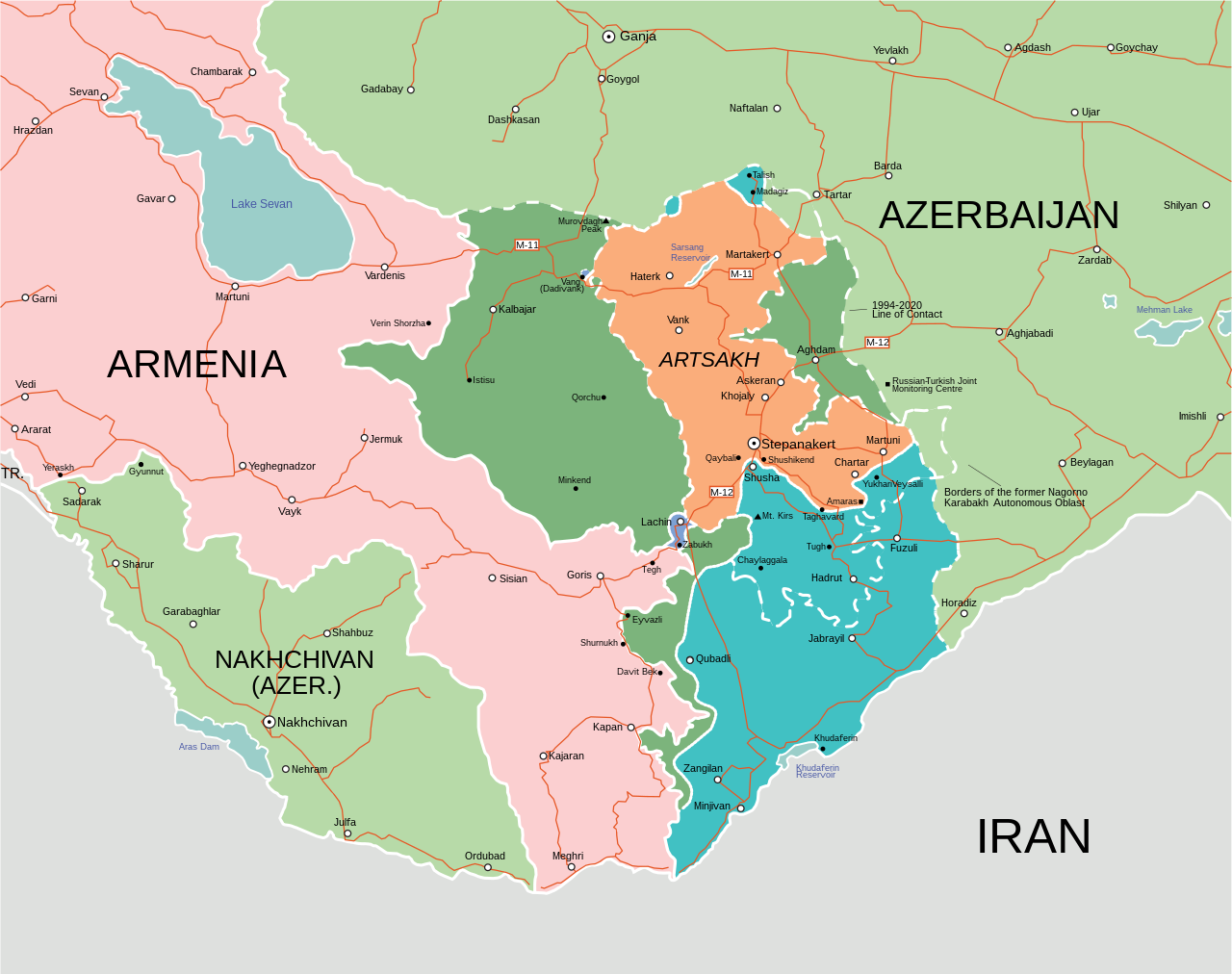
Map of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war.
“Let us note that a few days ago, the press secretary of the Russian President Dmitry Peskov confirmed the withdrawal of the Russian peacekeeping contingent from Karabakh.”
In April 2024, the government of Azerbaijan announced that the Russian peacekeeping mission had started withdrawing personnel, marking one of only a few instances a Russian peacekeeping mission in the Commonwealth of Independent States has ended.[i] The excerpted article from Azerbaijan’s news agency Trend reports that the Russian peacekeeping force from Nagorno-Karabakh has relocated to temporary deployment points in Armenia.[ii] Armenia’s Secretary of the Security Council noted that these units cannot remain in Armenia. Lastly, the article notes that Azerbaijan requested the removal of the Russian peacekeeping force and the Russian government complied but does not mention where Russian personnel will eventually be redeployed.
Additionally, a joint Russia-Turkey observation center in Azerbaijan that once monitored the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict has also closed. The excerpted article from Turkey’s state-run Anadolu Agency notes that the joint observation center had been based in Azerbaijan since early 2021 as part of an agreement between Russia and Turkey to observe the ceasefire agreement. The article notes that the work of the center is no longer needed since Azerbaijan took full control of Nagorno-Karabakh in September 2023.[iii] As a result, Russian and Turkish personnel, 60 from each country, are leaving. Overall, the total number of Russian personnel redeploying from the peacekeeping mission and the joint monitoring center is not significant but is worth noting as Russia has historically reached agreements to leave some units in place even after a peacekeeping mission has changed or ended. Russia will likely continue to be involved in developments between Armenia and Azerbaijan going forward, but Azerbaijan’s complete takeover of Nagorno-Karabakh frees up Russian forces to use elsewhere, potentially in Ukraine.[iv]
Sources:
Source: Rena Abdurakhmona, “Российские миротворцы направились из Карабаха в Армению (Russian peacekeepers have deployed from Karabakh to Armenia),” Trend (news agency in Azerbaijan), 23 April 2024. https://www.trend.az/azerbaijan/politics/3889409.html
Russian peacekeepers from Karabakh went to temporary deployment points in Gorus and Garakils (Sisian)…(the) Secretary of the Security Council of Armenia Armen Grigoryan told the Armenian media…
“Since Russian peacekeeping troops are leaving Karabakh, they, of course, cannot remain in the Republic of Armenia either. A group and convoy of peacekeepers from Karabakh headed to temporary deployment points in Goris and Garakils (Sisian),” he said.
Let us note that a few days ago, the press secretary of the Russian President Dmitry Peskov confirmed the withdrawal of the Russian peacekeeping contingent from Karabakh.
Assistant to the President of Azerbaijan – Head of the Department for Foreign Policy of the Presidential Administration Hikmet Hajiyev, answering a question from AZERTAG regarding information about the withdrawal of Russian peacekeepers from the territory of Azerbaijan, said that the top leadership of both countries made a decision on the early withdrawal of peacekeepers…
Source: Ruslan Rehimov, “Turkish-Russian joint center completes mission in Azerbaijan,” Anadolu Agency (state-run news agency of Turkey), 26 April 2024.https://www.aa.com.tr/en/asia-pacific/turkish-russian-joint-center-completes-mission-in-azerbaijan/3203012
The Turkish-Russian joint observation center established in Azerbaijan’s Aghdam region has completed its mission after three years of service.
The center was established to monitor cease-fire and prevent violations after the Second Karabakh War, when Azerbaijan liberated most of the Karabakh region from decades of occupation by Armenia.
Karim Valiyev, Azerbaijan’s chief of general staff, praised the center’s contributions to peace at a ceremony on Friday attended by Azerbaijani, Russian, and Turkish officials.
Valiyev said Azerbaijan has fully established its sovereignty in Karabakh, and therefore the mission of the monitoring center had been completed…The center, established near the Marzili village of Aghdam, opened on Jan. 30, 2021, with 60 Turkish and 60 Russian soldiers…Azerbaijan established full sovereignty in Karabakh after an “anti-terrorism operation” in September 2023, after which separatist forces in the region surrendered.
Notes:
[i] The Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) is made up of former Soviet Republics and remains an area where the Russian government has special relationships and works to maintain influence. Russian peacekeeping missions in the CIS in the past have typically been open-ended with Russian forces remaining in place in some capacity, which has allowed Russia to maintain influence. The Russian-led Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) peacekeeping mission to Kazakhstan in January 2022 marks the other example of Russian forces ending a peacekeeping mission in the CIS and withdrawing its forces. For background on Russian peacekeeping missions in the CIS, see: Matthew Stein, “The Evolutionary Russian View of Peacekeeping as Part of Modern Warfare,” FMSO’s Foreign Perspectives Brief, 24 March 2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/2023-03-24-the-evolutionary-russian-view-of-peacekeeping-as-part-of-modern-warfare-matthew-stein-update/
[ii] The Russian peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh deployed in November 2020 as part of the Russian-brokered ceasefire agreement between Armenia and Azerbaijan that ended the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War. The peacekeeping force included around 2,000 Russian personnel, who established two dozen observation posts in Nagorno-Karabakh to monitor the ceasefire under a five-year mandate that would automatically renew for an additional five years unless Armenia or Azerbaijan gave notice to the other two parties to the agreement to terminate the mission.
[iii] In September 2023, Azerbaijani forces carried out an operation in Nagorno-Karabakh which resulted in Azerbaijan regaining full control of the region from ethnic Armenians and ended the existence of the self-proclaimed breakaway region of Artsakh. The Russian peacekeeping mission in Nagorno-Karabakh closed a few observation posts following the September 2023 operation,but remained largely in place with the consent and cooperation of Azerbaijani authorities.
[iv] Russian peacekeepers dealt with several ceasefire violations from both sides in the years since then and notably allowed activists from Azerbaijan to blockade the Lachin Corridor, the single road connecting Nagorno-Karabakh with Armenia, starting in December 2022 until September 2023. For background on the blockade of the Lachin Corridor, see: Matthew Stein, “Ongoing Clashes In Nagorno-Karabakh Threaten Fragile Truce,” OE Watch, 05-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/ongoing-clashes-in-nagorno-karabakh-threaten-fragile-truce/
Image Information:
Image: Map of the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war.
Source:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:2020_Nagorno-Karabakh_war.svg
Attribution: CCA 3.0
