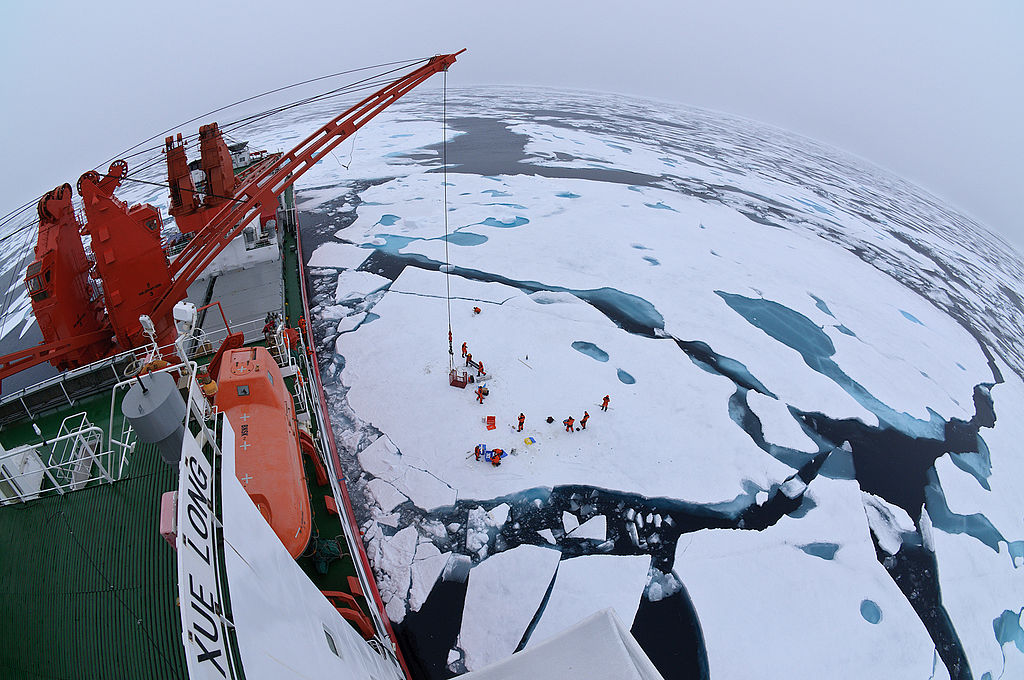
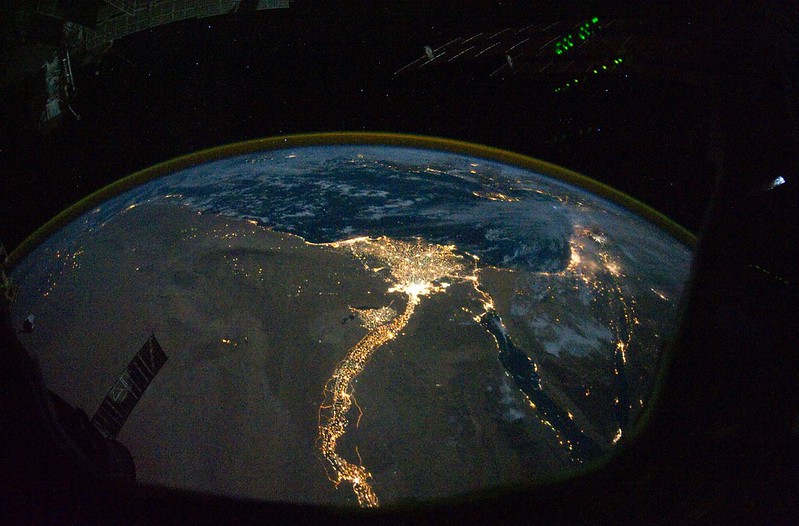
Drift ice camp in the middle of the Arctic Ocean as seen from the deck of icebreaker Xue Long.
“The Xuelong 2 is like a mobile laboratory at sea, sailing into many areas that were inaccessible in the past.”
China regards deep-sea[i] areas and polar regions as critical to its future development due to their abundant resources. President Xi Jinping even included them in his Holistic National Security Concept, which lays out domains that he regards as critical to China’s development and national security.[ii] However, both deep-sea exploration and polar regions pose significant technical challenges due to the extreme pressure or weather conditions encountered. As the following excerpts explain, China has made significant progress in overcoming these challenges.
The first excerpted article, from an early March 2023 edition of the official newspaper of China’s Ministry of Science & Technology, examines some of the equipment China has completed or is developing to explore deep sea and polar regions as part of its efforts to become a powerful maritime country. The article focuses on two technologies: icebreakers and deep-sea drilling rigs. The Xue Long 1 [GRLCUT(1] and Xue Long 2 [GRLCUT(2] icebreakers, originally based on a Ukrainian design, have improved China’s ability to explore polar regions. The article cites an acoustic engineer with experience studying polar environments, who highlighted how the Xuelong 2 had opened many previously inaccessible areas to exploration.
The latter half of the article focuses on deep sea drilling, noting the advances made with the “Manatee II” deep sea drilling rig, which is reportedly capable of operating at depths of 2,000 m or more and has set world records by drilling over 200 m into the ocean floor. A major priority for exploitation by this and future rigs is “combustible ice,” a mixture of frozen water and natural gas present on the sea floor in the deep sea. According to the article, the Manatee II has carried out exploration missions searching for combustible ice in many areas surrounding China, as well as for traditional offshore oil and gas deposits. Due to the experience from operating the Manatee, China has improved its technologies in this niche but important area, and the first of China’s next generation of deep-sea drilling ships is expected to be completed in 2024.[iii] It will reportedly be capable of drilling in waters deeper than 10,000 m.[iv] The minerals and natural gas potentially recoverable by these drills could create an economic bonanza and help China offset its reliance on imported energy. The second article is based on an interview with Sun Bo, Party Secretary of the China Polar Research Center Polar Research Institute of China, which is part of China’s Ministry of Natural Resources. Sun Bo noted how vital China’s second icebreaker, the Xuelong 2, completed in 2019,[v] has been for China’s polar exploration efforts, highlighting that having two icebreakers now allows China to effectively support research teams at both poles at the same time. While these articles underscore how China has clearly made important strides in overcoming technical bottlenecks, it might now face legal ones. The UN recently concluded negotiations about exploiting biological and mineral resources on the high seas, which might constrain China’s activities in polar and deep-sea regions.[vi]
Sources:
He Liang [何亮], “科技扬帆,引领海洋探索挺进深蓝” (Science and Technology Set Sail, Setting a Course for Ocean Exploration into the Deepest Blue Sea), Science & Technology Daily [科技日报] (Official newspaper of PRC Ministry of Science & Technology [MOST]), 6 March 2023. http://digitalpaper.stdaily.com/http_
www.kjrb.com/kjrb/html/2023-03/06/content_550015.htm?div=0
Accelerating [China’s] development into a maritime great power and making good use of marine resources is not possible the important support of science and technology. To protect the marine ecological environment, it is necessary to strengthen basic research and fully understand the ocean’s riches; to develop marine resources, it is necessary to address the urgent requirements of improving development of technologies and equipment of scientific research for technology and equipment, and concentrate efforts to develop more “national strategic weapons.”[i]
“With the help of more and more advanced equipment, China’s polar scientific research has maritime, land and aerial capabilities.” Yin Jingwei [殷敬伟], vice president of Harbin Engineering University[ii], has long been engaged in research on polar acoustic technology….According to Yin [Xuelong 2’s] superior ice-breaking capabilities allow more scientific research facilities and supplies to be transported into the Antarctic regions. “It is like a mobile laboratory at sea, sailing into many areas that were inaccessible in the past.”
As of September 28, 2021, China has completed 12 Arctic expeditions. However, China is not an Arctic nation, and its deep-sea and polar-related research work started relatively late compared to other countries, and its support capabilities have also been limited to a certain extent. There are still many weak links and capabilities in the fields of polar science and technology research, polar equipment development, and deep-sea polar exploration. missing.
Yin Jingwei told the Science and Technology Daily reporter of that China does not yet have nuclear-powered icebreakers and underwater equipment capable of breaking ice in the polar regions, and the ability to collect maritime below the ice is also very weak. Additional efforts are needed to overcome technological and environmental hurdles to move forward.
“深耕新疆域,推动极地科考再上新台阶——海洋领域专家谈建设海洋强国” (Exploring New Frontiers and Taking Polar Scientific Research to a New Level—Maritime Experts Discuss Building a Maritime Great Power), Science & Technology Daily [科技日报] (Official newspaper of PRC Ministry of Science & Technology [MOST]), 19 January 2023 http://digitalpaper.stdaily.com/http_
www.kjrb.com/kjrb/html/2023-01/19/content_547740.htm?div=0In today’s world polar regions have become a “new frontier” for development and a focal point for global governance, a new high ground for technological competition, an area with new sea routes and a new source of resources. The China Polar Research Center of the Ministry of Natural Resources adheres to the principle of “understanding, protecting, and using” these regions proposed by General Secretary Xi Jinping, and is committed to providing support for China’s polar scientific research. China continues to improve its independent innovation capabilities and overall there is momentum to continue improvements. The China Polar Research Center independently built the “Xuelong 2” icebreaker with, filling a major gap in China’s capabilities required for polar scientific research and developed a way to use both the Xuelong and Xuelong two effectively in concert. This new pattern of “Double Xuelong” Polar exploration (one assigned to each polar region) has greatly improved the on-site support capabilities for China’s polar scientific investigations.
Notes:
[i] Deep-sea areas are typically defined as those below 200 meters. According to the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, 80 percent of the Earth’s ocean floor remains unmapped and unexplored. “How much of the ocean have we explored?,” NOAA [Accessed March 2023]. https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/exploration.html
[ii] See: Peter Wood, “China’s Holistic Security Concept Explained,” OE Watch, 07-2018. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-singular-format/275650
[iii] The ship was developed by China State Shipbuilding Corporation’s (CSSC) 708 Research Institute and is subordinate to the China Geological Survey Bureau. The bureau also operates ships involved in mapping the seafloor in potential sensitive areas, which has drawn the alarm of nearby nations. See for example, Naoki Inoue, Tsukasa Hadano and Jun Endo, “Chinese survey ships straying into other nation’s EEZs, data shows”, Nikkei, 31 January 2021. https://asia.nikkei.com/Politics/International-relations/South-China-Sea/Chinese-survey-ships-straying-into-other-nations-EEZs-data-shows
[iv] “China’s first ultra-deepwater scientific research drilling ship achieved main hull penetration today” [我国首艘超深水科考钻探船今日实现主船体贯通], China Mining News [中国矿业报 ], 18 December 2022. https://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/ddyw/202212/t20221218_720062.html
[v] See: Les Grau, “China Developing More High Latitude Equipment”, OE Watch, 11-2019. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/337636
[vi] “UN delegates reach historic agreement on protecting marine biodiversity in international waters,” United Nations, 5 March 2023. https://news.un.org/en/story/2023/03/1134157
Notes:
[i] This phrase, 国之重器, is frequently used to describe strategically impactful or game-changing weapons systems (ballistic missile submarines, aircraft carriers etc.,) and civilian technologies such as nuclear reactors.
[ii] Harbin Engineering University is one of the “Seven Sons of National Defense,” which are universities that work closely with the Chinese People’s Liberation Army.
Image Information:
Image: Drift ice camp in the middle of the Arctic Ocean as seen from the deck of icebreaker Xue Long.
Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/8d/Teadlased_j%C3%A4%C3%A4l.jpg
Attribution: Timo Palo, CC BY-SA 3.0