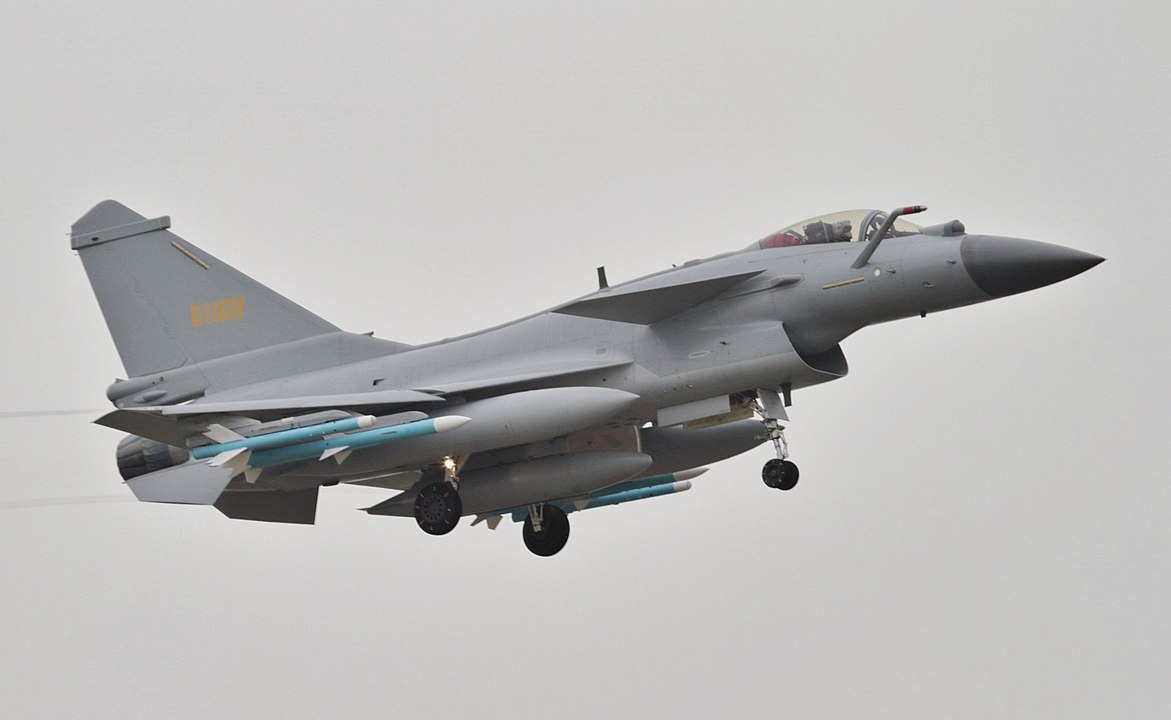
A J-10B carrying PL-10 and PL-12 air-to-air missiles landing at Zhuhai Jinwan airport ahead of Airshow China 2018.
“For the first time, Pakistan Air Force will introduce J10 C fighter jets during the fly past in collaboration with China and these fighter airplanes are an answer to Rafale jets…”
In late 2015 Pakistan announced it would conduct trials to find a new infantry rifle as the country’s army sought to phase out the Heckler & Koch G3. After a few years of testing, the government did not select a rifle from bids of several well-known companies and instead looked to the Pakistan Ordnance Factories (POF) for a potential replacement (See: “A New Domestically Produced Service Rifle in Pakistan?” OE Watch, December 2019). While Pakistan’s Army has yet to acquire a new service rifle, the accompanying excerpted articles report on a possible replacement for the G3 and other defense acquisition priorities.
The article from Pakistani defense focused news website Quwa.org reports on the POF’s introduction of the BW20 and BW21. The article notes that the POF is “pitching the BW20” as the next-generation rifle and that the cost of it could be lower due to “existing production infrastructure” for the G3. It also notes that BW20 “has some commonality with the G3,” though it is considered a new rifle and not an upgrade. The article also mentions that Pakistan’s Army “did not select any of the 7.62×51 mm designs for local adoption” and that one reason for not selecting a new rifle was that “the added improvement they offered may not have justified the total cost of adopting and locally manufacturing a foreign design.” While the cost of the BW20 and BW21 might be lower than purchasing a foreign rifle, it could still be some time until it is in a position to become the standard service rifle in Pakistan’s Army.
The article from independent Pakistani English-language newspaper Dawn reports on the country’s recent acquisition of J-10 multirole fighters from China. The article mentions the new fighters, but only in reference to them appearing as part of a fly over during Pakistan Day ceremonies on 23 March 2021. Pakistan did not make a widely publicized announcement of the acquisition of a reported two dozen J-10s, which are estimated to cost $28 million each. Dawn quoted the country’s Interior Minister as saying that the J-10s are an answer to India’s 2021 purchase of Rafale jets from France.
Source:
“Pakistan Reveals New Rifles – POF BW20 and POF BW21,” Quwa.org (news website focusing on defense issues in Pakistan), 19 December 2021. https://quwa.org/2021/12/19/pakistan-reveals-new-rifles-pof-bw20-and-pof-bw21-2/
Pakistan Ordnance Factories (POF) took the shrouds off its new in-house, original rifle projects – the BW20 and BW21. The POF BW20 and BW21 are chambered for 7.62×51 mm rounds.
…It seems that POF is pitching the BW20 for the PA’s next-generation rifle requirements…the BW20 is a new rifle design that delivers cost savings by re-leveraging POF’s existing production infrastructure, which is geared for the HK G3.
Though the BW20 has some commonality with the G3 (around 30%), the BW20 is not an upgrade of the HK G3. It is a new rifle…
In 2015, the Pakistan Army issued a tender for a new-generation assault rifle. It had tested many designs from all over the world, including the FN SCAR, Beretta ARX-200, CZ BREN, AK-103 and others. In the end, however, the Army did not select any of the 7.62×51 mm designs for local adoption…
Ultimately, it seems that POF was given the greenlight to design an original rifle. Part of the reason seems to stem from a sense that none of the foreign designs substantially improved upon the G3 in terms of its accuracy and durability. This is not to say the other rifles were not good, but the added improvement they offered may not have justified the total cost of adopting and locally manufacturing a foreign design…
Source: Aamir Yasin, “Every party seeks patronage of establishment, says minister,” Dawn (independent English-language newspaper from Pakistan), 30 December 2021.
https://www.dawn.com/news/1666604
Interior Minister Sheikh Rashid Ahmed on Wednesday said every party and politician wanted to be patronised by the establishment, terming the debate on the return of Pakistan Muslim League-Nawaz (PML-N) supremo Nawaz Sharif useless…
“It does not matter whether he comes or not; it will not make any difference to the government,” he said, adding it was strange that people who spent most of their lives in this country eventually left it instead of loving it…The minister reiterated his offer of a one-way ticket to Pakistan for Nawaz Sharif.
Talking about the Pakistan Democratic Movement (PDM), an alliance of opposition parties, the minister said he wanted the alliance to move the date of its protest from March 23 to the 30th as it coincided with Pakistan Day celebrations.
“For the first time, Pakistan Air Force will introduce J10 C fighter jets during the fly past in collaboration with China and these fighter airplanes are an answer to Rafale jets,” Mr Ahmed said…
Image Information:
Image: A J-10B carrying PL-10 and PL-12 air-to-air missiles landing at Zhuhai Jinwan airport ahead of Airshow China 2018.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chengdu_J-10#/media/File:J-10B_with_PL-10_and_PL-12.jpg
Attribution: CC BY-SA 4.0