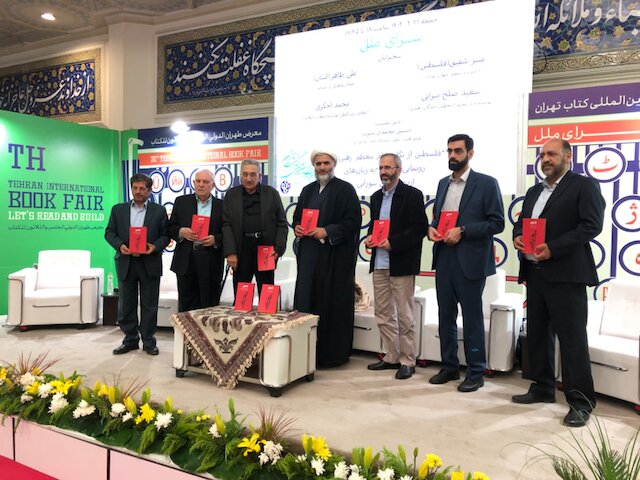
International Department of the Islamic Revolution Cultural & Research Institute unveils translations of Ali Khamenei’s book Palestine at the Tehran International Book Fair, May 10, 2024.
“Freedom fighters around the world will become familiar with the contents of this book.”
While Tehran propagating anti-Israeli vitriol is neither new nor remarkable, its choice about where to direct that propaganda does signal those people that the Iranian regime seeks to cultivate as allies. As reported by Dolat.ir, a government information center, the high-profile annual Tehran International Book Fair recently featured an updated collection of Khamenei’s writings and speeches about Israel and the Palestinians, dating to 1979.[i] Iranian press attention on translations of Khamenei’s writing on the Palestinians into both Urdu and Kurdish suggests renewed efforts by Khamenei to influence both Pakistani and Kurdish audiences. Over the past two decades, the Islamic Revolution Guard Corps (IRGC) has expanded its so-called “Axis of Resistance” to include not only Hezbollah and Bashar al-Assad’s Syrian regime, but also Iraqi militias and Houthi tribesmen in Yemen. In the early 1980s, the IRGC tried and failed to create a Hezbollah-like movement among Pakistani Shi’ites akin to its organization of Lebanese Shi’ites.
The effort to proselytize and disseminate Khamenei’s views to a Pakistani audience may suggest a renewed effort to cultivate the general Pakistani population. Such outreach would not limit itself to Pakistani Shi’ites but would seek to use Khamenei’s anti-Israel credentials to bolster Iran’s broader foreign policy leadership.[ii] The Iranian emphasis on cultivating Kurds suggests an effort to expand the Iranian regime’s influence among a population that has both been resistant to Khamenei’s worldview and has also cooperated closely with the U.S. military. While Iran maintains an open presence in Iraqi Kurdistan, the United States maintains a more overt presence. Both Iraqi Kurdistan and the Kurdish-dominated Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria impede the IRGC’s “land bridge” between Iran and the Eastern Mediterranean. Flipping the Kurds may not be imminent in the short-term, but Iran tends to play the long game.
Sources:
“کتاب «فلسطین؛ از منظر حضرت آیتالله سید علی خامنهای» خشم نخست وزیر اسراییل را موجب شد” (The book Palestine: from the perspective of Ayatollah Seyyed Ali Khamenei, angered the Prime Minister of Israel.),” Dolat.ir (Government Information Center of the Islamic Republic of Iran), 11 May 2024. https://dolat.ir/detail/448480
The book Palestine is a compilation of descriptions, analyses, and proposed solutions by the Leader of the Islamic Revolution on the issue of Palestine. Given the significance and influential position of Imam Khamenei’s perspective on the Palestinian matter, and the unique current circumstances, this book has been translated and made available in various languages such as Arabic, English, Russian, Turkish, and other languages….
Hujjat al-Islam Saeed Solh-Mirzaei, a member of the Assembly of Experts said, “Due to the importance of Palestine for Urdu and Kurdish speakers, this book has been translated into these two languages, and it is hoped that all Muslims and freedom fighters around the world will become familiar with the contents of this book and fulfill their duties towards Palestine. God willing, they will soon pray together in gratitude in the noble Al-Qods.”
Notes:
[i] Filistin az manzar-i Ayatullah Khamini’i (Palestine from the Perspective of His Holiness Ayatollah Khamenei), Tehran: Islamic Revolution Publication, 2011.
[ii] For discussion of Iranian efforts to create Afghan and Pakistani militias, see: Michael Rubin, “Iran Praises Revolutionary Guards’ Proxy Afghan Brigade,” OE Watch, 03-2023 https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/iran-praises-revolutionary-guards-proxy-afghan-brigade/; and Michael Rubin, “Cleric Speaks on Iran’s Foreign Militias,” OE Watch, February 2019. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-past-issues/266059/download
Image Information:
Image: International Department of the Islamic Revolution Cultural & Research Institute unveils translations of Ali Khamenei’s book Palestine at the Tehran International Book Fair, May 10, 2024.
Source: https://cdn-english.khamenei.ir/d/2024/05/11/3/40662.jpg
Attribution: Khamenei.ir