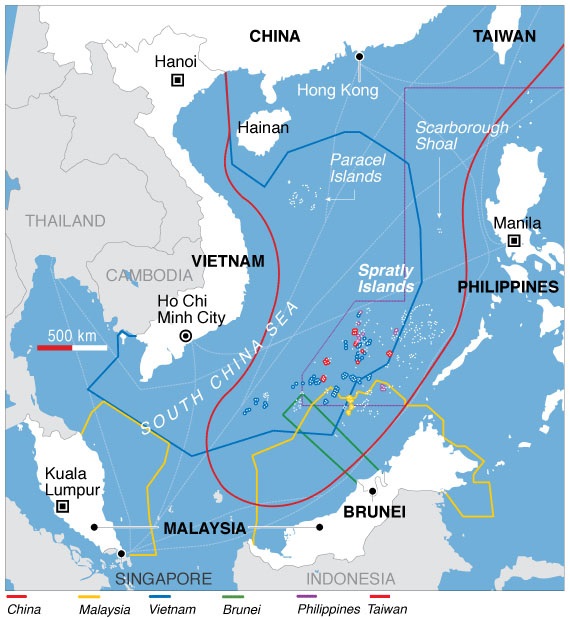
China claims a maximal amount of maritime territory in the South China Sea, which leads to disputes with all of its neighbors over reefs, shoals, islands, and other features.
“The People’s Liberation Army claims that compared with face-to-face conflict, this aerial sand-blowing tactic will not cause fatal harm to [Philippine] personnel and can prevent them from ‘causing chaos’.”
China often asserts its maritime territorial claims in the South China Sea by employing non-lethal tactics that are sufficient to prevent an adversary’s ships from approaching or landing on disputed features. Referred to as “salami slicing,” these tactics avoid provoking direct confrontation with naval adversaries, such as the Philippines, and their stronger allies, such as the United States, while allowing China to dictate when clashes occur and to incrementally control disputed shoals and reefs.[i] On 26 March, the Chinese-language website wenxucity.com published the excerpted article detailing specific tactics the Chinese Coast Guard (CCG) employs against Philippine vessels and personnel near the Tiexian Reef in the South China Sea. The Philippines occupy the Tiexian Reef, which lies in shallow water preventing larger ships from approaching, by dispatching smaller vessels to it from nearby Thitu Islands. Only several dozen Philippine personnel can land on the reef at any one time. The CCG have utilized the non-lethal tactic of flying a helicopter at low altitude over the reef to blow enormous amounts of sand and rock into Philippine vessels and personnel. The article claims that the deafening noise from the helicopter’s three turboshaft engines can cause dizziness and affect the internal organs of Philippine soldiers or researchers. As a result, the Philippines has been unable to station forces on the reef to enforce Philippine sovereignty. The article concludes that these methods are sufficient to evict Philippine personnel from disputed areas without causing fatalities, reducing the risk of escalation or retaliation from the Philippines or its allies, while allowing China to still assert its territorial claims.
OE Insight Summary:
CHN deploys helicopters to blow sand and rock and make deafening noises to prevent PHL personnel from stationing on disputed the Tiexian Reef as part of a broader CHN strategy to enforces its maritime territorial claims in SCS.
Sources:
“菲律宾再登铁线礁 中国用直升机掀“飞沙走石”驱离 (The Philippines once again lands on Tiexian Reef, but China uses helicopters to send ‘flying sand and rocks’ to force them out),” wenxuecity.com (Chinese-language website tailored towards educated Chinese outside mainland China), 26 March 2024. https://www.wenxuecity.com/news/2024/03/26/125489186.html
After the Philippines landed on Tiexian Reef, a disputed reef in the South China Sea, for the second time, it was immediately forced away by the Chinese Navy’s Z-8J [R1] helicopter at a very low altitude. Under the effects of the powerful airflow from the helicopter, there was nowhere to hide on the coast as sand and rocks were blown everywhere. The Philippine “scientific research team” who landed on the reef was escaping…. When operating at full strength, the noise is unbearable. If one is too close to the helicopter, it can even disturb a human’s internal organs.
The People’s Liberation Army claims that compared with face-to-face conflict, this aerial sand-blowing method will not cause fatal harm to personnel and may prevent them from “stirring chaos”, so it is more suitable for evicting Filipinos who land on the reef. The shallow water is not suitable for interception by large ships, and besides that Thitu Island has comprehensive facilities that can provide effective logistical support. For example, large aircraft can take off and land to pull people over, and then directly transfer to ships to ascend the reef.
Notes:
[i] “Salami slicing” refers to the taking of territory in a slow and gradual manner and is “a strategy that involves divide and conquer process of threats and alliances to overcome opposition and acquire new territories.” China has employed this strategy in the South China Sea and in the Himalayan region. Prabhash K Dutta, “What is China’s salami slicing tactic that Army chief Bipin Rawat talked about?,” India Today, 7 September 2017. https://www.indiatoday.in/india/story/doklam-china-salami-slicing-army-chief-general-bipin-rawat-1039864-2017-09-07
Image Information:
Image: China claims a maximal amount of maritime territory in the South China Sea, which leads to disputes with all of its neighbors over reefs, shoals, islands, and other features.
Source: Voice of America, https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:South_China_Sea_claims_map.jpg
Attribution: CCA 2.0


