While much of the rest of the Sahel has become engulfed in jihadist violence, Côte d’Ivoire, highlighted here, has had surprising success at avoiding the same violence.
“The goal is to reverse perceptions among border communities that the state has abandoned them. Doing so will reduce the risk that they are exploited by insurgents.”
For the past several years, a primary concern in the Sahelian region of West Africa has been the ability of groups associated with the Islamic State and Al-Qaeda to push southward as they march to the littoral of the Bight of Benin.[i] While Mali and Burkina Faso continue to be the epicenters of jihadist activity, even historically immune countries like Togo, Benin, and Ghana have seen their northern regions, which border Mali and Burkina Faso, experience violence from these groups.[ii] However, as the accompanying article from the pan-African think tank The Institute for Security Studies articulates, Cote d’Ivoire, which would reasonably experience similar threats, seems to have figured out how to protect itself from this southern push. According to the authors, the country’s success is due to its commitment to strategies of security and development. On the security side, the article notes that its “military and security interventions played a notable role in achieving the prevailing calm.” These included several standard practices: the creation of a nationwide counterterrorism strategy; the addition of new weapons and armored vehicles; and the creation of a new counterterrorism center. Yet from the authors’ perspectives, the real success story has been Côte d’Ivoire’s citizen-centric development efforts, targeting populations living in its rural north, who are most susceptible to violence and radicalization. To discourage their joining the insurgents, the government’s social program seeks to “improve civilians’ living conditions” to “reverse the perception among border communities that the state has abandoned them” so as to “reduce the risk that they are exploited by insurgents.” The development program has focused on improving infrastructure, health, youth employment, and social safety allowances. A recent report by the global think tank International Crisis Group draws similar conclusions,[iii] further underscoring the broader perception of Côte d’Ivoire’s efficacy on this front. As the United States and partner countries seek to stem the tide of jihadist violence, Côte d’Ivoire’s approach might bear attention as a model that could be replicated elsewhere in the region.
Sources:
William Assanvo, “Has Côte d’Ivoire found the solution to violent extremism?,” Institute for Security Studies (centrist pan-African security studies think tank), 25 July 2023. https://issafrica.org/iss-today/has-cote-divoire-found-the-solution-to-violent-extremism
No significant terror attacks have been reported in northern Côte d’Ivoire over the past two years, suggesting that its approach to addressing the problem has been effective. With many other states in West Africa still facing a growing threat, what is the country doing right?
Côte d’Ivoire’s border area with Burkina Faso was under substantial pressure from violent extremist groups between 2020 and 2021. Almost 20 attacks and incidents attributed to these groups were recorded in that period. These included attacks against positions and convoys of the defence and security forces, incursions into Ivorian territory, propaganda sermons, threats and intimidation of civilians.
In response, the government focused first on military and security operations, and then supplemented these with a social programme…
Following the Grand-Bassam attack, efforts to strengthen the security apparatus continued, including developing a national counter-terrorism strategy in 2018.
From 2019, the growing presence of extremists in Burkina Faso’s forests along the border with Côte d’Ivoire led to increased vigilance and a stronger military presence in the north. In May 2020, a joint military operation was conducted with Burkina Faso.
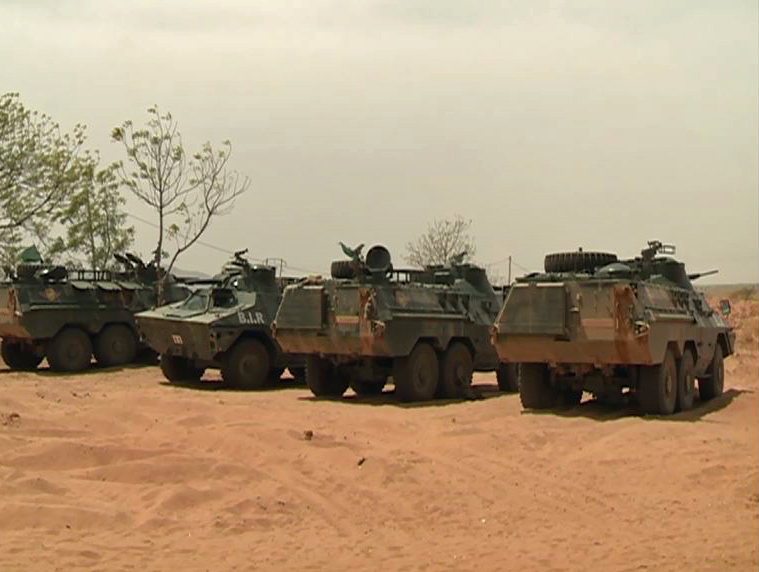
This saw the creation in July 2020 of an operational zone in the north, the set-up of military camps in some border localities, and significant investments in increasing the defence and security forces’ functional capacity. This included human resources, air assets, armoured transport vehicles and surveillance equipment.
A counter-terrorism intelligence centre, Centre de renseignement opérationnel antiterroriste, was created in August 2021 to improve intelligence gathering. Better regional cooperation between countries, particularly within the framework of the Accra Initiative in which Côte d’Ivoire participates, was another important part of the response.
The military and security interventions played a notable role in achieving the prevailing calm. Land, air and intelligence operations have contributed to reducing armed groups’ ability to carry out incursions, move around, and operate within Ivorian territory. And reinforcing the presence of soldiers along the border has reassured civilians. It is also possible that the lull is due to the extremists withdrawing across the border to continue their violence there or adopt a low profile.
While this period of calm prevailed, the social component of the Ivorian response to the terror threat was started. It is being implemented under the framework of the government’s second social programme (PS Gouv 2), which runs from 2022 to 2024. The programme’s first strategic axis includes addressing the fragility in the northern border areas.
The programme was announced in November 2021 and officially launched in January 2022. It aims to improve civilians’ living conditions by enhancing infrastructure and access to basic social services. The goal is to reverse perceptions among border communities that the state has abandoned them. Doing so will reduce the risk that they are exploited by insurgents. The programme focuses on education, health, access to electricity and drinking water, road maintenance, professional integration and youth employment, and providing social safety allowances.The Ivorian approach of combining a military, security and social response isn’t in itself innovative or fundamentally different from that used by neighbouring countries facing terrorism. Notable examples are in central Mali, the Burkina Faso region of the Sahel, and northern Togo. The difference in Côte d’Ivoire could lie in its implementation of these strategies.
Notes:
[i] For more on the push of Al-Qaeda and Islamic State militants towards the West African coast, see: Jason Warner, “UN Warns About Islamic State Surging in Africa and Afghanistan,” OE Watch, 03-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/un-warns-about-islamic-state-surging-in-africa-and-afghanistan/; Jason Warner, “Coastal West African States Brace for Wave of Terrorism From the Sahel,” OE Watch, 10-2022. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/428040
[ii] West African states have taken various approaches to dealing with jihadist insurgents, especially on the topic of negotiations. For more, see: Jason Warner, “Sahelian Countries Divided on Negotiating With Al-Qaeda, Islamic State Militants,” OE Watch 07-2023. https://fmso.tradoc.army.mil/2023/sahelian-countries-divided-on-negotiating-with-al-qaeda-islamic-state-militants/
[iii] The International Crisis Group report largely agrees that the dual security and development approach of Côte d’Ivoire has been important, but also notes that the country’s broader focus on economic development; the northern region’s importance as a base of power for the ruling party; religious tolerance; and an ethnically and regionally balanced military also played their own roles. To read the International Crisis Group study on the topic, see: International Crisis Group, “Keeping Jihadists Out of Northern Cote d’Ivoire,” International Crisis Group, 23 August 2023. https://www.crisisgroup.org/africa/west-africa/cote-divoire/b192-keeping-jihadists-out-northern-cote-divoire
Image Information:
Image: While much of the rest of the Sahel has become engulfed in jihadist violence, Côte d’Ivoire, highlighted here, has had surprising success at avoiding the same violence.
Source: https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/b/b2/Cote_d_Ivoire_in_Africa_%28-mini_map_-rivers%29.svg
Attribution: TUBS, CC BY-SA 3.0