Flag of the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan
“Suppose that the Pakistani government succeeds in deporting all Afghan refugees, will terrorism be eradicated? Obviously not.”
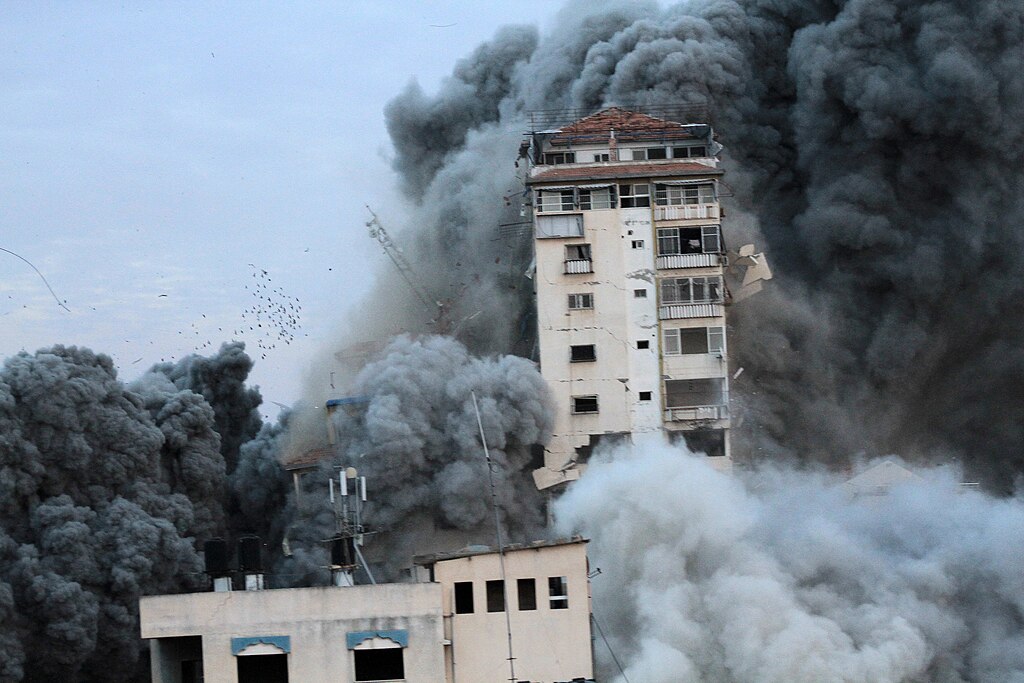
Pakistan continues to struggle with a series of terror attacks, leading the government to resort to mass deportations of Afghan refugees to curb the violence. According to the first excerpted article from the Pashto-language version of the German media company Deutsche Welle, terrorists carried out four separate attacks in Pakistan between 3 and 6 November 2023. The attacks, in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Punjab, and Balochistan provinces, resulted in the deaths of 17 soldiers, five civilians, with another 24 wounded. The article notes that ten militants were killed in response, and “security forces have received Afghan ID cards from six of the militants killed in the Zhob [Balochistan] attack.” Amid rising tensions due to the ongoing acts of terrorism, the regional government of the Balochistan province alleged that both border nations, Iran and Afghanistan, were involved in recent attacks to increase political pressure on Pakistan. No evidence was provided to substantiate these allegations. Pakistan’s proposed solution to counter the ongoing violence inside its borders includes the deportation of approximately 1.7 million undocumented Afghanis, some of whom have lived in Pakistan for up to 40 years, according to the second excerpt from the independent Afghan news outlet Hasht e Subh. As of December 2023, over 400,000 have left Pakistan.[i] A majority of the remaining refugees currently reside in either the Balochistan or Khyber Pakhtunkhwa provinces that border Afghanistan.[ii] The article notes that Pakistan has not been able to successfully contain the Pakistani Taliban (Tehreek-e-Taliban-e-Pakistan (TTP)) and has frequently accused the Afghan refugee population of collaborating with the TTP. The article alleges that the Pakistani military has used both the Afghan and Pakistani Taliban to further its own geopolitical agenda when convenient. Some Afghan refugees allege that the Pakistani government is committing acts of terrorism by expelling them from the land. A mass deportation of a long-standing population may also lead to an increase in grievances by that community and possibly increased support for the TTP and other like-minded groups, resulting in additional terrorist attacks.[iii] The mass expulsion of undocumented refugees has already created a burden on both the Afghan and Pakistani governments from an economic and human rights perspective.
Sources:
“پاکستان: په ۴۸ ساعتونو کې وسله والو ۴ بریدونه کړي دي (Pakistan: Militants have carried out 4 attacks in 48 hours),” Deutsche Welle (German news site), 6 November 2023. https://p.dw.com/p/4YRJH
According to security sources, militants carried out another attack in The Dera Ismail Khan district of Khyber Pakhtounkhwa yesterday, but this is the fourth attack on Pakistani security forces in the past 48 hours. Last night, police raided a police checkpoint in Ismail Khan district with heavy weapons. The exchange between the police and the armed forces lasted about half an hour, but the militants eventually fled. Police say they have cordoned off the area and are searching for suspected attackers. In the past three days, terrorists have carried out major attacks in Pakistan’s Khyber Pakhtounkhwa, Punjab and Balochistan provinces, killing 17 security forces, five civilians and wounding about 24 others, including police. Police claimed to have killed 10 people in the attack.
In recent days, attacks in different parts of Pakistan have increased. In the wake of the latest incidents, Balochistan’s regional government has claimed that two neighbouring countries are involved in the terrorist attacks because they want to pressure Pakistan. Balochistan’s Acting Information Minister, Jan Achakzai, told a news conference on Sunday that Pakistan was facing attacks “on both sides” but that it could not undermine the government’s will to defeat terrorists. He claimed that security forces had obtained identification cards from six of the militants killed in the attack. John Achakzai accused India of spreading insecurity in the region and that India’s intelligence agency, “Ro” is “involved in terrorist attacks in Pakistan.” Referring to the two terrorist attacks last week, he said: “We have repeatedly mentioned that India is involved in the terrorist attacks in the country, especially in Balochistan.”
“د کډوالو په اېستلو سره په پاکستان کې ترهګري له منځه نه ځي (Terrorism in Pakistan will not disappear by expelling refugees)” Hasht e Subh (independent Afghan news site), 5 November 2023. https://8am.media/ps/terrorism-in-pakistan-will-not-disappear-by-expelling-refugees/
The interim government of Pakistan has started deporting Afghan refugees en masse, which has provoked widespread protests. The interim prime minister of Pakistan has emphasized that all those illegal Afghan refugees who have been living in Pakistan for the past 40 years will be deported. This move has deepened the crisis which is not new for the Afghans and they have been dealing with it for decades. With the rule of the Taliban, the crisis of immigration has not decreased, but has expanded and increased… This has caused citizens to move to neighboring countries. This is not the only result of the arrival of the Taliban. The strengthening of terrorist groups and the development of their activities is also one of the destructive consequences of the Taliban rule in Afghanistan… The government of Pakistan, which is unable to control the TTP and has not given the desired result to the pressure on the Afghan Taliban to suppress this group, has increased the pressure on the Afghan refugees and accuses the Afghan refugees of terrorist attacks… There is no doubt that the Taliban is involved in many terrorist attacks in Pakistan and will continue to be in the future. But it cannot be that all Afghan refugees are considered terrorists or collaborators of terrorists and the solution is to seek their deportation. In reality, Afghan refugees have not only played an important role in the growth and strengthening of terrorism, but are considered the primary victims of the development of terrorist groups’ activities.
The terrorism that the government of Pakistan is using to expel Afghan refugees from their land today is the result of the deadly game that the soldiers of this country have skillfully played for years and the result was full of benefits for them. Thanks to the terrorist industry managed by the Pakistani army, the people of this country have not seen a stable civilian government and the army has control over all affairs. Terrorism is actually a pretense through which the soldiers introduce themselves as the saviors of Pakistan. If they are not there, the country will become food for wolves… It is not yet clear whether the TTP, as well as the Afghan Taliban, have really escaped the control of the Pakistani army or not; But what can’t be doubted is that the main threat to Pakistan is the soldiers, or to put it bluntly, the managers of the terrorist industry, not the Afghan refugees or the Pashtuns of this country. The Pashtuns on both sides of the Durand Line are the main victims of terrorism trained by the Pakistan Army.In the last few decades, one of the important tasks of the religious seminaries established in Pakistan with the support of the army was the training of the hard-line jihadi generation, who as proxy soldiers of the ESA during the invasion of the Soviet Union and also during the presence of the American forces in Afghanistan, the Pakistani army overthrew the western-backed government in Afghanistan and established its own proxy regime in the country. But now that the jihad in Afghanistan is over, according to the terrorists, how and where will the thousands of jihadists trained in the religious schools of Pakistan quench their thirst for jihad… Suppose that the Pakistani government succeeds in deporting all Afghan refugees, will terrorism be eradicated? Obviously not. The main supporter of terrorism in Pakistan is the army, which is in control of the entire country, and thus, the main source of terrorism in Pakistan is religious madrassas, which continue to operate whether they are children of Afghan refugees or not. and the army does not care about them. Are only Afghans committing suicide attacks? No. Pakistanis are ahead of Afghans in terrorism and extremism…
Notes:
[i] A supplemental report by the Associated Press detailing recent updates in the deportation of undocumented Afghanis in Pakistan: Sattar, Abdul and Munir Ahmed. “A Pakistani province aims to deport 10,000 Afghans a day,” Associated Press, November 30, 2023. https://apnews.com/article/pakistan-baluchistan-deport-migrants-afghans-7393238ace4c49acce9d7c77ebd708bf
[ii] For additional information on Afghan refugees in Pakistan, please visit the United Nations Refugee data website: “Registered Afghan refugees in Pakistan” United Nations Operational Data Portal. https://data.unhcr.org/en/country/pak
[iii] To learn more about the potential impact of grievances and their effect on terrorism globally, see:
Murphy, Natalie. “Why Grievances Matter: An Analysis of the Influence Grievances Have on Domestic Terrorism Globally,” Johns Hopkins University, [Thesis] May 2022. https://jscholarship.library.jhu.edu/server/api/core/bitstreams/0f722198-6850-4d16-8250-5fcad421430b/content
Image Information:
Image: Flag of the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Flag_of_the_Tehrik-i-Taliban_Pakistan.png#globalusage
Attribution: Public Domain