“The growing use of intelligent weapons and equipment increases the risk of losing control in a crisis.”
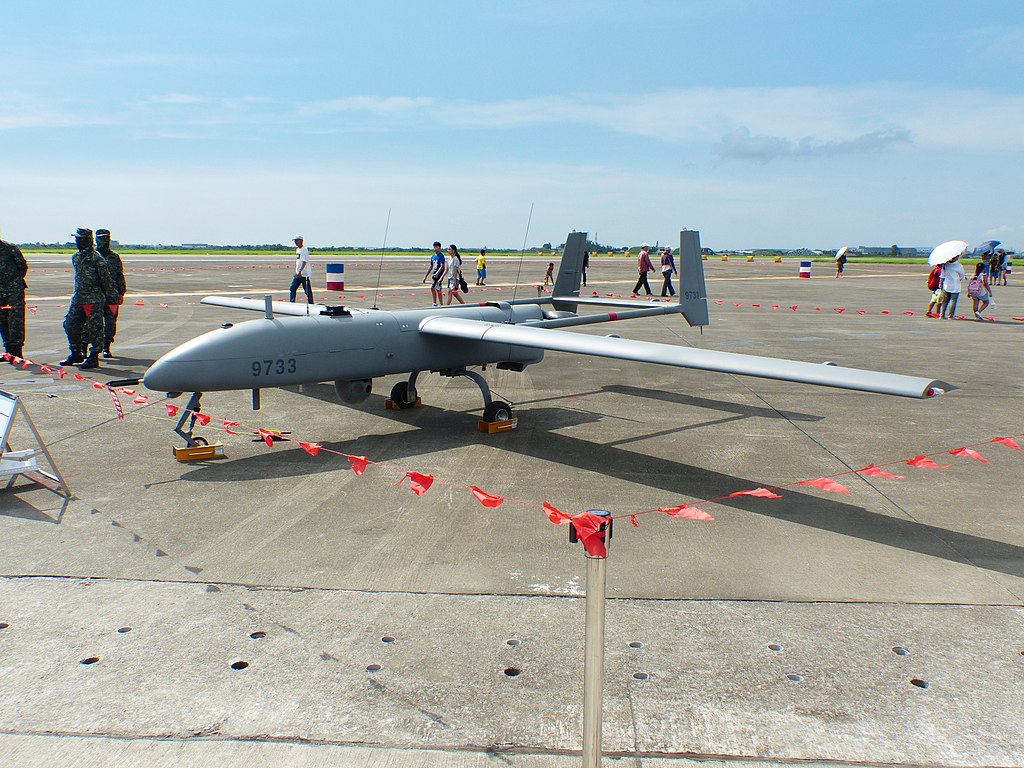
Chinese military strategists are increasingly focused on developing practices of military “intelligentization,” the next generation of warfare expected to improve the military’s combat efficiency.[i] Intelligentization, also referred to as intelligent warfare, is the Chinese concept of applying machine speed and processing power of artificial intelligence (AI) to military planning, operational command, and decision support.[ii] The rate of developing intelligent weapons and systems is progressing at such a rapid pace, however, that it comes with potential risks, according to the following article published in the People’s Liberation Army’s official newspaper PLA Daily. According to the article, the anti-jamming ability of current intelligent systems is too weak, making intelligent systems more vulnerable. For example, drone command and control relies on communication links that connect the drones to rear personnel. If the communication link is jammed, the operator will lose control of the drone. Therefore, improved anti-jamming capability is necessary to ensure communications links are not disrupted. The article also explains that the reliability of today’s AI technology is questionable. While the AI systems’ level of intelligence is superior to that of a human, there is not yet a reliable test to ensure they will not fail in a complex combat scenario.
The article also warns that using intelligent weapons and equipment increases the risk of losing control in a crisis. For example, military operations that rely on intelligent weapons and equipment could surpass the speed of political decision making. This could weaken the decision-maker’s ability to control the situation. The article further warns that the use of intelligent weapons and equipment in large-scale combat could increase tension between countries as well as lead to changing the psychology of combatants, potentially causing them to become more desensitized to killing because of their greater distance from the battlefield and gradually reducing caution in decision-making.
The article notes that countries are increasingly pouring money into AI technology to gain military advantage, and this struggle for predominance could lead to a dangerous arms race. With current AI technology, for example, the algorithms used to distinguish civilians from combatants are not yet reliable, thereby potentially putting the lives of civilians at risk. Based on the article, there is still a long way to go before China has perfected the software to not only drive AI weapons and equipment, but also to test them to ensure they are ready to meet all the demands of the battlefield.
Source:
Luo Zhaocheng, “关注智能化武器装备运用风险 (Pay Attention to Risks in Using Intelligentized Weapons and Equipment),” PLA Daily (Official newspaper of the Chinese People’s Liberation Army), 5 January 2023. http://www.81.cn/ll/2023-01/05/content_10209877.htm
… Currently, the world’s major countries are vigorously pursuing the development of military intelligentization of weapons and equipment across the different operational domains. While the new technology greatly enhances combat capabilities, it also could pose some great risks.
…the anti-jamming capability of intelligent weapons and equipment is weak. This could cause a loss of operational control over systems. The intelligent weapons and equipment currently used by various countries often require command and control to be conducted by rear area personnel who rely on communications links. As these links are jammed, it will be difficult to return them to operational effectiveness… Iran’s successful capturing of U.S. drones through jamming technology is a typical example…
Artificial intelligence technology in certain fields is shown to far exceed human intelligence. However, its reliability and interpretability are questionable… Presently, countries have conducted repeated simulation tests and even actual combat using intelligent weapons and equipment. However, there is still no reliable testing method to ensure its dependability should it run into a complex battlefield environment.
Wide-scale application of intelligent operations could trigger an arms race, leading to the risk of disposition for unsafe AI systems…
The use of intelligent weapons and equipment can impact the international strategic balance and increase the risk of war breaking out. The use of smart weapons and equipment increases the risk of “firing the first shot.”
The growing use of intelligent weapons and equipment increases the risk of losing control in a crisis…
…Intelligent weapons and equipment put participating personnel further away from the battlefield. Participants’ apathy will grow as distance increases…
Notes:
[i] For other Chinese insights on intelligentization, see Cindy Hurst, “China: ‘New Concepts’ in Unmanned Combat,” OE Watch, October 2020. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/376077 and Peter Wood, “A Chinese Perspective on Intelligent Warfare and Future Urban Operations,” OE Watch, November 2020. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/376999
[ii] For an example of intelligent warfare, see Cindy Hurst, “The ‘Blade of Victory’: A Chinese Perspective on Drone Swarms,” OE Watch, March 2020. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-2-singular-format/358341