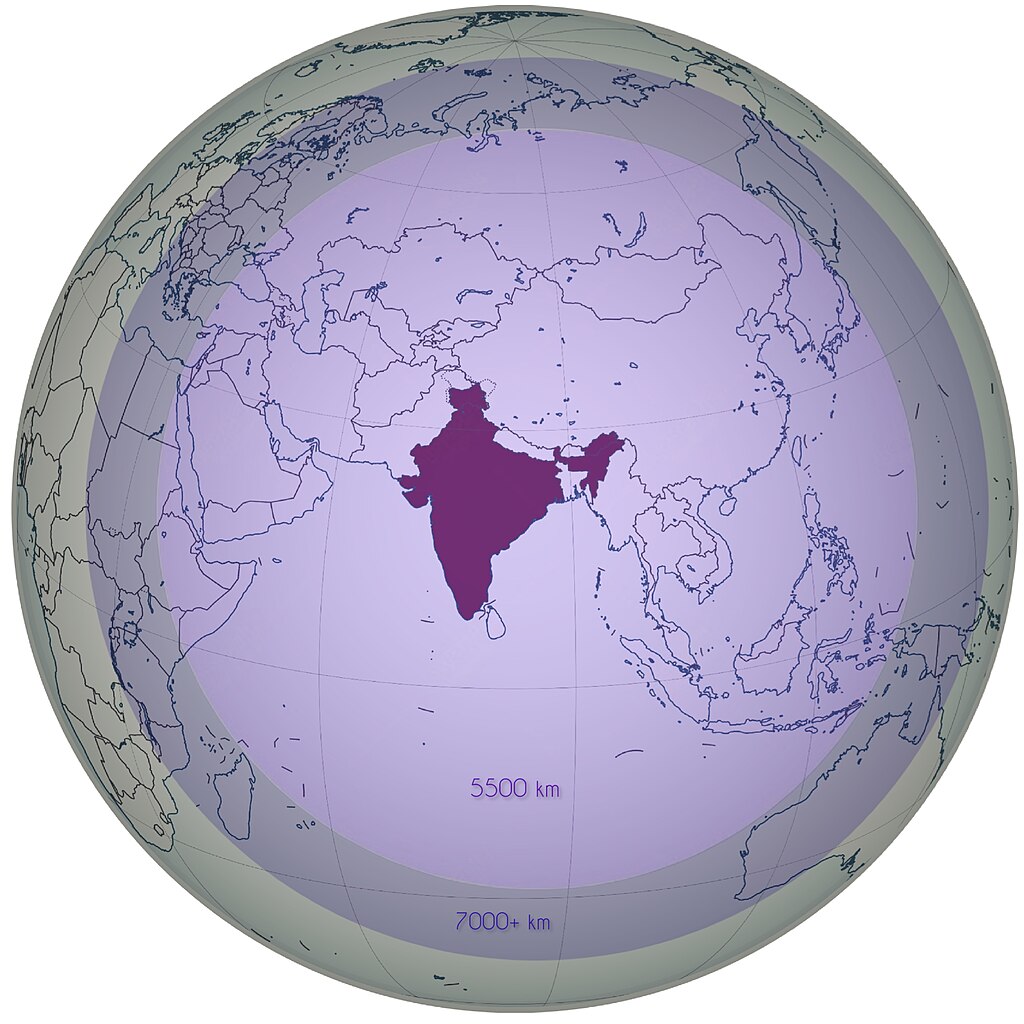
Agni-V ICBM Range Envelope centered at Integrated Test Range, Odissa. Declared range of 5500 km in pale indigo and estimated expanded range of 7000+ km in faded circumference.
“The opacity surrounding this MIRV missile is about the number of warheads it can carry, which in all likelihood would remain classified.”
India’s ability to carry out a strategic or tactical nuclear strike has been limited compared to that of its adversary, China. However, in recent years, India has made efforts to match Chinese capabilities. In early March 2024, India announced the successful test of a multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) for its Agni-V ballistic missile, further strengthening India’s nuclear strike capabilities even as it maintains a “no first use” policy.[i] The accompanying excerpted article from the conservative-leaning English-language newspaper The Hindu, reports on the recent MIRV test for the Agni-V and considers what it means for India. The article suggests that with a MIRV capable 3100 mile range Agni-V missile, India has now achieved more balance in its nuclear deterrence capability with China. The article acknowledges that some of its specific capabilities remain unknown, critical being how many warheads it can carry (the authors speculate that it carries three) and whether it can carry decoys. Finally, the article mentions that India’s defense industry will test a long-range submarine-launched ballistic missile, likely the latest variant of the K-series, at some point in the future.[ii] Altogether, the successful MIRV test for the Agni-V, and future testing for its submarine-launched ballistic missile, indicate that India will continue to seek nuclear parity with China.
OE Insight Summary:
In March 2024 IND successfully tested a MIRV, with a reported three-warhead capacity, for its Agni-V ICBM as part of a long-term deterrence effort to match CHN strategic nuclear strike capabilities.
Sources:
Harsh V. Pant and Kartik Bommakanti, “The MIRV leap that fires up India’s nuclear deterrence,” The Hindu (privately owned, conservative-leaning English-language newspaper in India), 19 March 2024. https://www.thehindu.com/opinion/op-ed/the-mirv-leap-that-fires-up-indias-nuclear-deterrence/article67965762.ece
The Agni-5 ballistic missile test dubbed the “Divyastra”, that was conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is strategically consequential. With a range of over 5,000 kilometres, the Agni-5 is the longest-range missile India has tested so far. But it is not simply its range but, equally, its potency which represents a watershed moment for India’s nuclear deterrent. The potency of India’s nuclear deterrent is enhanced because this variant is integrated with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicles (MIRVs)…
Though MIRV technology is not new, it is to India…MIRV-tipped missiles are a necessity simply because they strike multiple targets simultaneously and help evade ballistic missiles defences. China is building ballistic missile defences such as the Hongqi (HQ-19) ground-based ballistic missile interceptors, which have been tested, but their capacity to intercept Intermediate Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBMS) such as the Agni-5 is still suspect…
Now that India has integrated the Agni-5 with multiple warheads, greater balance has been restored in the Sino-Indian nuclear deterrent relationship. To be sure, more testing of the MIRV-capable Agni-5 will be required…
The opacity surrounding this MIRV missile is about the number of warheads it can carry, which in all likelihood would remain classified. Going by speculation, it is improbable that it can carry more than three warheads. Further, the yield of the nuclear warheads is likely to be limited due to the small number of atomic tests India has conducted. In addition, it is unclear whether the Agni-5 can carry decoys and chaff, especially during the boost and intermediate phase of the missile’s flight. Agni-5 will in all probability be launched from a road mobile platform.This is a China-specific missile. There could be more to come from the DRDO and AEC with India adding more punch to its nuclear arsenal when it tests a long-range Submarine Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), which India’s nuclear ballistic missile submarines can launch. The Agni-5 with MIRV capability bolsters India’s nuclear capabilities vis-à-vis China. It puts China on notice — that India is preparing itself to counter the advances Beijing has made with its missile and missile defence programmes…
Notes:
[i] India adopted its “no first use” policy shortly after its first successful nuclear test in the late 1990s. In August 2019, Defense Minister Rajnath Singh mentioned that India’s policy might change depending on the circumstances, but India continues to have a no first use policy when it comes to its nuclear arsenal.
[ii] In November 2018, Indian officials announced the country had joined the ranks of nuclear triad governments when the INS Arihant, a nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine, carried out its first deterrence deployment that month. While India reportedly only maintains the triad when one of its ballistic missile submarines are deployed, the 2018 deployment demonstrated India’s long-term goals of nuclear deterrence. For background, see: Matthew Stein, “Is India’s Nuclear Triad Complete?,” OE Watch, January 2019. https://community.apan.org/wg/tradoc-g2/fmso/m/oe-watch-articles-singular-format/296884
Image: Agni-V ICBM Range Envelope centered at Integrated Test Range, Odissa. Declared range of 5500 km in pale indigo and estimated expanded range of 7000+ km in faded
circumference.
Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Agni-V_ICBM_Range_Envelope_
centered_at_Integrated_Test_Range,_Odissa.jpg;
Attribution: CCA 4.0
